08.96 1 Introduction
1.6.2 Averaging
1.6.2 Averaging
Averaging in combination with higher-order measurement weighting has proved a suitable
means to do this.
The formula of the average-value generation chosen is:
Av
old
– D
i
Av
new
Av
new
Av
old
k
D
i
=
=
=
=
=
Average value new = amount of correction
Average value of last measurement
Weighting factor for calculating the average value (R29)
Set/actual difference measured (minus empirical value, if any)
Av
old
–
k
This formula takes into account the trend of the dimensional deviations of a series of
machining operations. The weighting factor k (R29), on the basis of which the average value is
generated, can be chosen.
A new measurement result affected by random dimensional deviations, as mentioned above,
only influences the new tool offset to some extent, depending on the weighting factor.
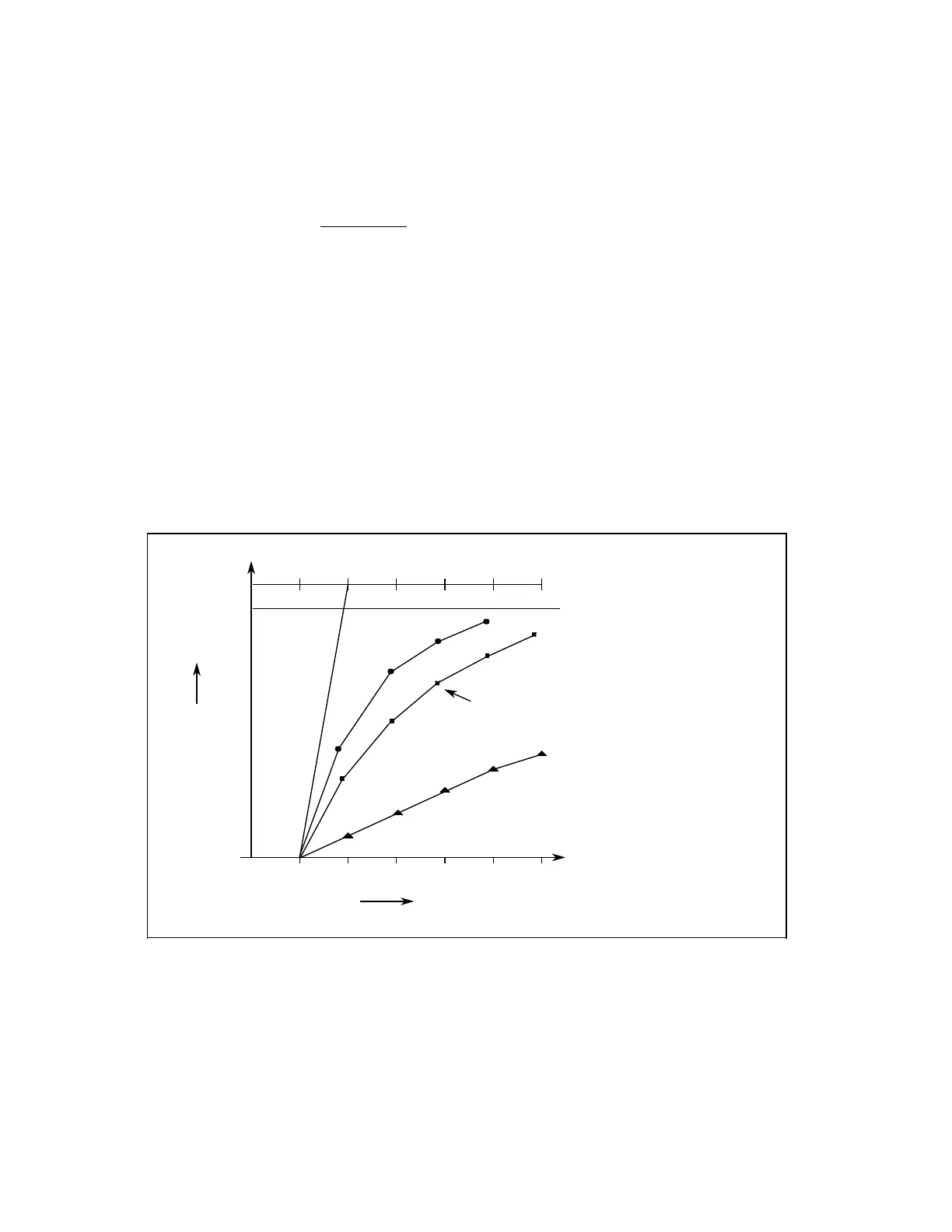
Fig. 1.19 Computational variation of the average value with different weightings k
k=10
k=3
k=2
k=1
6543210
Setpoint
(R42)
D
i
Average values
calculated
Set/actual difference
Number of averaging operations (workpieces)
Lower limit (R33) = ”Zero offset”
Average value
calculated
© Siemens AG 1990 All Rights Reserved 6FC5197- AB70 1–21
SINUMERIK 840/850/880 (BN)

 Loading...
Loading...
















