81
Ste
Command
Remarks
6. Associate the SNMP group with the
ACL.
snmp-agent group { v1 | v2c } group-
name [ read-view read-view ] [ write-
view write-view ] [ notify-view notify-
view ] [ acl acl-number ]
snmp-agent group v3 group-name
[ authentication | privacy ] [ read-view
read-view ] [ write-view write-view ]
[ notify-view notify-view ] [ acl acl-
number ]
when creating the
community, the SNMP
group, and the user.
For more information
about SNMP, see
Network Management
and Monitoring
Configuration Guide.
7. Associate the user with the ACL.
snmp-agent usm-user { v1 | v2c }
user-name group-name [ acl acl-
number ]
snmp-agent usm-user v3 user-name
group-name [ [ cipher ] authentication-
mode { md5 | sha } auth-password
[ privacy-mode { 3des | aes128 |
des56 } priv-password ] ] [ acl
acl-number ]
Source IP-based login control over NMS users configuration
example
Network requirements
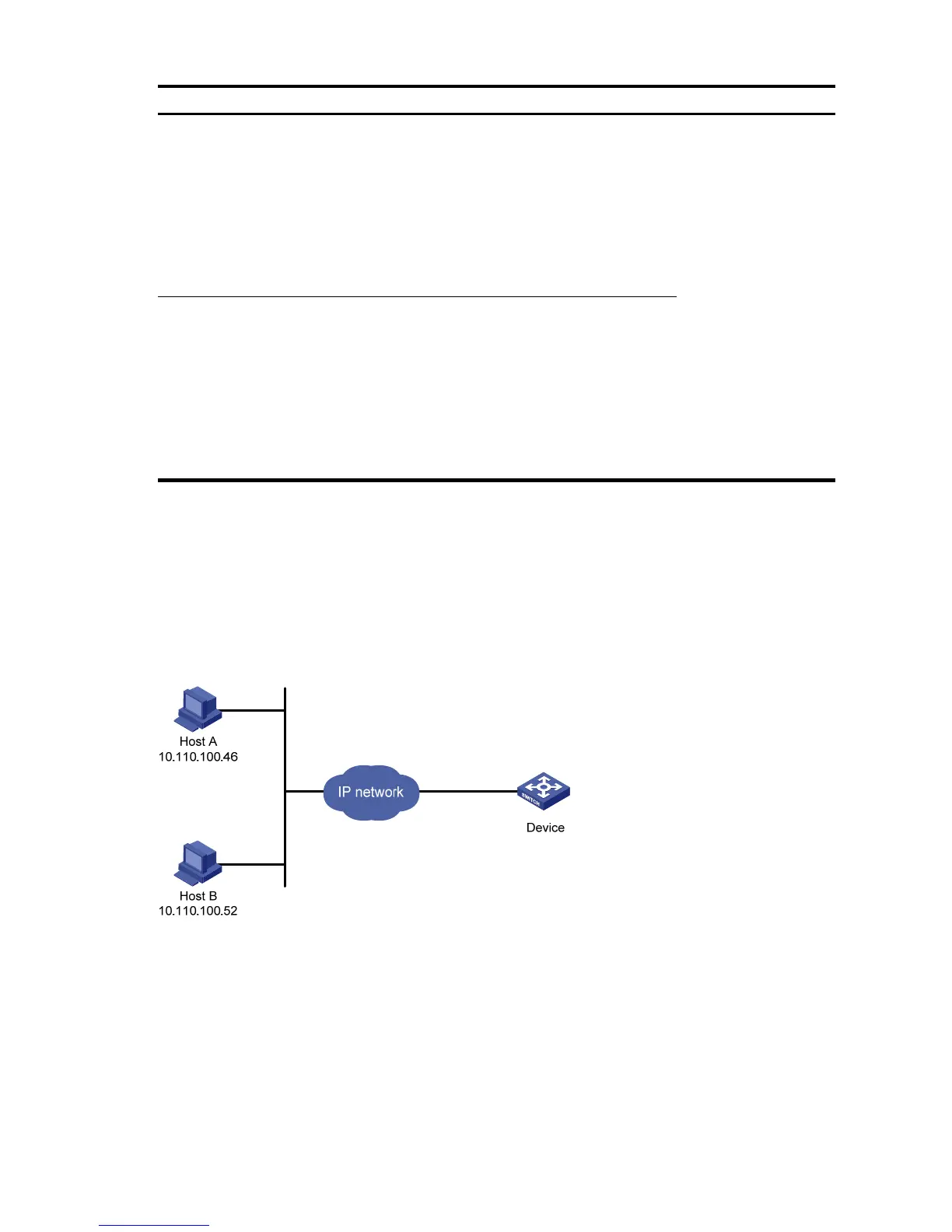
As shown in Figure 10, configure the device to allow only NMS users from Host A and Host B to access.
Figure 10 Network diagram for configuring source IP-based login control over NMS users
Procedure
# Create ACL 2000, and configure rule 1 to permit packets sourced from Host B, and rule 2 to permit
packets sourced from Host A.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] acl number 2000 match-order config
[Sysname-acl-basic-2000] rule 1 permit source 10.110.100.52 0
[Sysname-acl-basic-2000] rule 2 permit source 10.110.100.46 0
[Sysname-acl-basic-2000] quit
 Loading...
Loading...