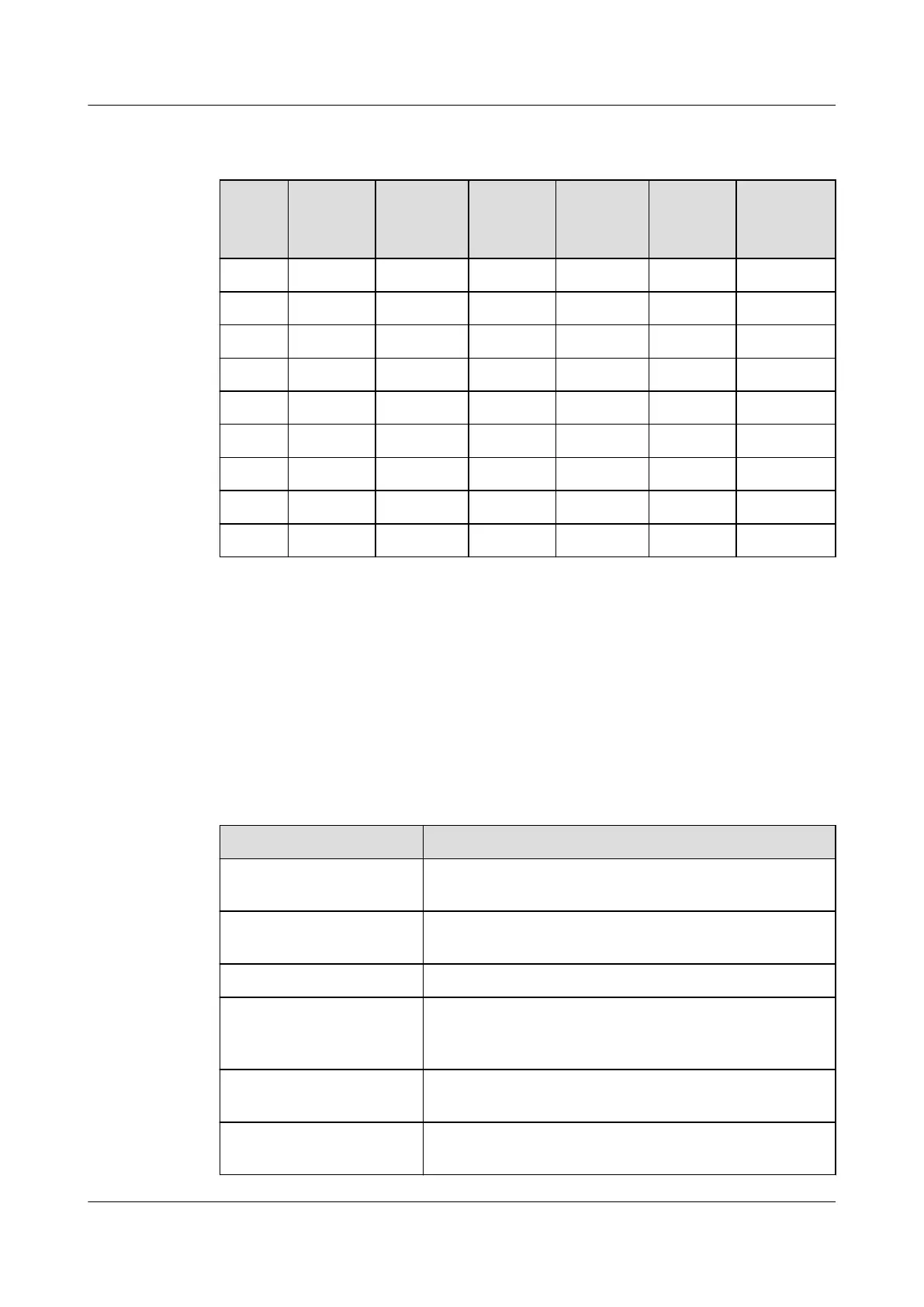
Table 7-3 Air cleanliness classification by particle concentration of ISO 14664-1 and
maximum allowable concentrations (particles/m
3
) for particles
ISO
Class
Particle
Size
≥ 0.1 μm
Particle
Size
≥ 0.2 μm
Particle
Size
≥ 0.3 μm
Particle
Size
≥ 0.5 μm
Particle
Size
≥ 1 μm
Particle
Size
≥ 5 μm
Class 1 10 2 - - - -
Class 2 100 24 10 4 - -
Class 3 1000 237 102 35 8 -
Class 4 10,000 2370 1020 352 83 -
Class 5 100,000 23,700 10,200 3520 832 29
Class 6 1,000,000 237,000 102,000 35,200 8320 293
Class 7 - - - 352,000 83,200 2930
Class 8 - - - 3,520,000 832,000 29,300
Class 9 - - - - 8,320,000 293,000
7.4 Corrosive Airborne Contaminants
Corrosive airborne contaminants and other negative environmental factors (such as abnormal
temperature and humidity) may expose IT equipment to higher risks of corrosive failure. This
article specifies the limitation on corrosive airborne contaminants with an aim at avoiding
such risks.
Table 7-4 lists common corrosive airborne contaminants and their sources.
Table 7-4 Common corrosive airborne contaminants and their sources
Symbol
Sources
H
2
S Geothermal emissions, microbiological activities, fossil fuel
processing, wood rot, sewage treatment
SO
2
, SO
3
Coal combustion, petroleum products, automobile
emissions, ore smelting, sulfuric acid manufacture
S Foundries, sulfur manufacture, volcanoes
HF Fertilizer manufacture, aluminum manufacture, ceramics
manufacture, steel manufacture, electronics device
manufacture
NO
X
Automobile emissions, fossil fuel combustion, chemical
industry
NH
3
Microbiological activities, sewage, fertilizer manufacture,
geothermal emissions, refrigeration equipment
OceanStor 2600 V3
Product Description
7 Environmental Requirements
Issue 09 (2019-05-15) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 138

 Loading...
Loading...











