239
INT, INTP, DINT, DINTP
1
2
3
4
6
7
8
6.3 Data conversion instructions
6.3.5 INT, INTP, DINT, DINTP
DINT
(1) Converts 32-bit floating decimal point type real number designated by to BIN 32-bit data, and stores the result at the
device number designated by .
(2) The range of 32-bit floating decimal point type real numbers that can be designated at +1 or is from -2147483648 to
2147483647.
(3) The integer value stored at +1 and is stored as BIN 32 bits.
(4) After conversion, the first digit after the decimal point of the real number is rounded off.
Operation Error
(1) In any of the following cases, an operation error occurs, the error flag (SM0) turns ON, and an error code is stored into
SD0.
Program Example
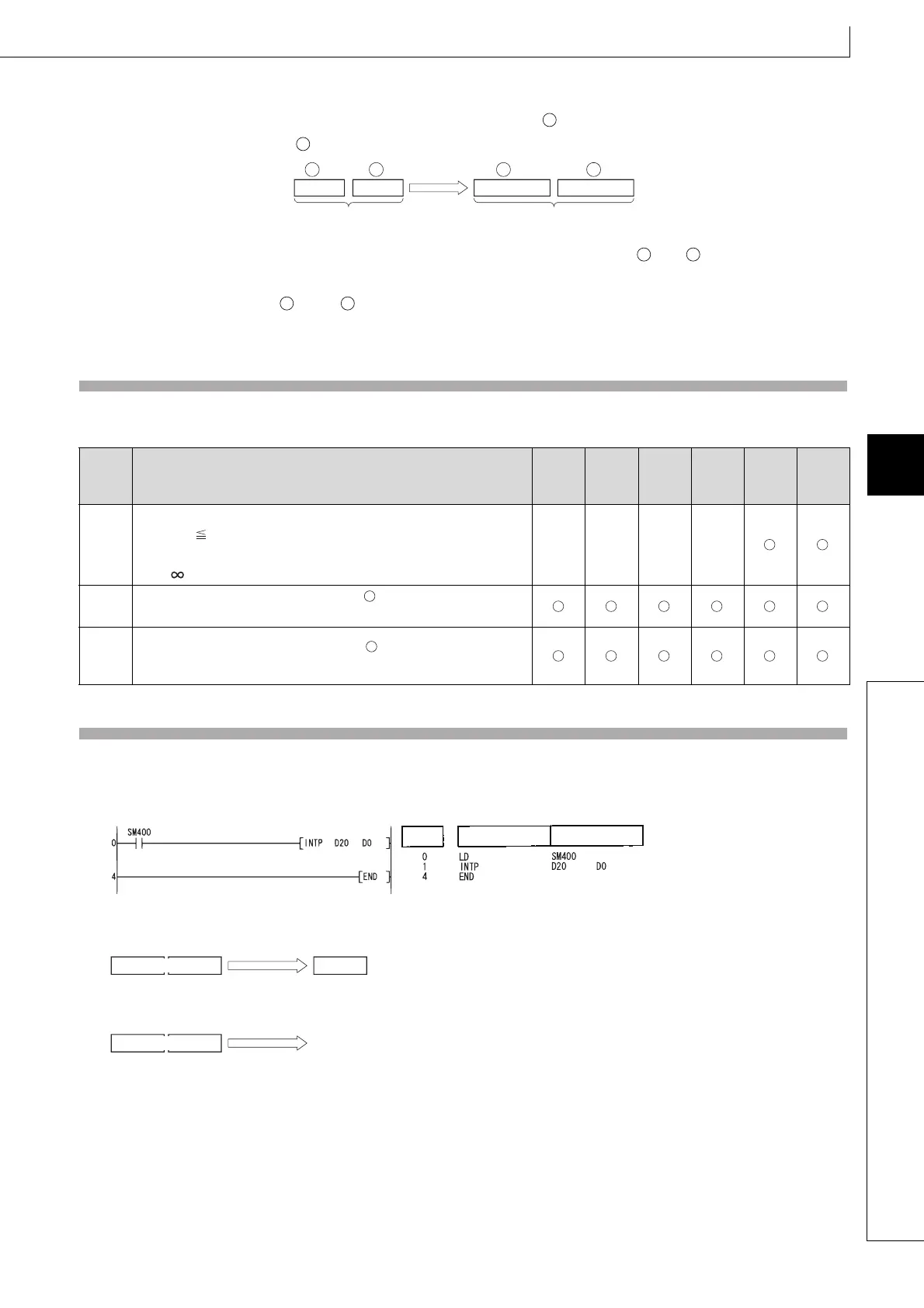
(1) The following program converts the 32-bit floating decimal point type real number at D20 and D21 to BIN 16-bit data, and
stores the result at D0.
[Ladder Mode] [List Mode]
[Operation]
Error
code
Error details
Q00J/
Q00/
Q01
QnH QnPH QnPRH QnU LCPU
4140
The specified device value is not within the following range:
0, 2
-126
| Specified device value | < 2
128
The specified device value is 0, unnormalized number, nonnumeric,
and ± .
–– –– –– ––
4100
The 32-bit floating point data specified by when the INT instruction is
used is outside the
-32768 to 32767 range.
4100
The 32-bit floating point data specified by when the DINT instruction
is used is outside the -2147483648 to 2147483647 range.
S
D
BIN 32 bits
Lower 16 bitsUpper 16 bits
32-bit floating-point
real number
+1
S
+1
DS D
S S
D D
S
S
Step
Instruction
Device
Integer
conversion
BIN value
D0
25916
Integer
conversion
An operation error occurs
since "setting data < -32768."
32-bit floating-point
real number
D21
-33562.3211
D20
32-bit floating-point
real number
D21
25915.6796
D20

 Loading...
Loading...











