15
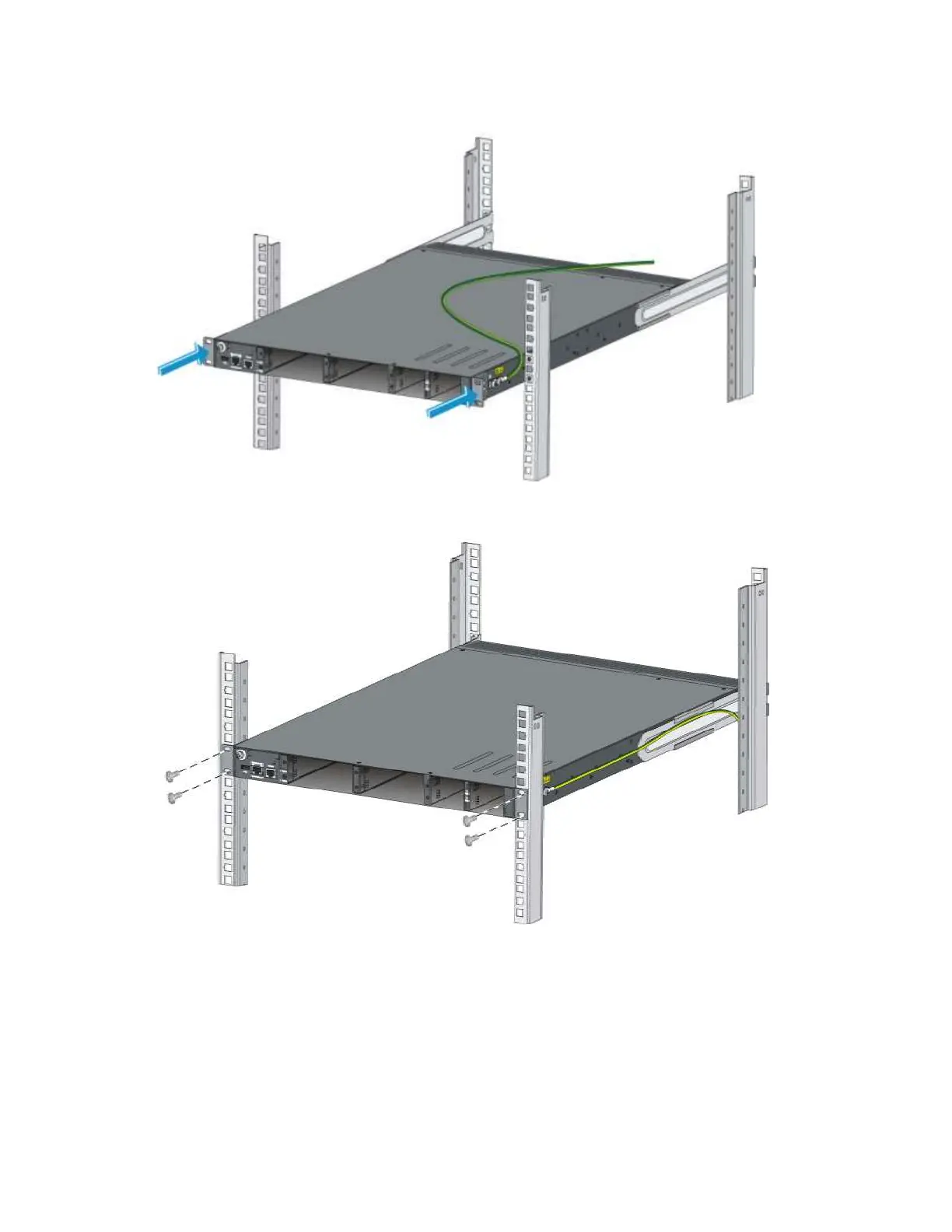
Figure 17 Mounting the switch in the rack (I)
Figure 18 Mounting the switch in the rack (II)
Rack-mounting an A5800/A5820X switch except the
A5800AF-48G/A5820AF-24XG
This installation task requires two persons. To mount the switch in a rack:
1. Wear an ESD-preventive wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is well
grounded.
2. Check that the mounting brackets have been securely attached to the switch chassis.

 Loading...
Loading...











