175
E=, E<>, E>, E<=, E<, E>=
1
2
3
4
6
7
8
6.1 Comparison Operation Instructions
6.1.3 E=, E<>, E>, E<=, E<, E>=
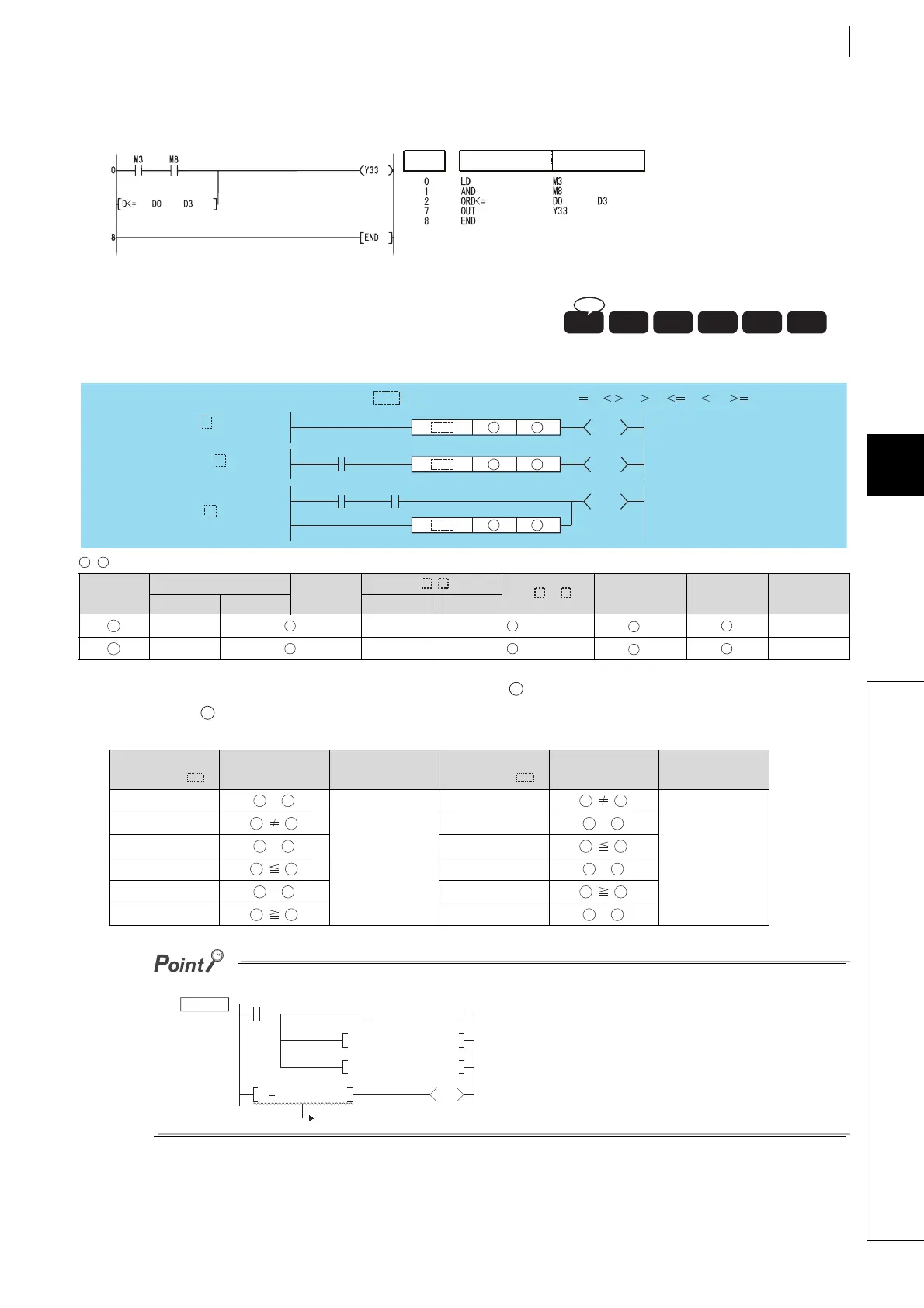
(4) The following program compares the data in D0 and D1 with the data in D3 and D4, and establishes continuity if the data
in D0 and D1 is equal to or less than the data in D3 and D4.
[Ladder Mode] [List Mode]
, : Data for comparison or head number of the devices where the data for comparison is stored (real number)
*1: Available only in multiple Universal model QCPU and LCPU
(1) The 32-bit floating decimal point data from device designated by and 32-bit floating decimal point data from device
designated by as A normally-open contact, and performs comparison operation.
(2) The results of the comparison operations for the individual instructions are as follows:
Note that use of the E= instruction can on occasion result in situations where errors cause the two values not to be equal.
6.1.3 E=, E<>, E>, E<=, E<, Floating-po int data comparison s (Single precis ion)
E>=
6.1.3
E=, E<>, E>, E<=, E<, E>=
• Basic model QCPU: The serial number (first five digits) is
"04122" or later.
Setting
Data
Internal Devices
R, ZR
J\
U\G
Zn
Constants
E
Other
Bit Word Bit Word
–– ––
*1
––
–– ––
*1
––
Instruction
Symbol in
Condition
Comparison
Operation Result
Instruction
Symbol in
Condition
Comparison
Operation Result
E=
=
Continuity
E=
Non-continuity
E<>
E<>
=
E>
>
E>
E<=
E<=
>
E<
<
E<
E>=
E>=
<
Step
Instruction
Device
Basic
Process
High
performance
Redundant
Universal
LCPU
Ver.
LD
AND
OR
S1
S2
S1
S2
S1
S2
EE EE E E
/////
Command
Command Command
indicates an instruction symbol of .
S1 S2
S1
S2
S1
S2
S2
S1 S1
S2
S1
S2 S2
S1
S1
S2
S1
S2
S1
S2
S1
S2
S1
S2
S1
S2
S1
S2
S1
S2
EMOV E1.23
D0
E D0
M0D2
X0
D0 E4.56
D2
D2 E4.56
D2
E*
E/
Two values may not be equal.
Example

 Loading...
Loading...











