483
HEX, HEXP
1
2
3
4
4
6
7
8
7.11 Character string processing instructions
7.11.14 HEX, HEXP
: Head number of the devices where a character string to be converted to BIN data is stored (character string)
: Head number of the devices where the converted BIN data will be stored (BIN 16 bits)
n : Number of characters to be stored (BIN 16 bits)
Function
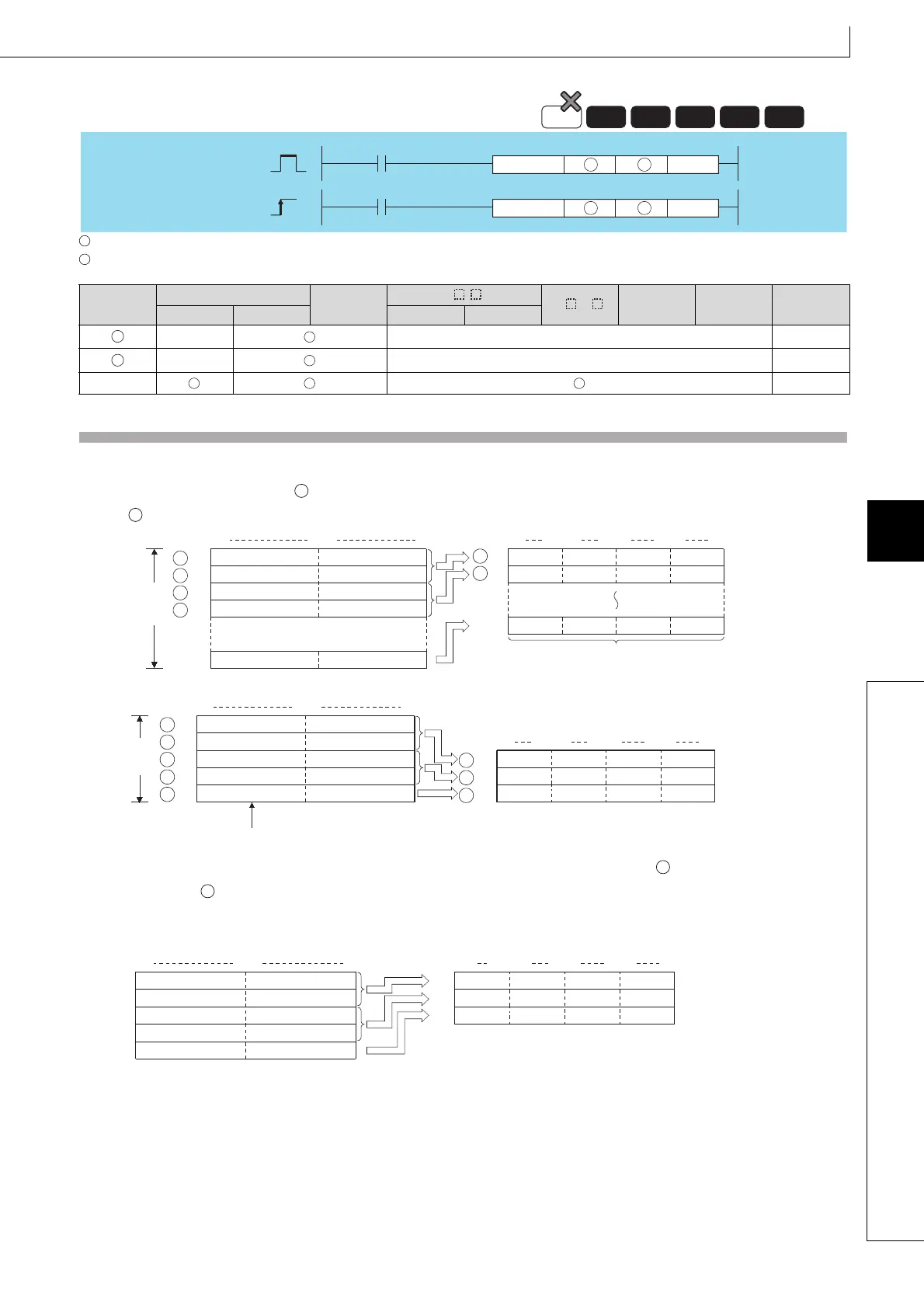
(1) Converts the number of characters of hexadecimal ASCII data designated by n stored in the area starting from the
device number designated by into BIN values and stores them in the area starting from the device number designated
by .
For example, if the number 9 has been designated by n, the operation would be as follows:
(2) When the number of characters is specified for n, the range of characters designated by as well as the device range
designated by in which the BIN data will be stored are automatically decided.
(3) Accurate processing will be conducted even in cases where the range of devices where the ASCII code to be converted
is being stored overlaps with the range of devices that will store the converted BIN data.
7.11.14 HEX, HEXP C onversion from ASCII to hexa decimal BIN
7.11.14
HEX, HEXP
Setting
Data
Internal Devices
R, ZR
J\
U\G
Zn
Constants
K, H
Other
Bit Word Bit Word
–– –– ––
–– –– ––
n ––
Process
High
performance
Redundant
Universal
LCPU
Basic
Command
Command
HEX
HEXP
n
n
S D
S D
HEX
HEXP
S
D
S
D
S
D
BIN data
+1
+2
+3
Number of
characters
designated
by n
+1
ASCII code for the 1th digitASCII code for the 2nd digit
ASCII code for the 3th digit
ASCII code for the 4nd digit
ASCII code for the 1rd digitASCII code for the 2st digit
ASCII code for the 3rd digitASCII code for the 4st digit
4th digit 3rd digit 2nd digit 1st digit
4th digit 3rd digit 2nd digit 1st digit
b15 b8b7 b0
b15 b12 b8b11
b7
b4 b0b3
S
S
S
S
D
D
34
H
(4)33
H
(3)
32
H
(2)31
H
(1)
36
H
(6)42
H
(B)
39
H
(9)41
H
(A)
38
H
(8) 45
H
(E)
0
H
0
H
E
H
A
H
9
H
B
H
6
H
1
H
2
H
3
H
4
H
+1
+2
+3
When "9"
is set
for n
+1
+2
+4
0
H
Code "38H" remains unchanged since the designated number of characters is "9".
S
S
S
S
S
D
D
D
b15 b12 b8b11 b7 b4 b0b3
b15 b8b7 b0
S
D
D12
D13
D11
D12
D13
D14
D11
31
H
(1)32
H
(2)
33
H
(3)34
H
(4)
35
H
(5)36
H
(6)
37
H
(7)38
H
(8)
41
H
(A)
39
H
(9)
D10
0
0
H
A
H
9
H
8
H
H
7
H
6
H
5
H
4
H
3
H
2
H
1
H
b15 b8b7 b0
b15
b12
b8b11 b7 b4 b0b3

 Loading...
Loading...











