173
Automatic configuration
Overview
Automatic configuration enables a device without any configuration file to automatically obtain and execute
a configuration file during startup. Automatic configuration simplifies network configuration, facilitates
centralized management, and reduces maintenance workload.
To implement automatic configuration, the network administrator saves configuration files on a server and a
device automatically obtains and executes a specific configuration file.
Typical automatic configuration network
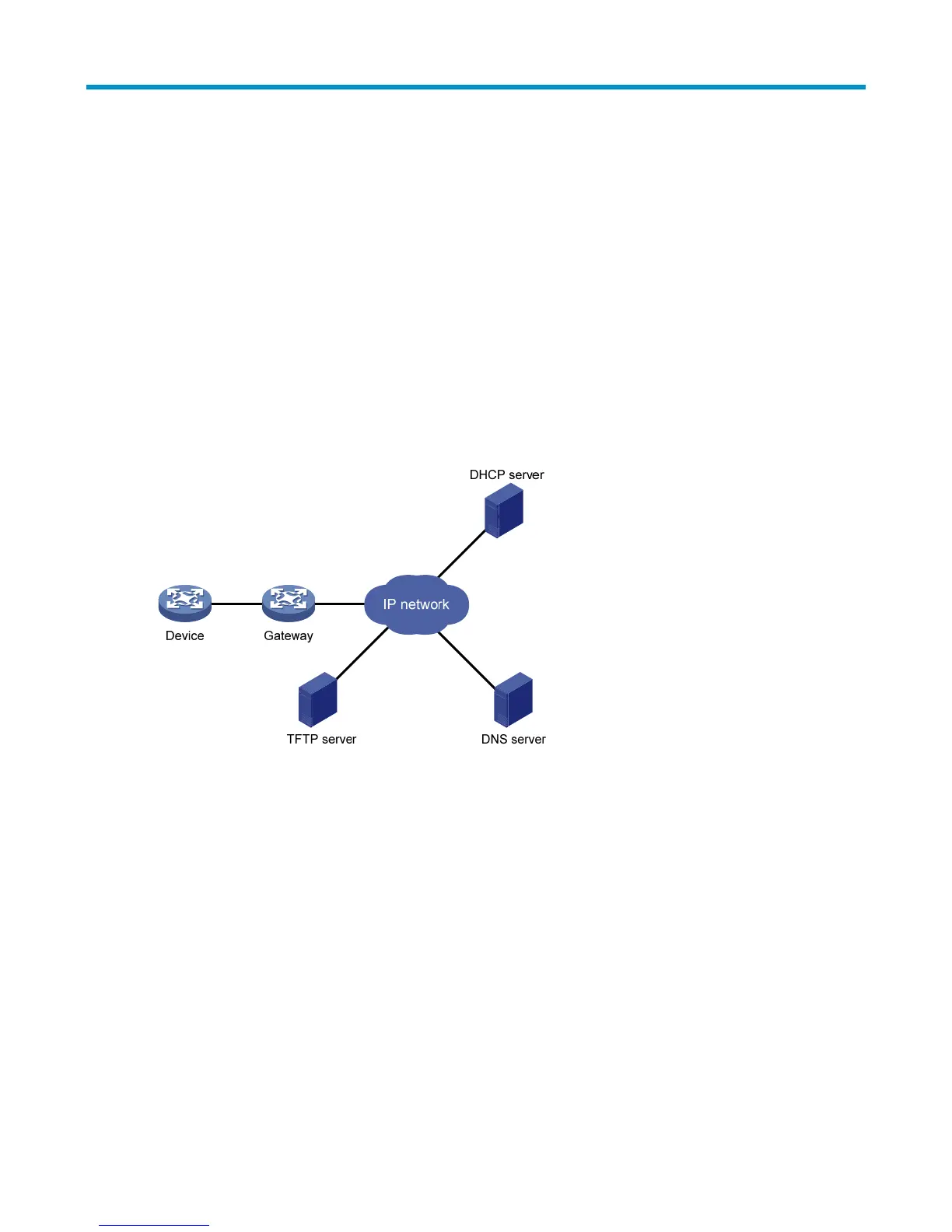
Figure 2 Network diagram for automatic configuration
As shown in Figure 1, the device implements automatic configuration with the cooperation of the following
servers: a DHCP server, TFTP server, and DNS server:
• DHCP server—Assigns an IP address and other configuration parameters such as the configuration file
name, TFTP server IP address, and DNS server IP address to the device.
• TFTP server: Saves files needed in automatic configuration such as the host name file and the
configuration file.
• DNS server—IP addresses-host name resolution. In some cases, the device resolves its IP address to the
host name through the DNS server, and then uses the host name to request the configuration file with the
same name (hostname.cfg) from the TFTP server. If the device gets the domain name of the TFTP server
from the DHCP response, the device can also resolve the domain name of the TFTP server to the IP
address of the TFTP server through the DNS server.
If the DHCP server, TFTP server, DNS server, and the device are not in the same network segment, you must
configure the DHCP relay agent on the gateway.

 Loading...
Loading...