Rockwell Automation Publication 7000-UM202H-EN-P - November 2023 35
Chapter 2 Power Component Definition and Maintenance
7. Replace ring lugs on terminals. Plug in ribbon cables making sure that
cables are positioned properly and fitting is secure (locking mechanism
is engaged).
8. For personnel and equipment safety, ensure both grounding connections
are re-connected to the sensing board.
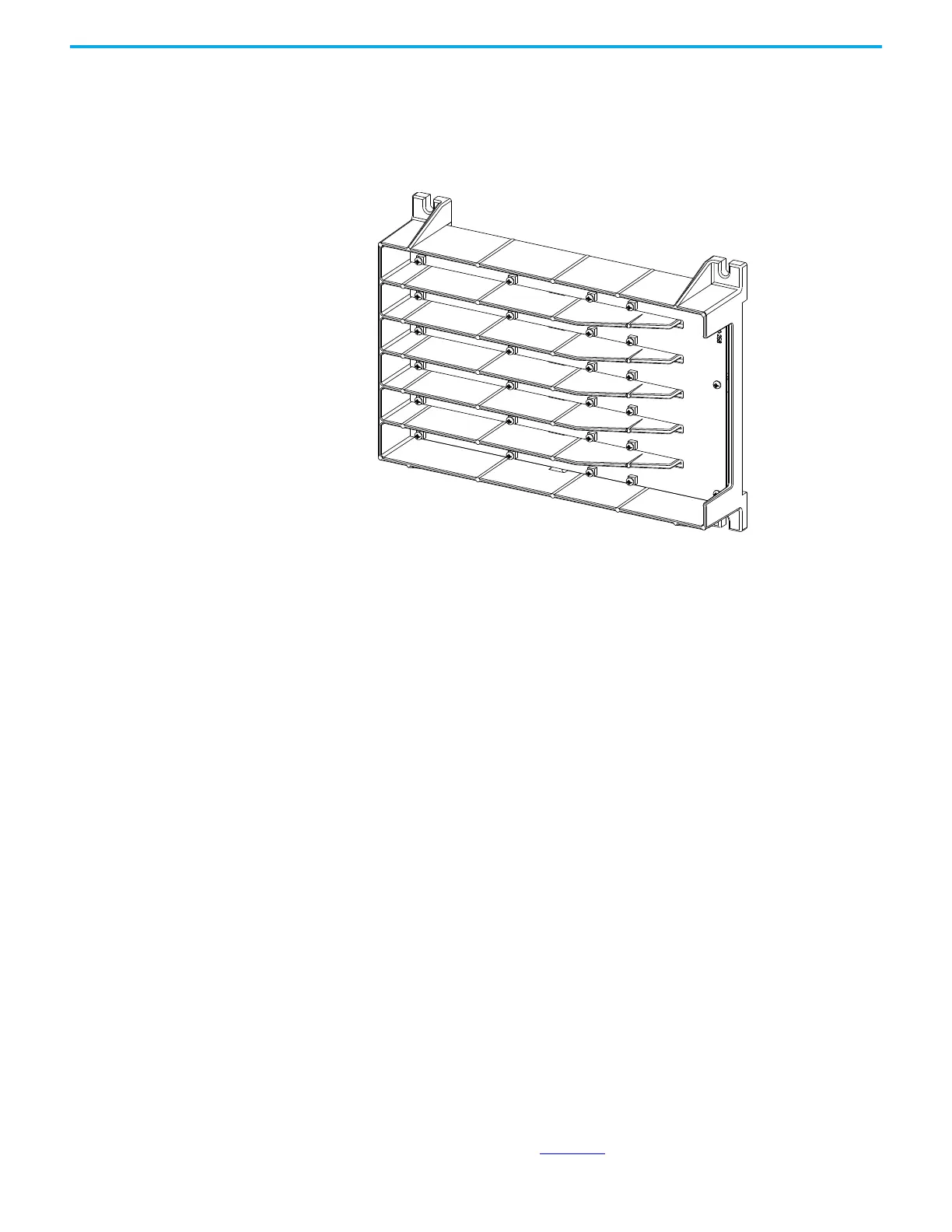
Figure 27 - Sensing Board with Mounting Hardware Placement
Input Transient Protection The drive provides input transient protection in one of two forms:
• Transient suppression network (TSN), or
• Surge arresters
The TSN is optimized for 18-pulse rectifier designs. Surge arresters are
optimized for AFE and Direct-to-Drive™ rectifier designs.
Transient Suppression Network (TSN)
The TSN module consists of an assembly of suppressors connected to each of
the three phase input lines and the structure ground bus. There are three
assemblies for an 18-pulse drive.
A transient voltage spike in excess of the semiconductor rating will destroy or
shorten the lifespan of the device. The TSN module suppresses transient
overvoltages on the drive input, and is a standard feature of the drive. The two
basic blocks of the TSN module are the MOV suppressor and the MOV fuse.
MOV Suppressor
The transient suppressors used in the module are heavy-duty metal oxide
varistors (MOVs). Varistors are voltage dependent, nonlinear resistors. They
have symmetrical voltage/current characteristics similar to back-to-back
connected Zener diodes. The varistor has very high resistance below its voltage
rating and appears as an open circuit.
The leakage current through the device would be very small in this region.
When a voltage transient occurs in which the voltage exceeds the ‘knee’ in the
curve, the varistor resistance changes from its high state by several orders of
magnitude to a very low level. The voltage is clamped for a change in current of
several orders of magnitude (Figure 28
).

 Loading...
Loading...











