8 - 12
MELSEC-Q
8 OPR CONTROL
8.2.5 OPR method (3): Stopper method 2)
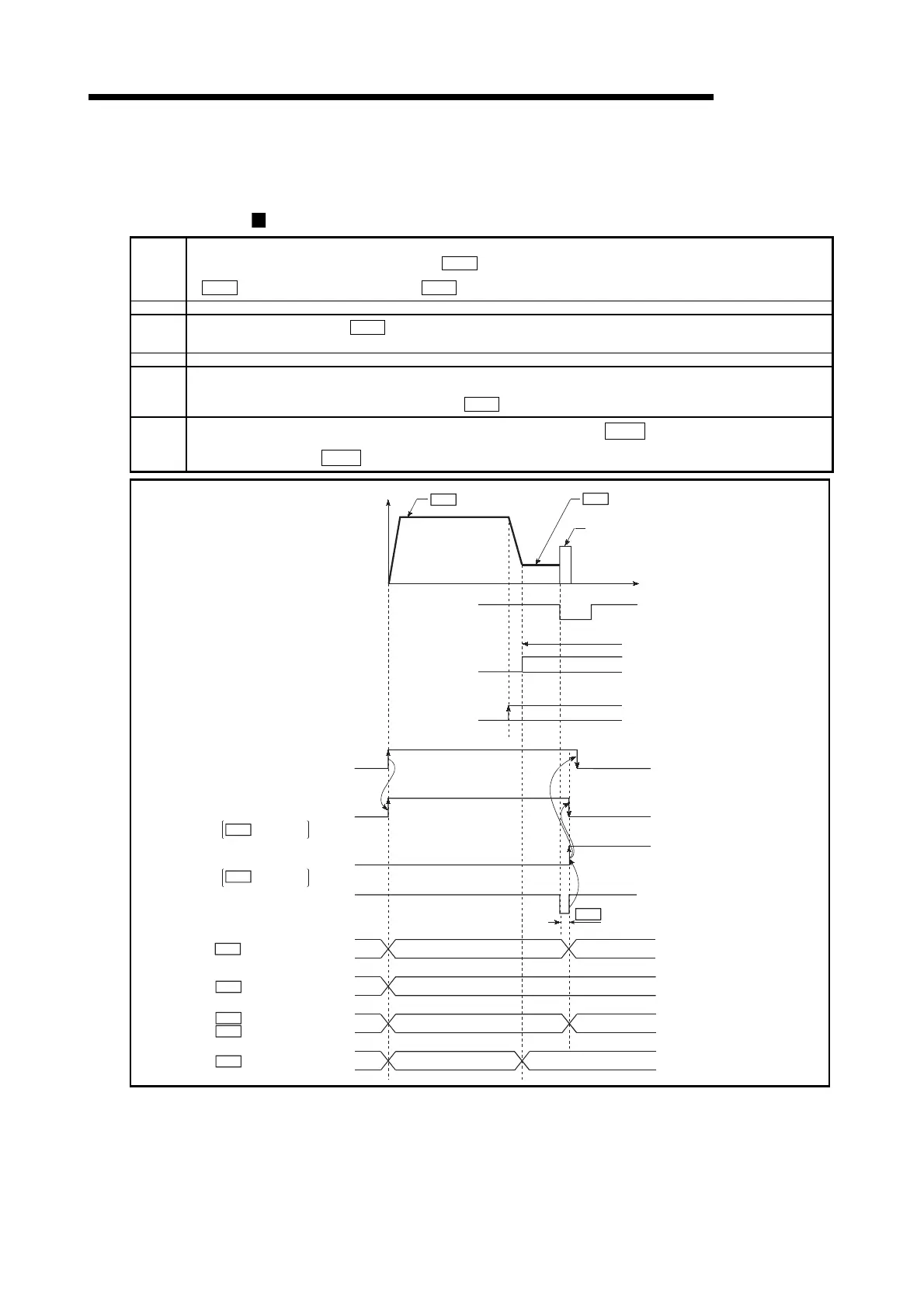
The following shows an operation outline of the "stopper method 2)" OPR method.
Operation chart
1)
The machine OPR is started.
(The machine begins the acceleration designated in "
Pr.51
OPR acceleration time selection", in the direction designated in
"
Pr.44
OPR direction". It then moves at the "
Pr.46
OPR speed" when the acceleration is completed.)
2) The machine begins decelerating when the near-point dog ON is detected.
3)
The machine decelerates to the "
Pr.47
Creep speed", and subsequently moves at that speed.
(Torque limiting is required at this time. If the torque is not limited, the servomotor may fail in step 4).)
4) The machine presses against the stopper at the creep speed and stops.
5)
The pulse output from the QD75 will stop at the zero signal after the machine stops, outputting the "deviation counter clear output" to the
drive unit.
(A "deviation counter clear signal output time" is set in the
Pr.55
.)
6)
After a "deviation counter clear output" is output to the drive unit, the OPR complete flag (
Md.31
Status: b4) turns from OFF to ON,
and the OPR request flag (
Md.31
Status: b3) turns from ON to OFF.
t
ON
OFF
OPR speed
Creep speed
Valid torque limit range
Torque limit
ON
OFF
OFF
ON
Standby
OPR Standby
Inconsistent
0
Movement amount
after near-point dog
ON
Inconsistent
Value the machine moved is stored OP address
Inconsistent Torque limit setting value OPR torque limit value
Current feed value
V
Near-point dog
ON
OFF
Stops at stopper
Zero signal
Deviation counter clear output
OPR request flag
OPR complete flag
Md.31
Md.31
Md.26
Md.34
Torque limit stored
value
Md.35
Md.20
Md.21
Pr.46
Pr.47
1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6)
Pr.55
Machine feed value
Machine OPR start
(Positioning start signal)
[Y10,Y11,Y12,Y13]
Status : b3
Status : b4
Axis operation
status
Deviation counter clear
signal output time
Fig. 8.7 Stopper method 2) machine OPR

 Loading...
Loading...











