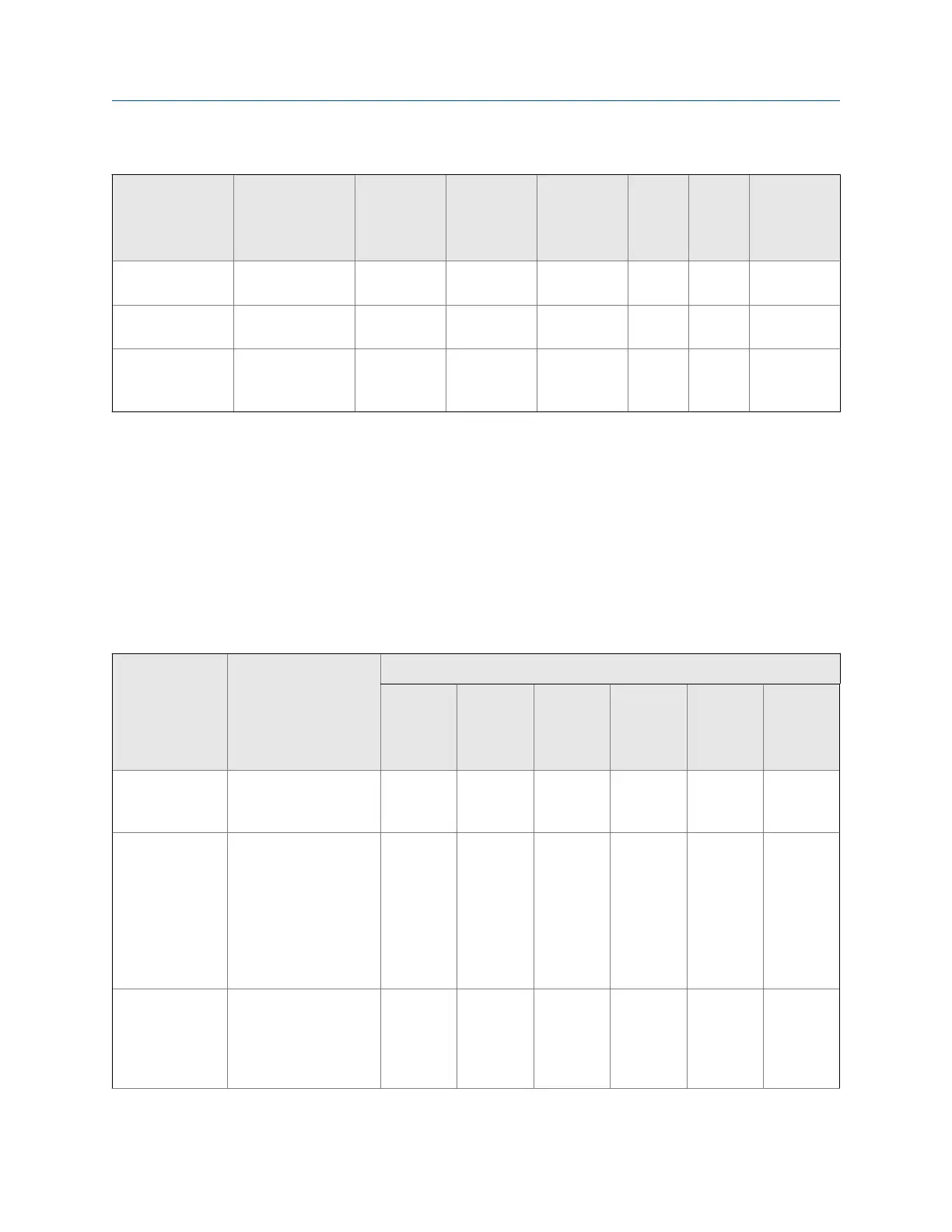
Concentration matrices, names, ranges, units, and derived variable (continued)Table E-2:
Process fluid Matrix file name
Default ma-
trix name
Concentra-
tion range
Tempera-
ture range
Density
unit
Tem-
pera-
ture
unit
Derived var-
iable
HCl 0–32% 0–
49C.xml
HCl 0–32% 0–49 °C g/cm³ °C Concentration
(Density)
Methanol Methanol 35–60%
0–40C.xml
Methanol 35–60% 0–40 °C g/cm³ °C Concentration
(Density)
Ethylene glycol Ethylene Glycol
10–50% –20 –
40C.xml
Eth. Glycol 10–50% −20 – +40 °C g/cm³ °C Concentration
(Density)
E.3 Derived variables and calculated process
variables
The concentration measurement application calculates a different set of process variables
from each derived variable. The process variables are then available for viewing or
reporting.
Derived variables and calculated process variables Table E-3:
Derived Variable Description
Calculated process variables
Density at
reference
tempera-
ture
Standard
volume
flow rate
Specific
gravity
Concen-
tration
Net mass
flow rate
Net vol-
ume flow
rate
Density at Refer-
ence
Mass/unit volume, cor-
rected to a given refer-
ence temperature
✓ ✓
Specific Gravity The ratio of the density
of a process fluid at a
given temperature to
the density of water at
a given temperature.
The two given temper-
ature conditions do not
need to be the same.
✓ ✓ ✓
Mass Concentration
(Density)
The percent mass of
solute or of material in
suspension in the total
solution, derived from
reference density
✓ ✓ ✓ ✓
Concentration measurement matrices, derived variables, and process variables
202 Micro Motion
®
Fork Density Meters (FDM)
 Loading...
Loading...