22/72 About this product
BoschRexrothAG, axial piston variable pump A4VSO, RE 92050-01-X-B1/2019.08.23
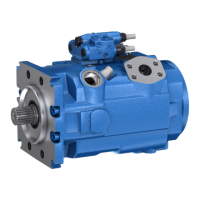
5.2.2 Functional description
Torque and rotational speed are applied to the drive shaft(1) by a drive motor.
Thedrive shaft is connected to the cylinder(10) by splines, causing the cylinder to
rotate. With every revolution, the pistons(11) complete a stroke in the
cylinderbores, the size of which depends on the pitch of the cradle(13). The
slipperpads(12) are held on with the pistons and guided along the glide surface of
the cradle by the retaining plate(2). The pitch oftheswashplate during arevolution
causes each piston tomove over thebottom and top dead centers and back toits
initial position. During this sequence, hydraulic fluid is fed in and drained out
through the two control slots in the distributor plate(6) according to displacement.
On the high-pressure side (5), the hydraulic fluid is pushed out of the cylinder
chamber and into the hydraulic system by the pistons. At the same time, hydraulic
fluid flows into the expanding piston chamber on the low-pressure side(9). In an
open circuit, this sequence is supported by the return flow and boost pressure.
The swivel angle of the cradle(13) is continuously adjustable. Controlling
theswashplate swivel angle changes thepiston stroke and, therefore,
thedisplacement. The swivel angle is changed hydraulically via the
controlvalve(4)or the stroking piston (3). The cradle is mounted in swivel bearings
for easy movement and the neutral position is spring-centered. Increasing theswivel
angle increases thedisplacement; reducing theangle reduces displacement
accordingly.
Additional information on the control devices, e.g. the circuit diagram or
characteristic curves, can be found in technical data sheet (Part II).
The following warning note relates to all axial piston units with central position as
basic setting of the pump:
CAUTION
The spring feedback feature in the control module is not a safety device!
The control module can stick in an undefined position by internal contamination
(contaminated hydraulic fluid, abrasion or residual contamination from system
components). Asaresult, the flow inthe axial piston unit will nolonger respond
correctly tothe operator's specifications.
▶ Check whether the application onyour machine requires additional safety
measures tobring the driven consumer toasafe position (immediate stop).
Ifnecessary, make sure these are appropriately implemented.
Pump
Control

 Loading...
Loading...