8 CIP Message Communications
8-18
NJ/NX-series CPU Unit Built-in EtherNet/IP Port User’s Manual (W506)
For a CIP commincations instruction, you prepare a variable to store the request path. In this variable,
you specify the object to access with the user program.
A structure in which the Class ID, Instance ID and Attribute ID are specified is provided for the data type
of a variable for a request path.
There are two types of structures: standard structure (_sREQUEST_PATH) and extension structure
(_sREQUEST_PATH_EX). When you use an extension structure, it is possible to specify the size
according to the size of values of the Class ID, Instance ID and Attribute ID of the object that you
access. When you use a standard structure, the size is always set to 16 bits.
A CPU Unit with unit version 1.11 or later and Sysmac Studio version 1.15 or higher are required
to specify extension structure (_sREQUEST_PATH_EX).
When a Standard Structure Variable Is Used
Example: Using a standard structure variable to input values into RqPath (Request Path) for the
CIPSend instruction
1
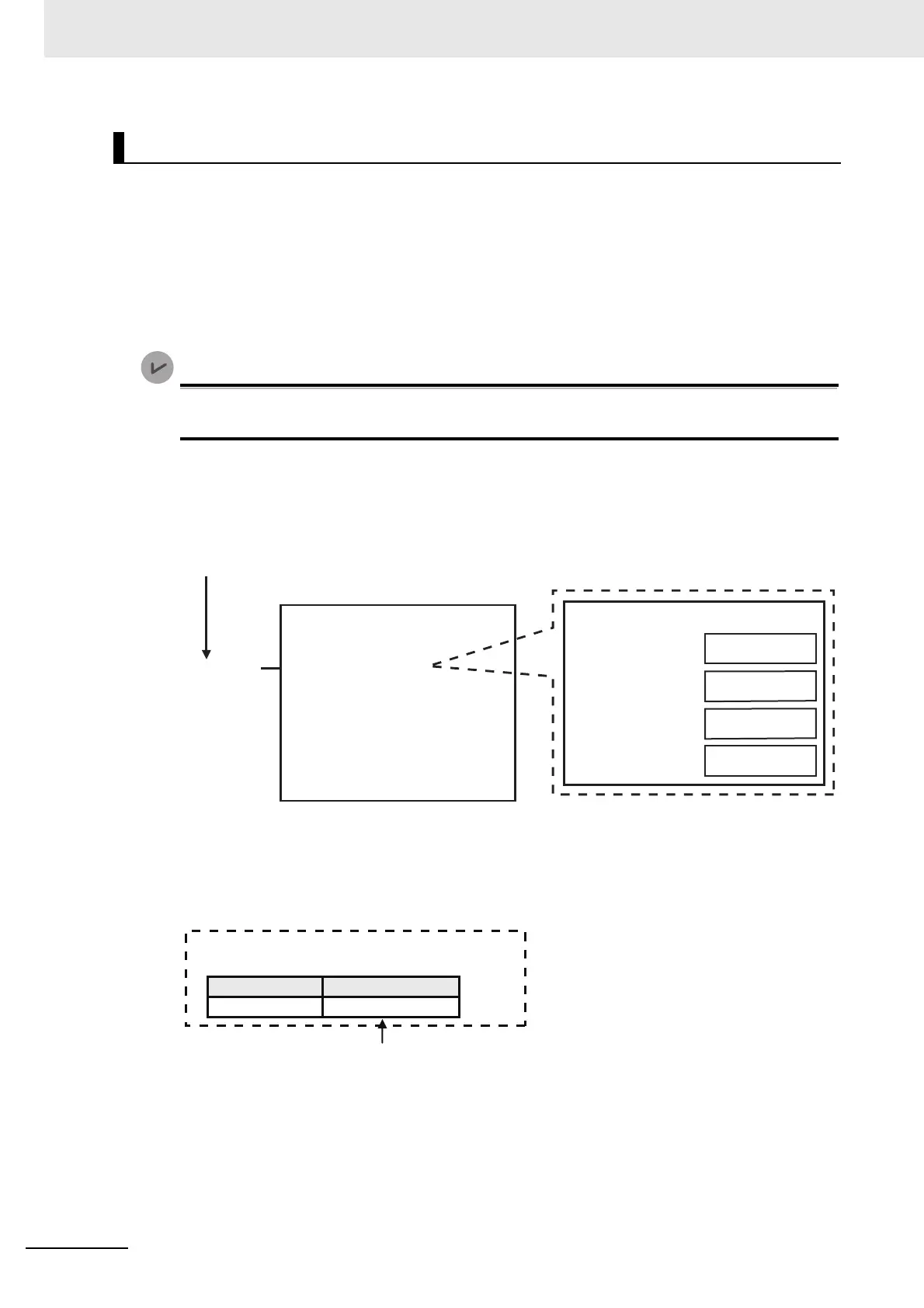
Create a standard structure variable.
To use a standard structure variable to input values into RqPath (Request Path) for a CIP com-
munications instruction, first you need to create a standard structure user-defined variable.
When you create a variable in a variable table, select the pre-registered standard structure
(sREQUEST_PATH) for a CIP communications instruction.
Providing the Structure Variables to Input Request Paths
InstanceID
(Instance ID)
Create variable A with a variable with
the standard structure (_sREQUEST_PATH).
CIP communications instruction
Variable A
CIPSend
RqPath
(Request Path)
RqPath data type
Value
ClassID
(Class ID)
Member
AttributeID
(Attribute ID)
2
3
1
TRUE
isAttributeID
(Attribute usage)
Select a standard structure for the data type of variable A.
Variable table
Data type
_sREQUEST_PATH
A
Name
 Loading...
Loading...











