•
At the endpoint, the remote information (destination) is configured using the tp destination command
after you enter the interface tunnel-tp number command. The tp destination command includes the
destination node ID, and optionally the global ID and the destination tunnel number. If you do not specify
the destination tunnel number, the source tunnel number is used.
•
At the endpoint, the LSP number is configured in working-lsp or protect-lsp submode. The default is 0
for the working LSP and 1 for the protect LSP.
•
When configuring LSPs at midpoint devices, ensure that the configuration does not deflect traffic back
to the originating node.
MPLS-TP Linear Protection with PSC Support
MPLS-TP Linear Protection with PSC Support Overview
The Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Transport Profile (TP) enables you to create tunnels that provide
the transport network service layer over which IP and MPLS traffic traverse.
Network survivability is the ability of a network to recover traffic deliver following failure, or degradation,
of network resources. The MPLS-TP Survivability Framework (RFC-6372) describes the framework for
survivability in MPLS-TP networks, focusing on mechanisms for recovering MPLS-TP label switched paths
(LSPs)
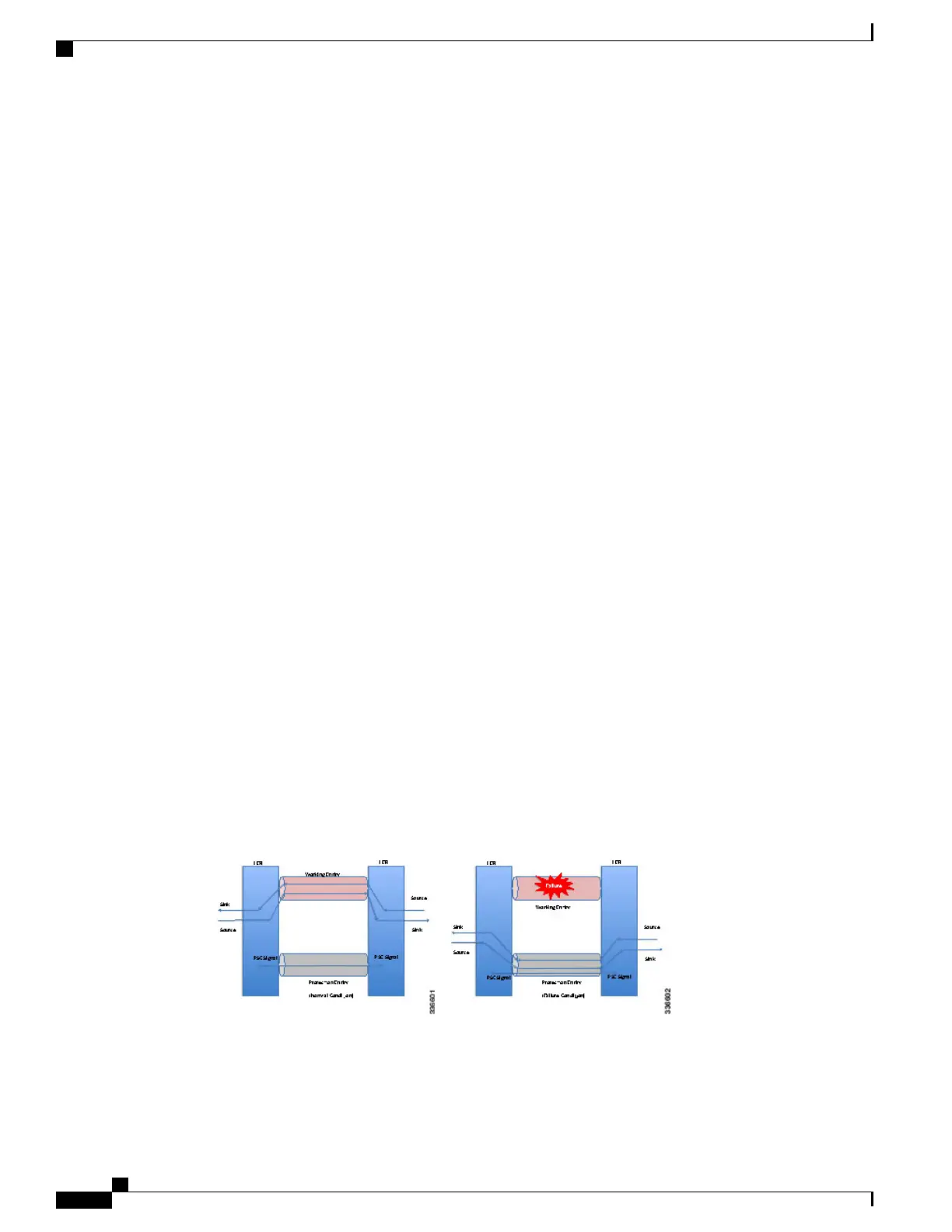
Linear protection provides rapid and simple protection switching because it can operate between any pair of
points within a network. Protection switching is a fully allocated survivability mechanism, meaning that the
route and resources of the protection path are reserved for a selected working path or set of working paths.
For a point-to-point LSPs, the protected domain is defined as two label edge routers (LERs) and the transport
paths that connect them.
Protection switching in a point-to-point domain can be applied to a 1+1, 1:1, or 1:n unidirectional or
bidirectional protection architecture. When used for bidirectional switching, the protection architecture must
also support a Protection State Coordination (PSC) protocol. This protocol is used to help coordinate both
ends of the protected domain in selecting the proper traffic flow. For example, if either endpoint detects a
failure on the working transport entity, the endpoint sends a PSC message to inform the peer endpoint of the
state condition. The PSC protocol decides what local action, if any, should be taken.
The following figure shows the MPLS-TP linear protection model used and the associated PSC signaling
channel for state coordination.
In 1:1 bidirectional protection switching, for each direction, the source endpoint sends traffic on either a
working transport entity or a protected transport entity, referred to as a data-path. If the either endpoint detects
a failure on the working transport entity, that endpoint switches to send and receive traffic from the protected
MPLS Basic Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Everest 16.5.1 (Cisco ASR 900 Series)
14
MPLS Transport Profile
MPLS-TP Linear Protection with PSC Support

 Loading...
Loading...