5-6
SECTION 5
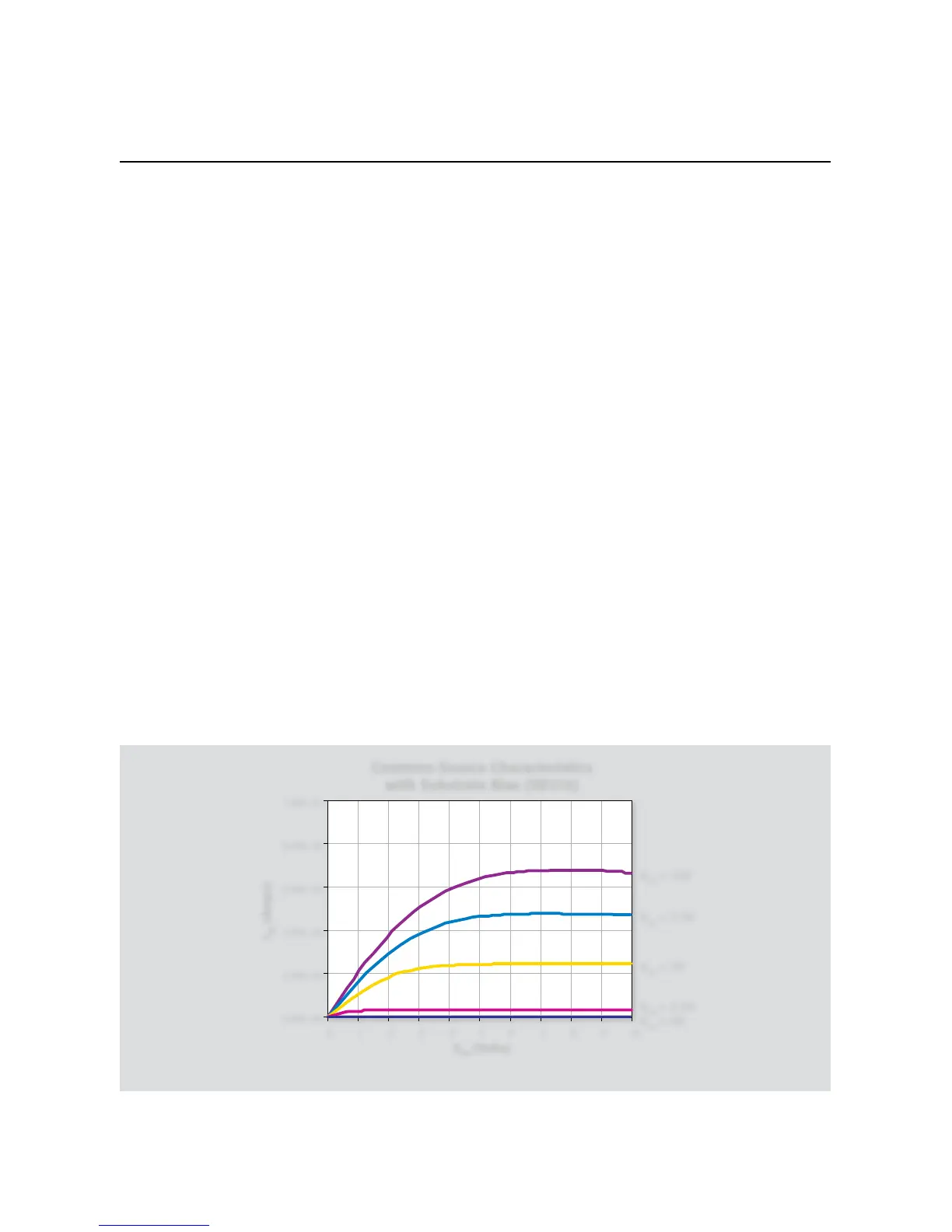
Using Substrate Bias
6. Select the TSPLINK_CFG menu. (If the Series 2600
instruments used have firmware Revision 1.4.0 or later
installed, the menu name should be TSPLINK.)
7. Select the RESET to initialize the TSP-Link.
Turn on the computer and start Test Script Builder (TSB). 5.
Once the program has started, open a session by connecting
to the master instrument. For details on how to use TSB, see
the Series 2600 Reference Manual.
You can simply copy and paste the code from Appendix A in
this guide into the TSB script editing window (Program 13),
manually enter the code from the appendix, or import the
TSP file ‘FET_Comm_Source_Vsb.tsp’ after downloading it to
your PC.
If your computer is currently connected to the Internet, click
on the following link to begin downloading: http://www.
keithley.com/data?asset=50921.
Install an NPN FET such as an SD210 in the appropriate tran-6.
sistor socket of the test fixture.
Now, we must send the code to the instrument. The simplest 7.
method is to right-click in the open script window of TSB and
select ‘Run as TSP file’. This will compile the code and place
it in the volatile run-time memory of the instrument. To store
the program in non-volatile memory, see the “TSP Program-
ming Fundamentals” section of the Series 2600 Reference
Manual.
Once the code has been placed in the instrument run-time 8.
memory, we can run it at any time simply by calling the
function ‘FET_Comm_Source_Vsb()’. This can be done by
typing the text ‘
FET _ Comm _ Source _ Vsb()
’ after the
active prompt in the Instrument Console line of TSB.
In the program ‘9. FET_Comm_Source_Vsb().tsp’, the function
FET _ Comm _ Source _ Vsb(vgsstart, vgsstop,
vgssteps, vdsstart, vdsstop, vdssteps,
vsbsource)
is created.
vgsstart
• represents the start value for the gate-source
voltage sweep
vgsstop
• represents the stop value for the gate-source
voltage sweep
vgssteps
• represents the number of steps in the sweep
vdsstart
• represents the start value for the drain-source
voltage sweep
vdsstop
• represents the stop value for the drain-source
voltage sweep
vdssteps
• represents the number of steps in the sweep
vsbsource
• represents the substrate bias voltage
If these values are left blank, the function will use the default
values given to the variables, but you can specify each vari-
able value by simply sending a number that is in-range in the
function call. As an example, if you wanted to have the gate-
source (V
GS
) voltage sweep start value at 1V, the gate-source
sweep stop value at 12V and the number of steps to be 10,
the drain-source (V
DS
) voltage sweep start value at 1V, the
drain-source sweep stop value at 12V and the number of steps
to be 80, and the substrate bias to be –2V, you would send

 Loading...
Loading...











