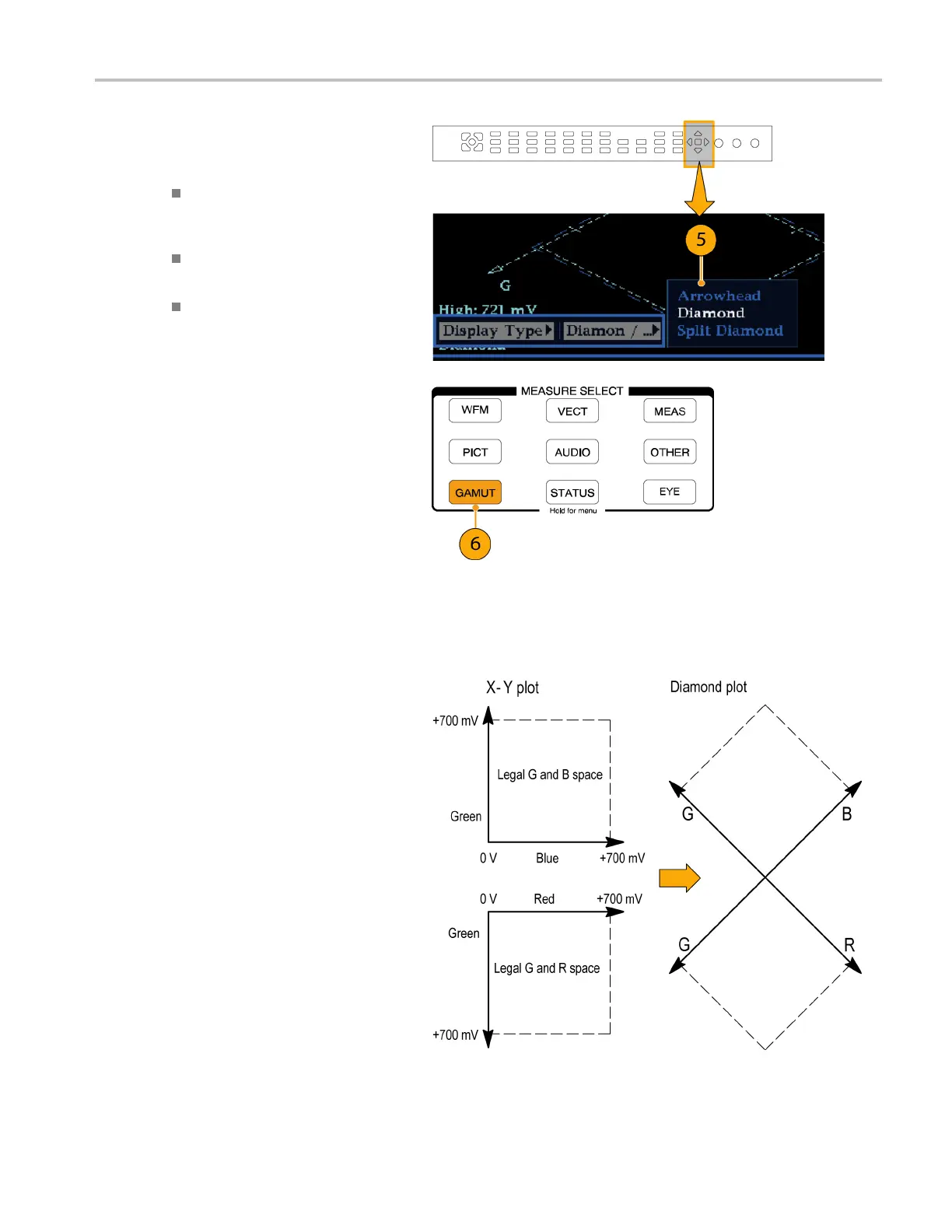
Checking Gamut
5. Use the arrow keys and SEL button to
set the menu to one of these three gamut
displays:
Diamond. Use to
detect, isolate,
and correct RG B component gamut
errors.
Split Diamond. Use to reveal
hard-to-find b
lack gamut errors.
Arrowhead. Us
e to detect composite
gamut errors, without employing a
composite encoder.
6. Press the GAMUT button to c lose the
menu.
Checking RGB Gamut
The Diamond display effectively shows
how the R, G, and B signals relate, making
it a good tool for detecting gamut errors.
The instrument converts the Y, P
b,
and P
r
components recovered from the serial signal
to R, G, and B to form the Diamond display.
To predictably display all three components,
they must lie between peak white, 700 mV,
and black, 0 V.
For a signal to be in gamut, all signal vectors
must lie within the G-B and G-R diamonds.
Conversely, if a signal vector extends outside
the diamond, it is out of gamut. The direction
of an excursion out of gamut indicates
which signal is excessive. E rrors in green
amplitude affect both diamonds equally,
while blue amplitude errors affect only the
top diamond and red errors affect only the
bottom diamond.
Waveform Rasterizers Quick Start User Manual 47

 Loading...
Loading...











