819
Subroutines Section 3-19
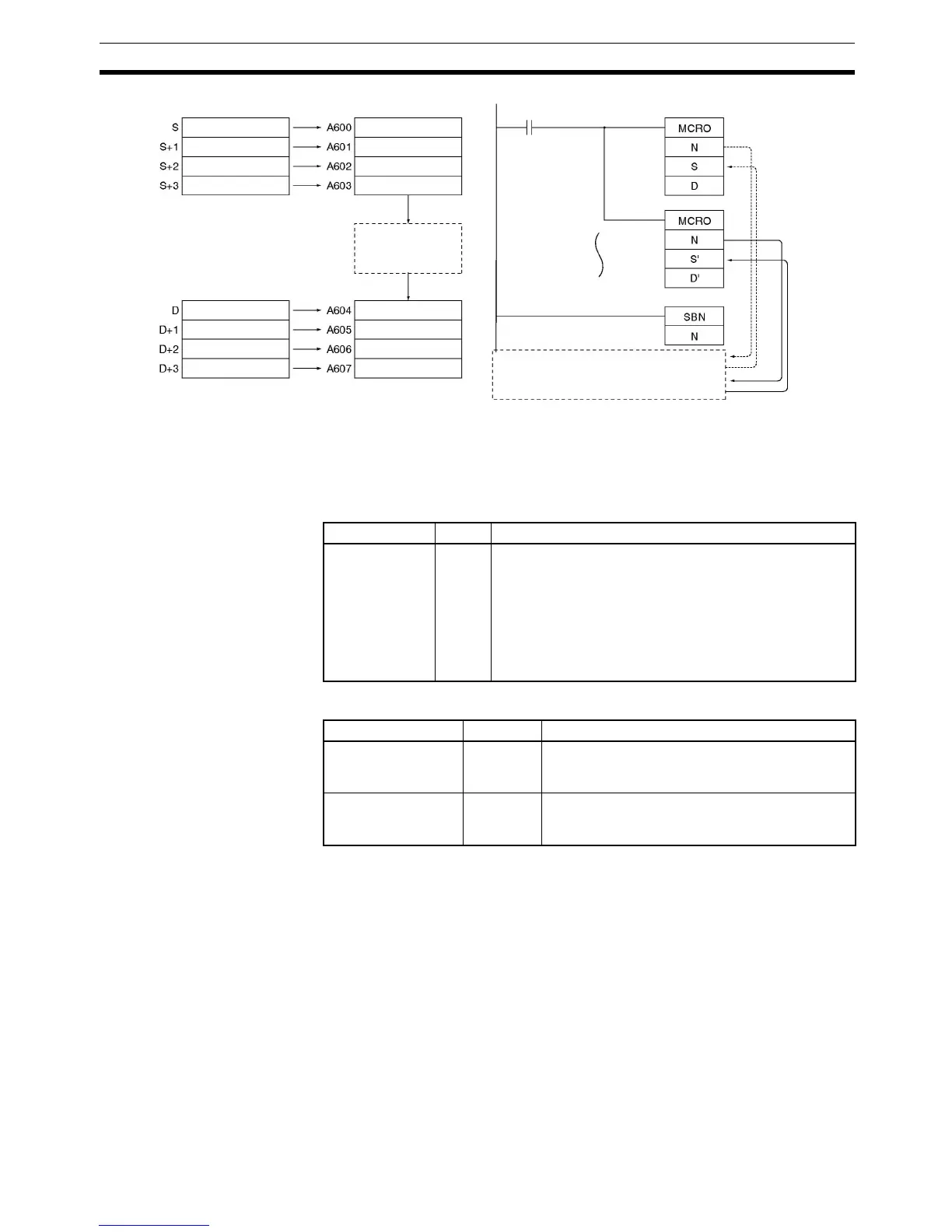
MCRO(099) can be used to consolidate two or more subroutines with the
same structure but different input and output addresses into a single subrou-
tine program. When MCRO(099) is executed, the specified input and output
data is transferred to the specified subroutine.
Flags
The following table shows relevant words in the Auxiliary Area.
Precautions The four words of input data (words or bits) in A600 to A603 and the four
words of output data (words or bits) in A604 to A607 must be used in the sub-
routine called by MCRO(099). It is not possible to pass more than four words
of data.
It is possible to nest MCRO(099) instructions, but the data in the macro area
input and output words (A600 to A607) must be saved before calling another
subroutine because all MCRO(099) instructions use the same 8 words.
Example When CIO 000000 is ON in the following example, two MCRO(099) instruc-
tions pass different input and output data to subroutine 1.
1,2,3... 1. The first MCRO(099) instruction passes the input data in CIO 0100 to
CIO 0103 and executes the subroutine. When the subroutine is complet-
ed, the output data is stored in CIO 0300 to CIO 0303.
MCRO(099)
MCRO(099)
Execution of subrou-
tine between
SBN(092) and
RET(093).
The subroutine uses A600 to
A603 as inputs and A604 to
A607 as outputs.
Name Label Operation
Error Flag ER ON if nesting exceeds 16 levels.
ON if the specified subroutine number does not exist.
ON if a subroutine calls itself.
ON if a subroutine being executed is called.
ON if the specified subroutine is not defined in the current
task.
OFF in all other cases.
Name Address Operation
Macro area input
words
A600 to
A603
When MCRO(099) is executed the four words
from S to S+3 are copied to A600 to A603. These
input words are passed to the subroutine.
Macro area input
words
A604 to
A607
After the subroutine specified in MCRO(099) has
been executed, the output data in these output
words and copied to D to D+3.
 Loading...
Loading...











