IS620P User Manual Chapter 6 Troubleshooting
- 121 -
■
Fault and Alarm Records
The servo drive has the function of recording faults and alarms. It can record the names of the
recent ten faults and alarms and the drive state parameters at the occurrence of these faults
and alarms. If a fault or an alarm occurs ve times recently, the servo drive records the fault/
alarm only once.
After the fault/alarm is reset, the servo drive still records the fault/alarm. To clear the fault/
alarm record, use the system initialization function (H02-31 = 1 or 2).
You can select the fault/alarm record No. in H0B-33, view the corresponding fault/alarm code
in H0B-34 and view related drive state parameters in H0B-35 to H0B-42. For details of these
parameters, refer to Chapter 3 Wiring of Servo System. If no fault occurs, the operation panel
displays Er.000 in H0B-34.
When you view fault/alarm code in H0B-34, the operation panel displays "Er.xxx", where
"xxx" is the fault/alarm code. When you read H0B-34 through the servo debugging platform
of Inovance or communication, the decimal data must be converted to hexadecimal data. The
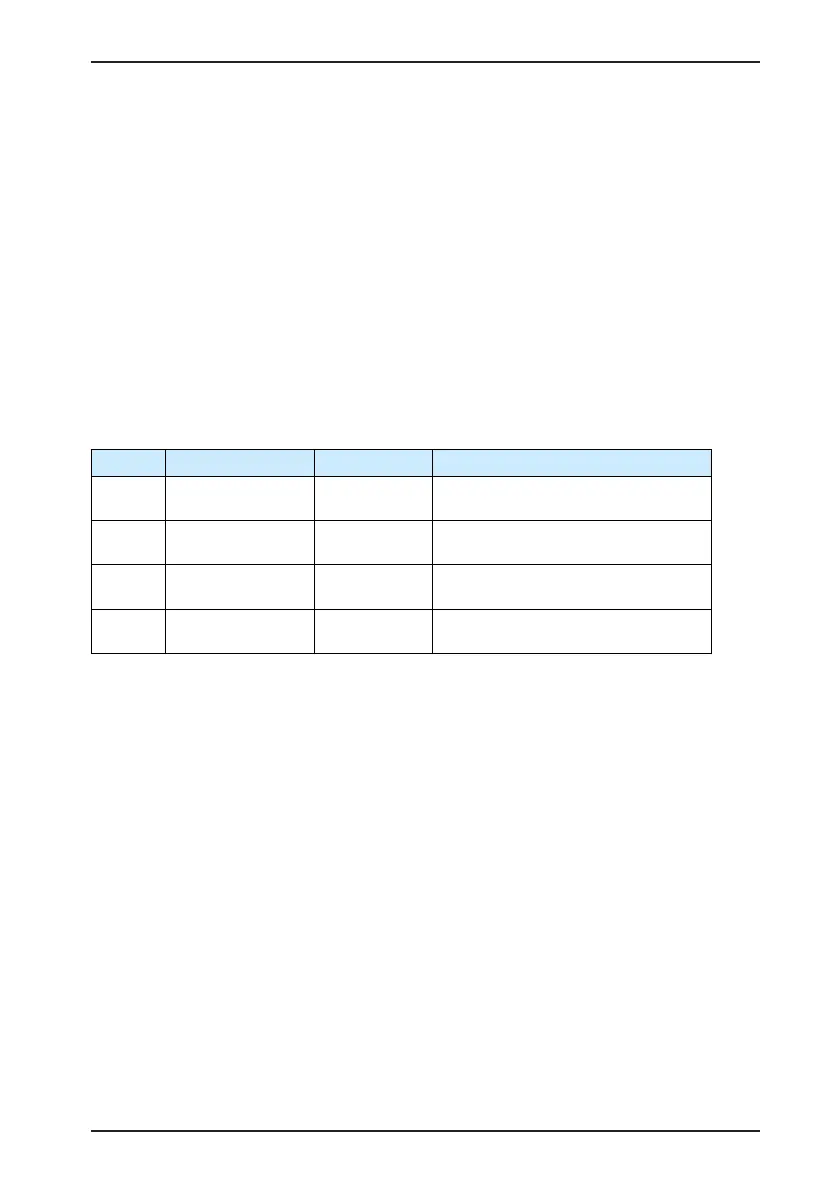
following table gives examples of data conversion.
Er.xxx H0B-34 (Decimal) H0B-34 (Hex) Description
Er.101 257 0101
0: No.1 non-resettable fault
101: Fault code
Er.130 8496 2130
2: No.1 resettable fault
130: Fault code
Er.121 24865 6121
6: No.2 resettable fault
121: Fault code
Er.110 57616 E110
E: No.3 resettable alarm
110: Alarm code
■
Fault/Alarm DO Output
The servo drive can output the current highest-level fault/alarm code.
To implement the fault/alarm DO output function, allocate three DO terminals with DO functions
FunOUT.12: ALMO1 (3-digit fault code output), FunOUT.13: ALMO2 (3-digit fault code output)
and FunOUT.14: ALMO3 (3-digit fault code output). When different faults/alarms occur, the
level of the three DOs changes.
ALMO1, ALMO2 and ALMO3 are shorted as AL1, AL2 and AL3, respectively.

 Loading...
Loading...











