190-02692-00 Rev. A
Garmin G1000 Pilot’s Guide for the Piper PA-32 Saratoga
9
SYSTEM OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
OVERVIEW
FLIGHT
INSTRUMENTS
EIS
AUDIO PANEL
& CNS
FLIGHT
MANAGEMENT
HAZARD
AVOIDANCE
AFCS
ADDITIONAL
FEATURES
APPENDICES INDEX
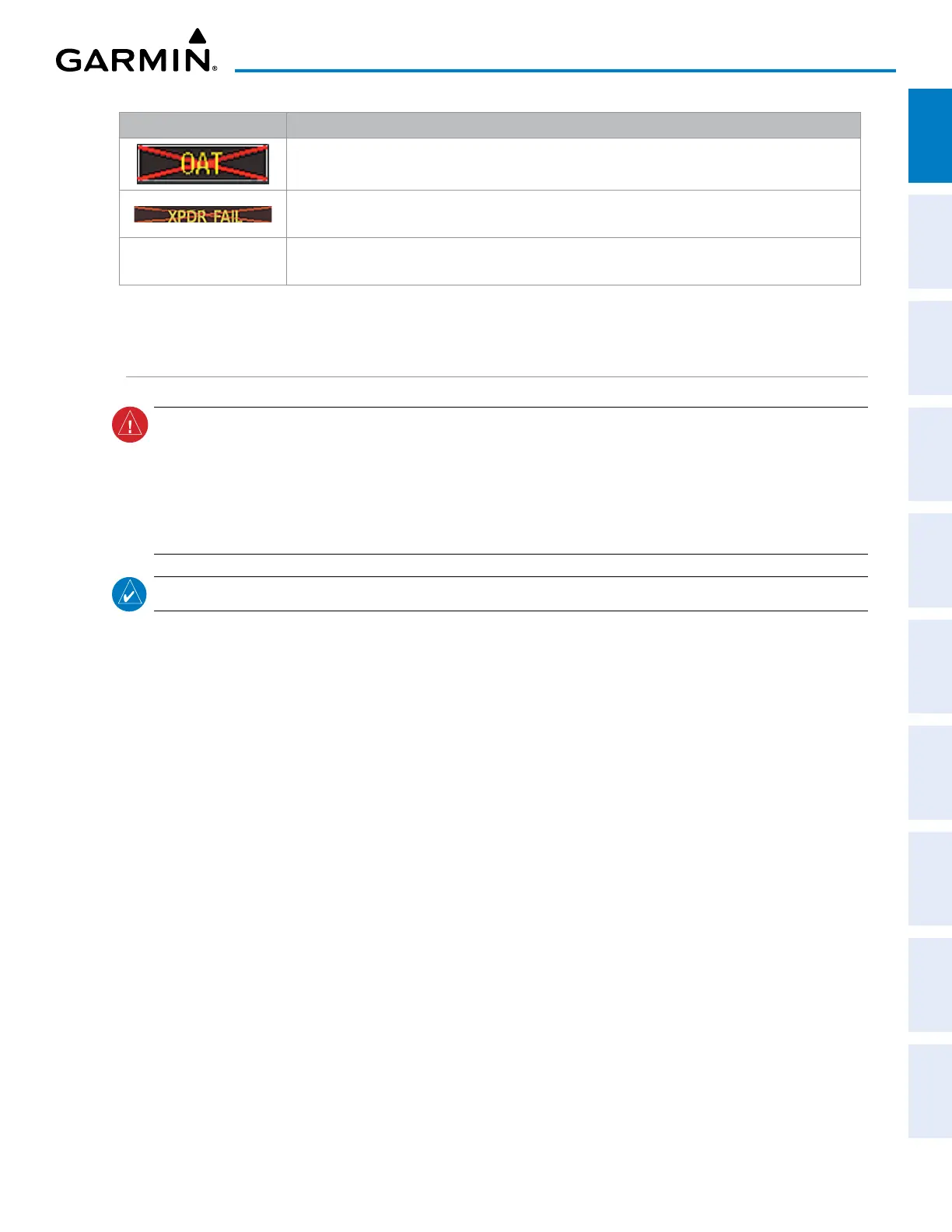
System Annunciation Comment
Display system is not receiving valid OAT information from the Air Data Computer.
Display system is not receiving valid transponder information.
Other Various Red X
Indications
A red ‘X’ through any other display field (such as engine instrumentation fields) indicates the
field is not receiving valid data.
Table 1-1 System Failure Annunciations
AHRS OPERATION
WARNING
:
Do not rely on the accuracy of attitude and heading indications in the following geographic
areas (due to variations in the earth’s magnetic field): North of 72° North latitude at all longitudes; South
of 70° South latitude at all longitudes; North of 65° North latitude between longitude 75° W and 120° W.
(Northern Canada); North of 70° North latitude between longitude 70° W and 128° W. (Northern Canada);
North of 70° North latitude between longitude 85° E and 114° E. (Northern Russia); South of 55° South
latitude between longitude 120° E and 165° E. (Region south of Australia and New Zealand).
NOTE: Aggressive maneuvering while AHRS is not operating normally may degrade AHRS accuracy.
In addition to using internal sensors, the AHRS uses GPS information, magnetic field data and air data to assist
in attitude/heading calculations. In normal mode, the AHRS relies upon GPS and magnetic field measurements.
If either of these external measurements is unavailable or invalid, the AHRS uses air data information for
attitude determination. Four AHRS modes of operation are available (see following figure) and depend on the
combination of available sensor inputs. Loss of air data, GPS, or magnetometer sensor inputs is communicated
to the pilot via message advisory alerts.
The AHRS corrects for shifts and variations in the Earth’s magnetic field by applying the Magnetic Field
Variation Database. The Magnetic Field Variation Database is derived from the International Geomagnetic
Reference Field (IGRF). The IGRF is a mathematical model that describes the Earth’s main magnetic field
and its annual rate of change. The database is updated approximately every 5 years. See the Appendices for
information on updating the Magnetic Field Variation Database. The system will prompt you on startup when
an update is available. Failure to update this database could lead to erroneous heading information being
displayed to the pilot.

 Loading...
Loading...