1.3
General Information on Drive Units
~~
1.3.1
When using
a
stepper motor
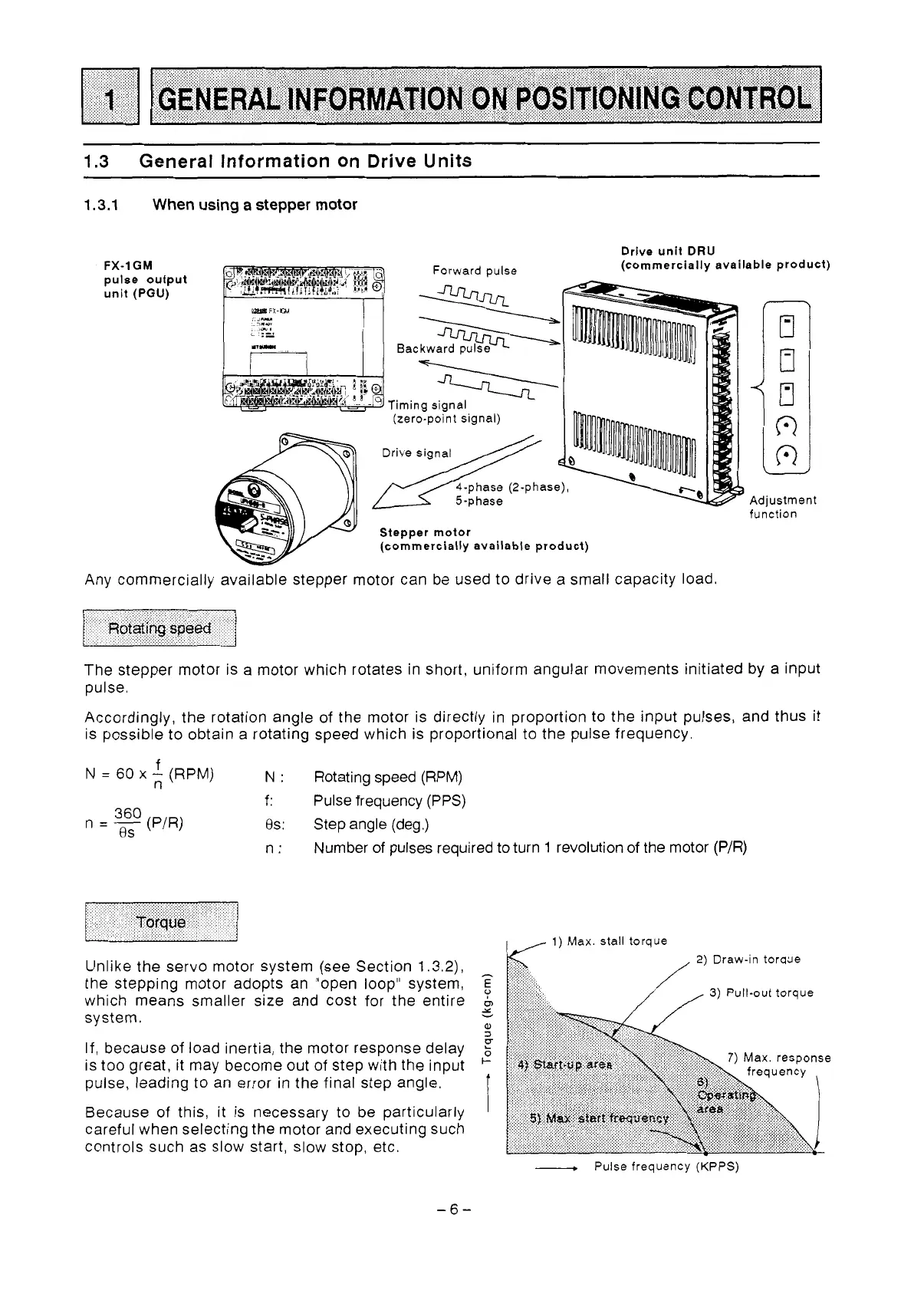
Drive unit DRU
AI
FX-1
GM
pulse
output
unit
(PGU)
iy commerci
Forward pulse
(commercially available product)
(zero-point signal)
Drive signal
//
1
~
lrnnrnnnnr
7
Adjustment
function
Stepper motor
(commercially available product)
ally available stepper motor can be used to drive a small capacity load,
The stepper motor is a motor which rotates in short, uniform angular movements initiated
by
a
input
pulse.
Accordingly, the rotation angle of the motor is directly in proportion
to
the input pulses, and thus it
is possible to obtain a rotating speed which is proportional
to the pulse frequency.
N
=
60
X
-
(RPM)
f
n
N
:
Rotating speed (RPM)
f: Pulse frequency
(PPS)
n
=
-
(P/R)
Os:
Step angle (deg.)
n
:
Number of pulses required to turn
1
revolution of the motor
(P/R)
360
OS
Unlike the servo motor system (see Section 1.3.2),
the stepping motor adopts an "open loop" system,
E
which means smaller size and cost for the entire
cT)
Y
system.
t
If,
because of load inertia, the motor response delay
6
is
too
great, it may become out of step with the input
c-
pulse, leading to an error in the final step angle.
Because of this, it is necessary to be particularly
careful when selecting the motor and executing such
controls such as slow start, slow stop, etc.
0
2
0-
i
,
2)
Draw-in torque
..............
...........
..
.
.
. .
.....
, ,
Pulse frequency (KPPS)
-6-

 Loading...
Loading...











