Technical Instructions LMV Series
Document No. LV3-1000
Section 5 Page 10 SCC Inc.
Centrifugal Blower Fundamentals
Since a centrifugal blower is the piece of machinery being controlled by the LMV3, a brief mention of its
basic characteristics is warranted. Specifically, there are three fundamental "fan laws" that a person
working with such equipment should be aware of. These are:
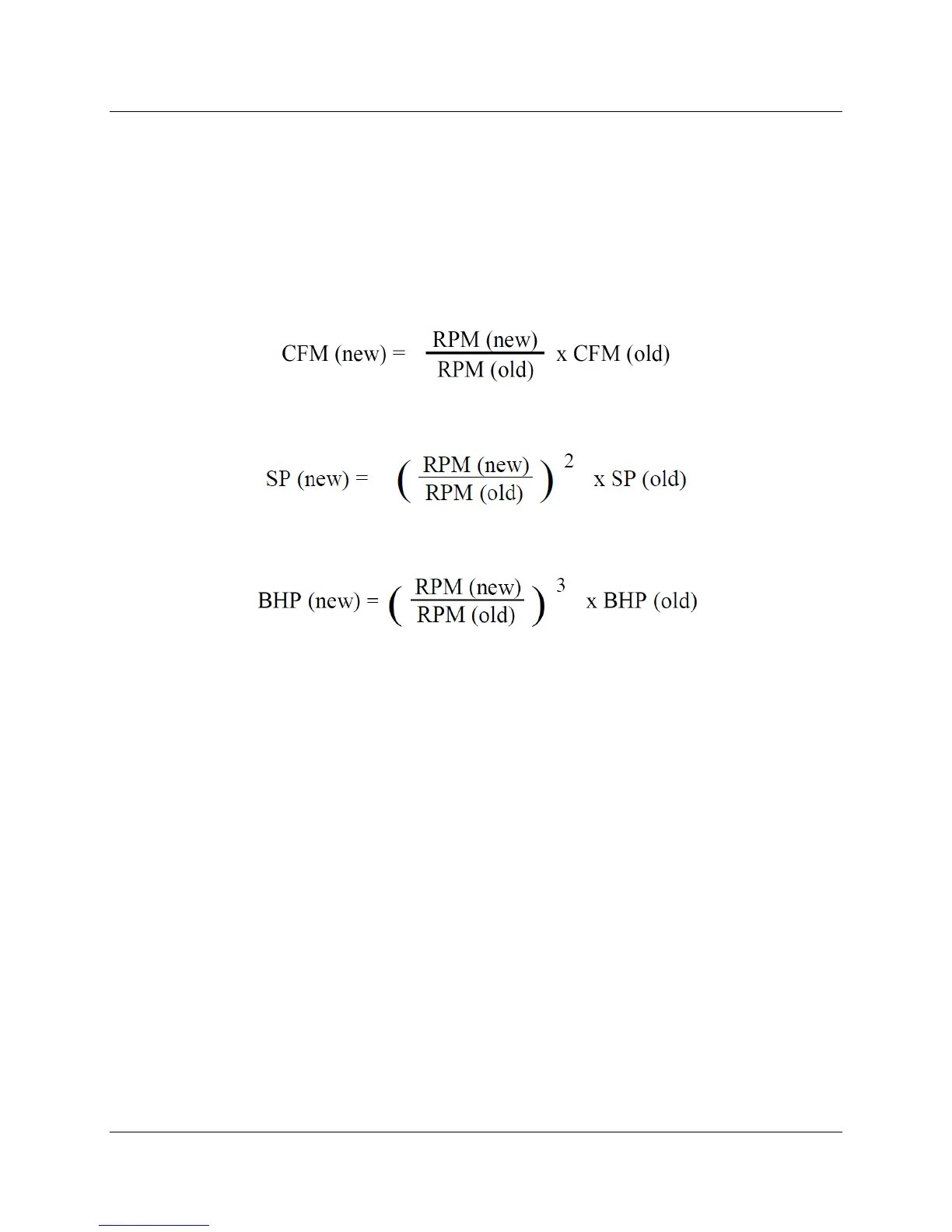
1. Air flow varies linearly with the speed of the blower. In other words, the CFM of the blower is
directly proportional to the RPM of the blower.
2. The static output pressure of the blower (SP) varies by the square of the change in RPM:
3. The required brake horsepower of the blower (BHP) varies by the cube of the change in RPM:
Example: A blower spinning at 1750 RPM produces 10 in WC of static pressure, 4500 CFM of flow, and
requires 20 BHP. What happens if the RPM is increased to 2750 RPM?
Assumptions: Air damper is wide open, and system effects (such as the restriction due to the boiler's
heat exchanger, the burner’s diffuser, etc...) are not taken into account.
Flow: CFM (new) = (2750 / 1750) * 4500 = 7071 CFM
Pressure: SP (new) = (2750 / 1750)
2
* 10 = 24.7 in WC
Power: BHP (new) = (2750 / 1750)
3
* 20 = 78 BHP

 Loading...
Loading...











