TPS-1 User’s Manual: Hardware 3. Host Interface
R19UH0081ED0107 Rev. 1.07 page 26 of 86
Jul 30, 2018
3.3.1.2. Structure of a command byte
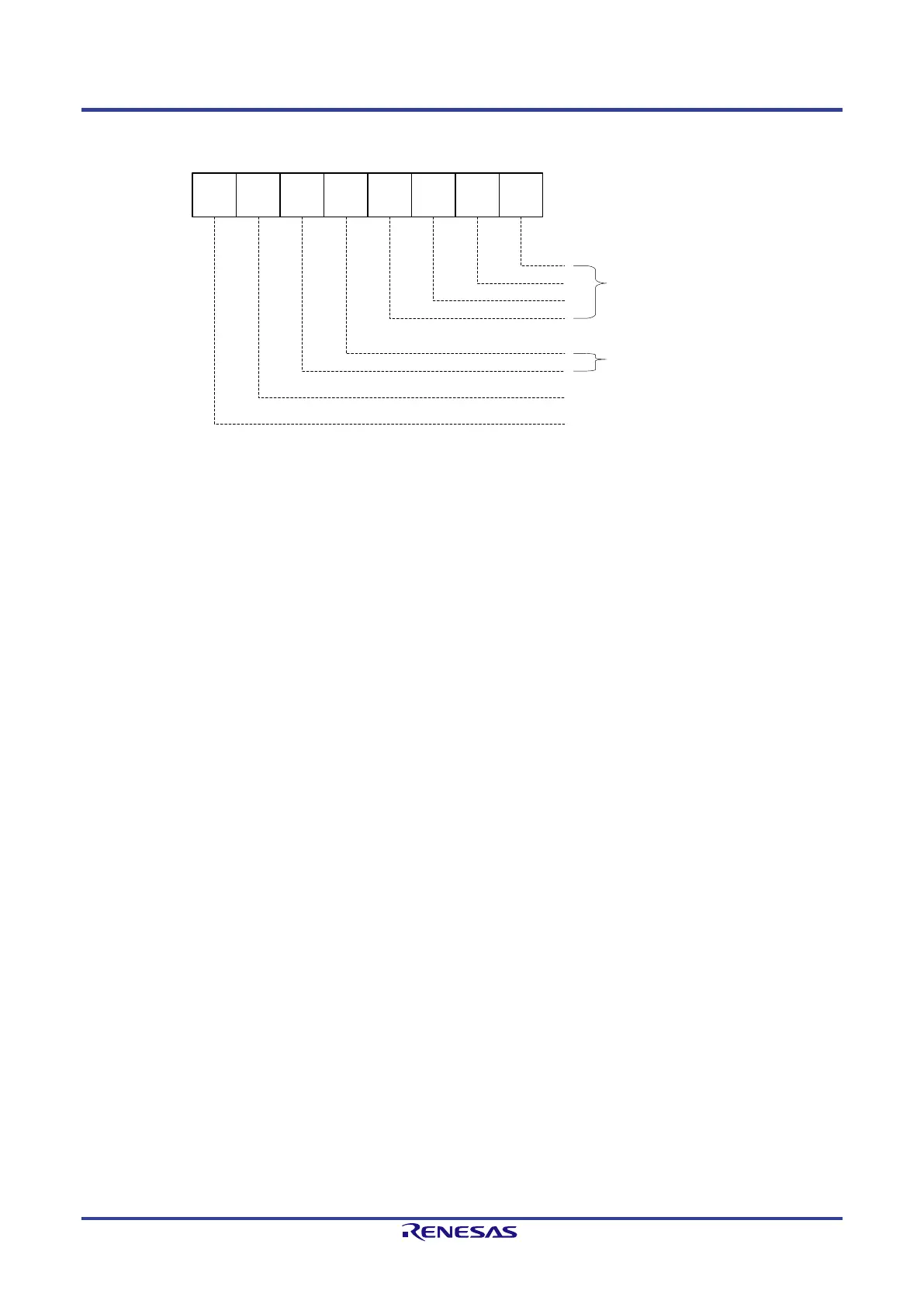
Figure 3-9 shows the format of a command byte. A command byte can be followed by an address area, length area and data.
b7 b6
b
5 b
4
b3
b2
b
1 b0
Access Area
Direct IO Length
b6 = 1 (write)
b7 = 1 (read)
Figure 3-9: Command byte for SPI slaves (host interface)
The bits of the command byte have the following meaning:
• b7 indicates a read command,
• b6 indicates a write command,
• b5 and b4 describe the addressing range:
„00“: MEM access to the complete shared memory (64 Kbyte)
„01“: IO access to the input/output area
„10“: access to a multicast provider CR (only write)
„11“: fractional access to an I-CR (b6 = 1) or MC-CR (b6 = 0)
• b3 .. b0 contain the length for an optimized direct data access
„= 0000“: no direct access.
„≠ 0000“: direct access length information (maximum of 15 byte)
 Loading...
Loading...