99
6-1-3 Structure of ST and Example
Using general expressions, ST programming requires no special knowledge.
Remember the following two rules:
(1) Use a colon and an equals sign (:=) to assign a value to a variable.
(2) Statements must end with a semicolon (;).
Example
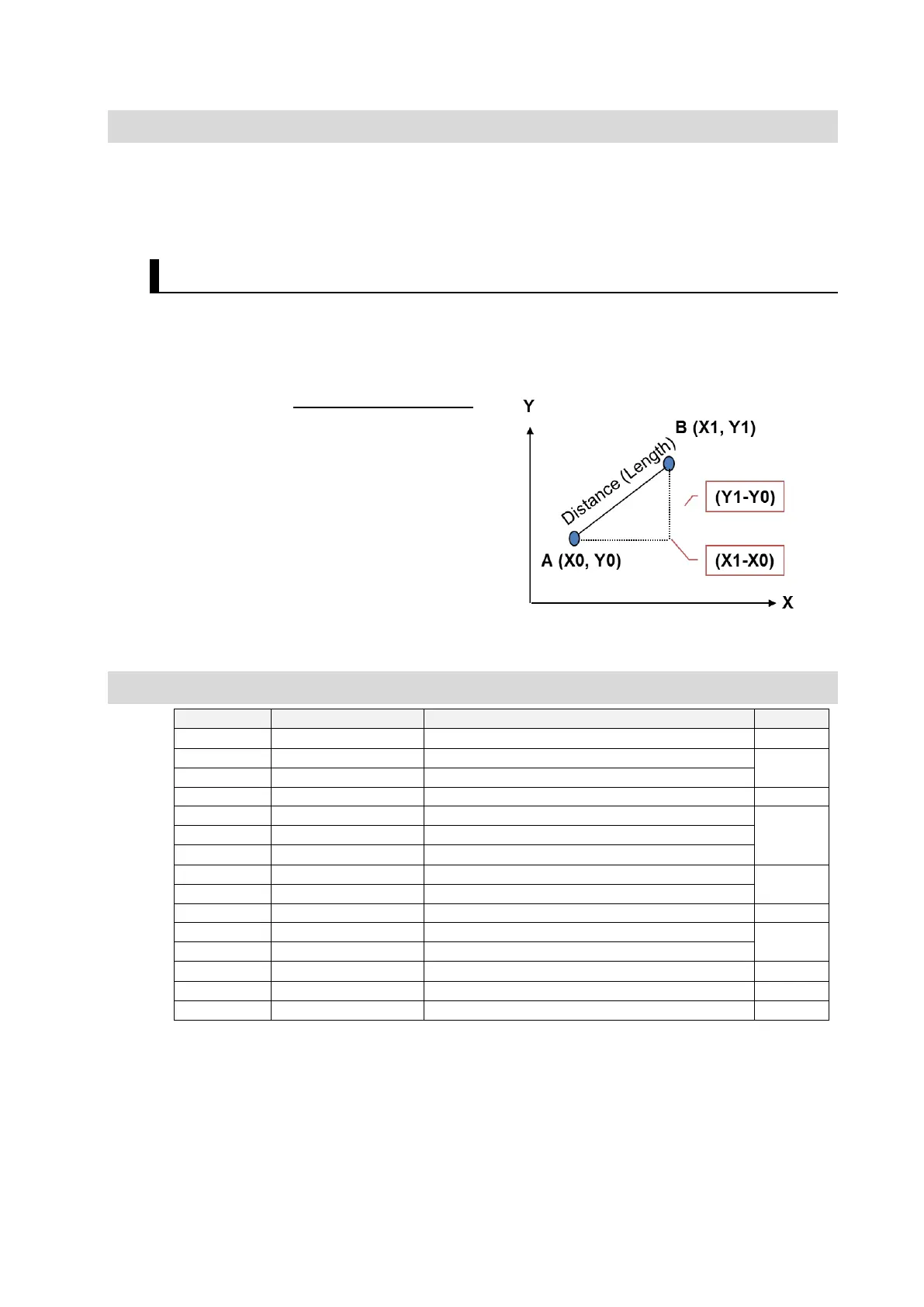
An example of the statement to calculate the distance between two points using Pythagoras'
theorem is shown below.
Just apply the formula.
■ Formula
𝐋𝐞𝐧𝐠𝐭𝐡 =
�
(𝐗𝟏 − 𝐗𝟎)
𝟐
+ (𝐘𝟏 − 𝐘𝟎)
𝟐
■ ST program
Length := SQRT((X1-X0)**2+(Y1-Y0)**2);
* SQRT: Square Root
6-1-4 Operators
Operator Operation Notation example Priority
Value := (1+2)*(3+4); // Value is 21
-, + Sign +100, -100
2
Value := NOT TRUE; // Value is FALSE
** Exponent Value := 2**8; // Value is 256 3
Value := 8*100; // Value is 800
4 / Division Value := 200/25; // Value is 8
Value := 10 MOD 6; // Value is 4
+ Addition Value := 200+25; // Value is 225
5
Value := 200-25; // Value is 175
<, >, <=, >= Comparison Value := 60>10; // Value is TRUE 6
Value := 8=7; // Value is FALSE
7
<> Does not match Value := 8<>7; // Value is TRUE
Value := 2#1001 AND 2#1100; // Value is 2#1000
XOR Logical exclusive OR Value := 2#1001 XOR 2#1100; // Value is 2#0101 9
Value := 2#1001 XOR 2#1100; // Value is 2#1101
 Loading...
Loading...











