177
Obtaining the configuration file
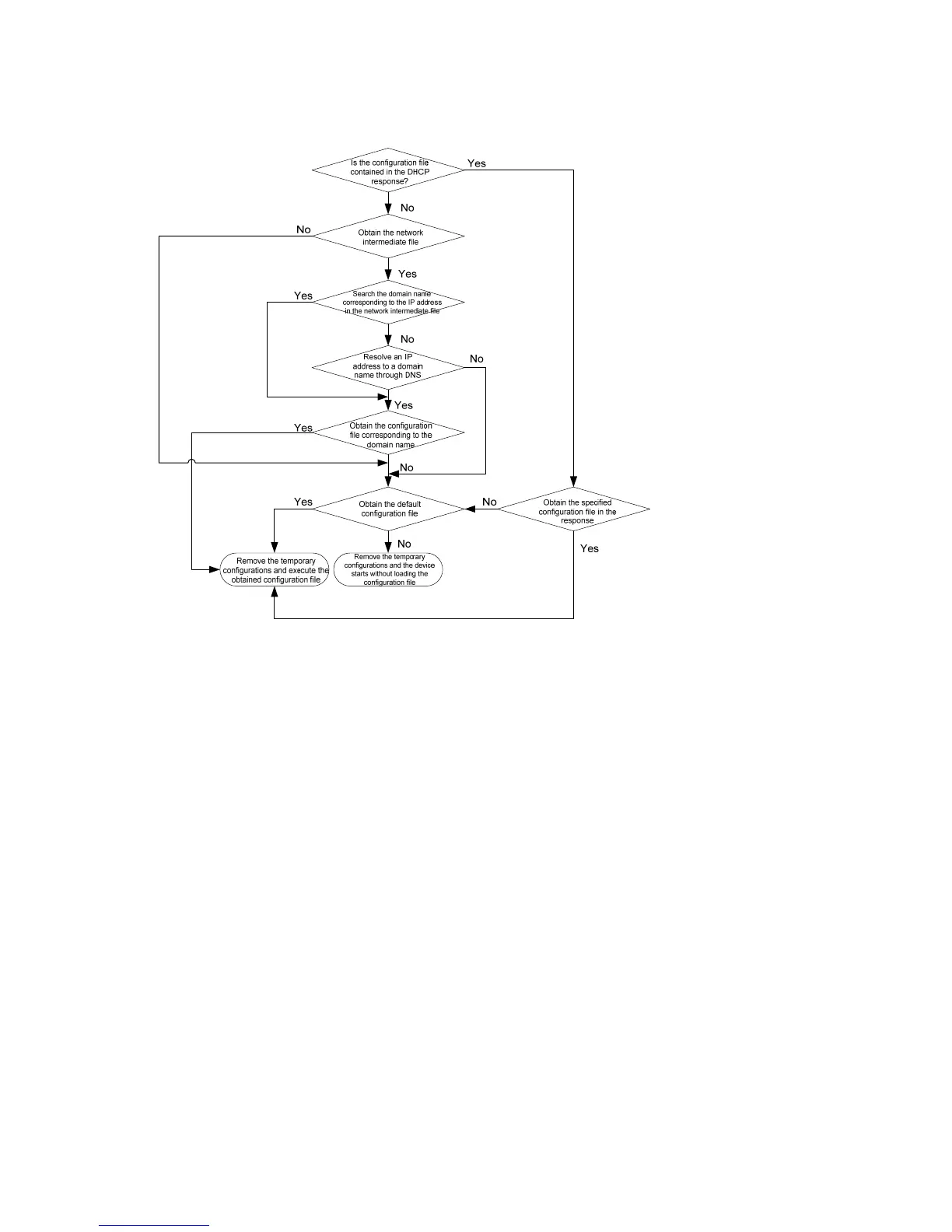
Figure 4 Obtain the configuration file
A device obtains its configuration file by using the following workflow:
• If the DHCP response contains the configuration file name, the device requests the specified
configuration file from the TFTP server.
• If the DHCP response does not contain the configuration file name, the device tries to get its host name
from the host name file obtained from the TFTP server. If it fails, the device resolves its IP address to the
host name through DNS server. Once the device gets its host name, it requests the configuration file with
the same name from the TFTP server.
• If all operations fail, the device requests the default configuration file from the TFTP server.
TFTP request sending mode
The device selects to unicast or broadcast a TFTP request by using the following workflow:
• If a legitimate TFTP server IP address is contained in the DHCP response, the device unicasts a TFTP
request to the TFTP server.
• If no legitimate TFTP server IP address is contained in the DHCP response, the device resolves the TFTP
server domain name contained in the DHCP response to the IP address through the DNS server. If
successful, the device unicasts a TFTP request to the TFTP server; if not, the device broadcasts a TFTP
request.
• If the IP address and the domain name of the TFTP server are not contained in the DHCP response or
they are illegitimate, the device broadcasts a TFTP request.
 Loading...
Loading...