106
The device range is checked even though indexing is executed.
An error occurs when the head device number of the devices with indexing exceeds the device range.
With changing the settings of the PLC parameter, the device range is not checked.*
2
*2: For changing the settings of the PLC parameter on GX Developer, refer to the following manual.
• QCPU User's Manual (Function Explanation, Program Fundamentals)
(c) Character string data
Because all character string data is of variable length, device range checks are performed.
In cases where the corresponding device range has been exceeded, an operation error will be returned.
For example, in a case where the data register has been allocated 12k points, there will be an error if it exceeds
D12287.
However, with the Basic Model QCPU, High Performance model QCPU, Process CPU, and Redundant CPU, when
indexing is executed and the head device number is outside the device range, no error occurs and the other devices
are accessed.
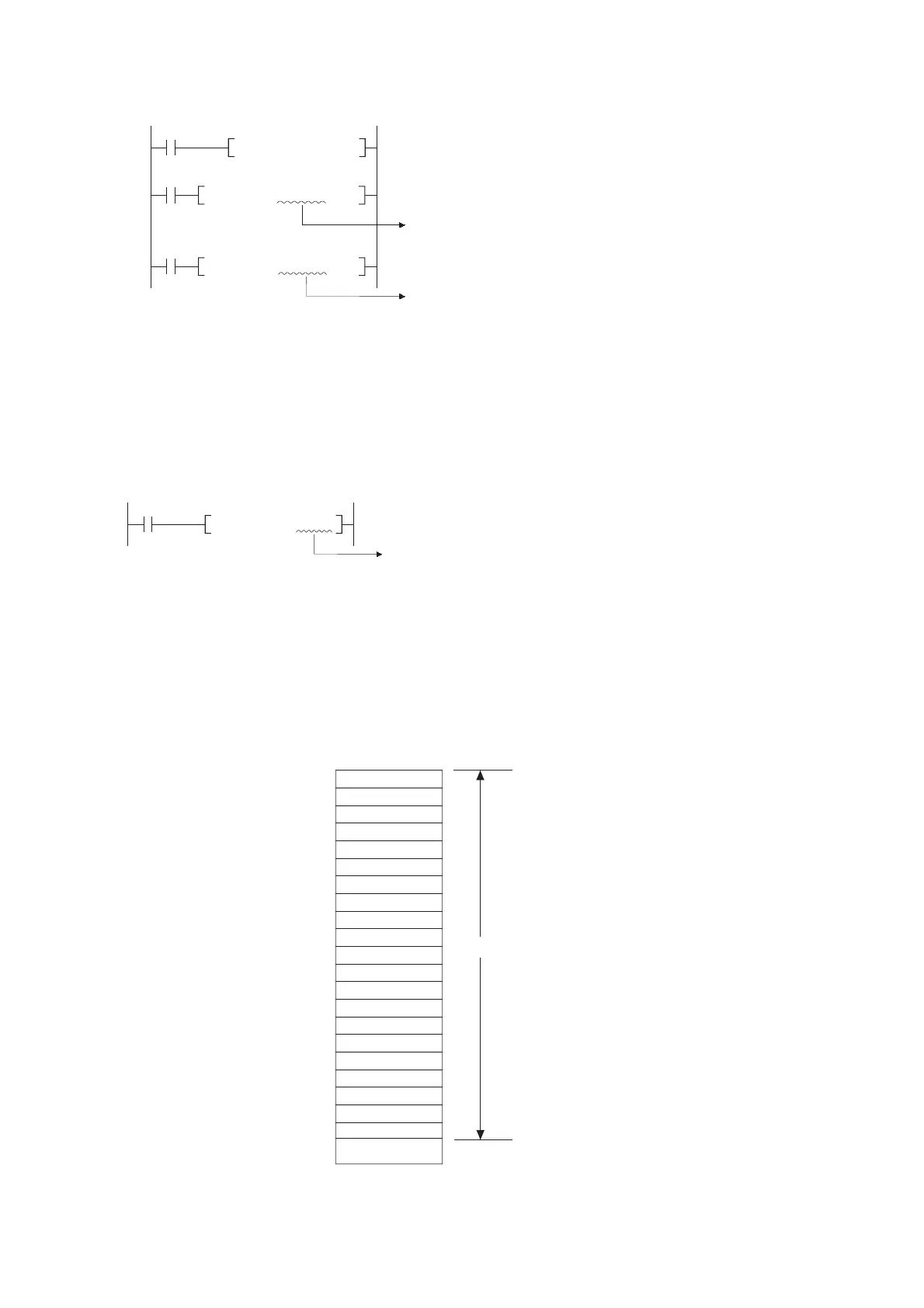
When performing the following access in Universal model QCPU or LCPU, an error (error code: 4101) occurs.
1) Access crossing the boundary of devices caused by indexing
(range of A area)
The allocation order of individual devices is shown below:
2) Access crossing the boundary of file registers caused by indexing
3) Access to file registers (R, ZR) without setting file register files
D0 D12285Z1
K2
BMOV
D0 D12287Z1 K2BMOV
K2 Z1MOV
When D12287 is specified with the BMOV instruction,
the target devices are D12287 and D12288.
However, an operation error occurs because D12288
does not exist.
An operation error occurs since head device number
is D12289 that exceeds the device range.
$
MOV
"ABC"
D12287
This designates D12287 and D12288 as the
target devices for executing the $MOV instruction.
However, since D12288 does not exist,
an operation error occurs.
SM
SD
X
Y
M
L
B
F
SB
V
S
D
W
SW
Empty area
Contact and coil of T
Contact and coil of ST
Contact and coil of C
Present value of T
Present value of ST
Present value of C
File register
(32K points)
Boundary B
Area A

 Loading...
Loading...











