Publication 1762-RM001C-EN-P
6-18 Using High-Speed Outputs
PWM - Pulse Width
Modulation
Instruction Type: output
PWM Function
The PWM function allows a field device to be controlled by a PWM wave
form. The PWM profile has two primary components:
•
Frequency to be generated
•
Duty Cycle interval
The PWM instruction, along with the HSC and PTO functions, are
different than all other controller instructions. Their operation is
performed by custom circuitry that runs in parallel with the main system
processor. This is necessary because of the high performance
requirements of these instructions.
The interface to the PWM sub-system is accomplished by scanning a PWM
instruction in the main program file (file number 2), or by scanning a
PWM instruction in any of the subroutine files. A typical operating
sequence of a PWM instruction is as follows:
1. The rung that a PWM instruction is on is solved true (the PWM is
started).
2. A waveform at the specified frequency is produced.
3. The RUN phase is active. A waveform at the specified frequency with
the specified duty cycle is output.
4. The rung that the PWM is on is solved false.
5. The PWM instruction is IDLE.
While the PWM instruction is being executed, status bits and data are
updated as the main controller continues to operate. Because the PWM
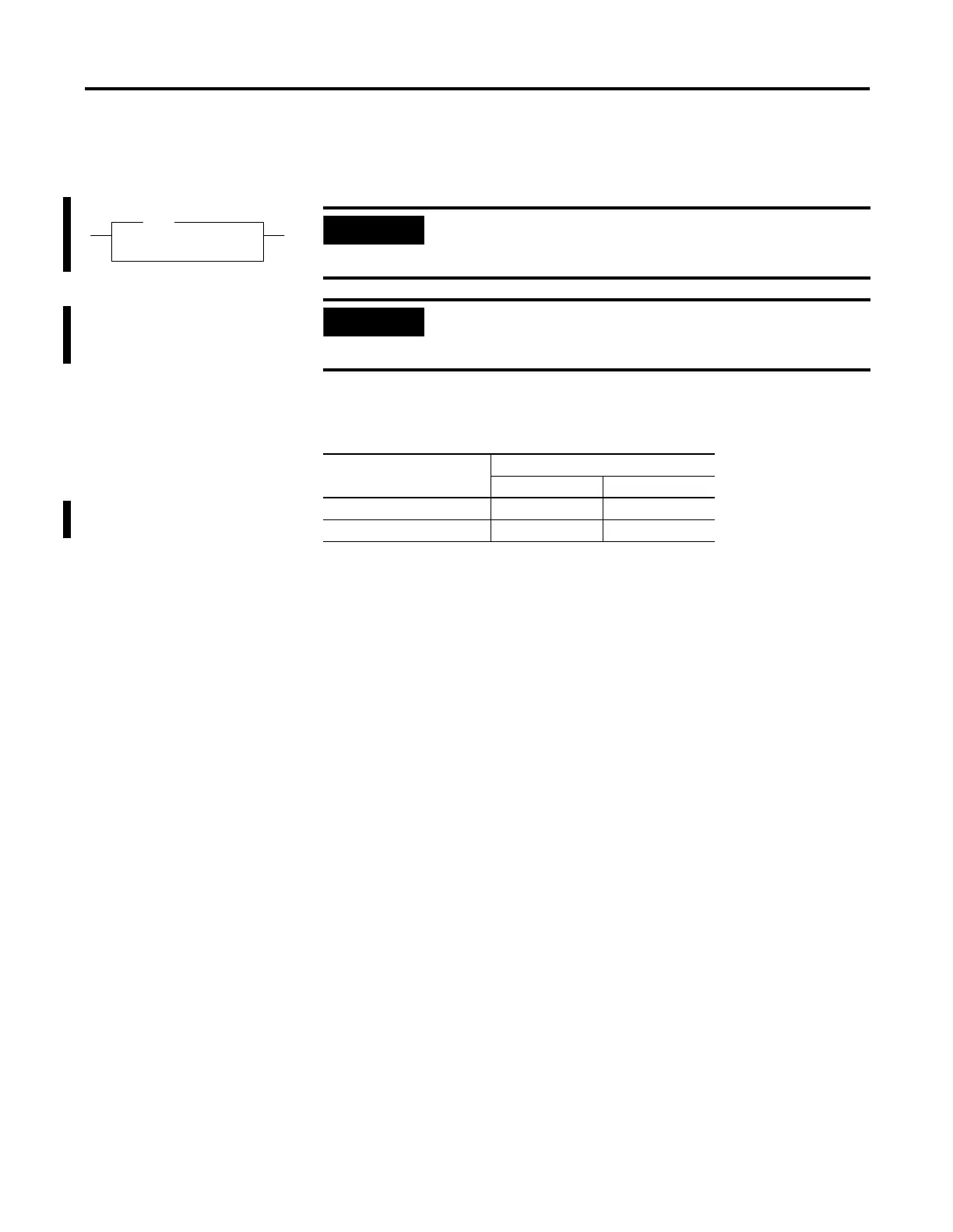
PWM
Pulse Width Modulation
PWM Number 1
PWM
IMPORTANT
The PWM function can only be used with the controller’s
embedded I/O. It cannot be used with expansion I/O
modules.
IMPORTANT
The PWM instruction should only be used with MicroLogix
1200 and 1500 BXB units. Relay outputs are not capable of
performing very high-speed operations.
Table 6.4 Execution Time for the PWM Instruction
Controller When Rung Is:
True False
MicroLogix 1200 126.6
µ
s 24.7
µ
s
MicroLogix 1500 107.4
µ
s 21.1
µ
s

 Loading...
Loading...











