219
Step Command Remarks
message for DAD. disabled.
Enabling ND proxy
About ND proxy
ND proxy enables a device to answer an NS message requesting the hardware address of a host on
another network. With ND proxy, hosts in different broadcast domains can communicate with each
other as they would on the same network.
ND proxy includes common ND proxy and local ND proxy.
• Common ND proxy.
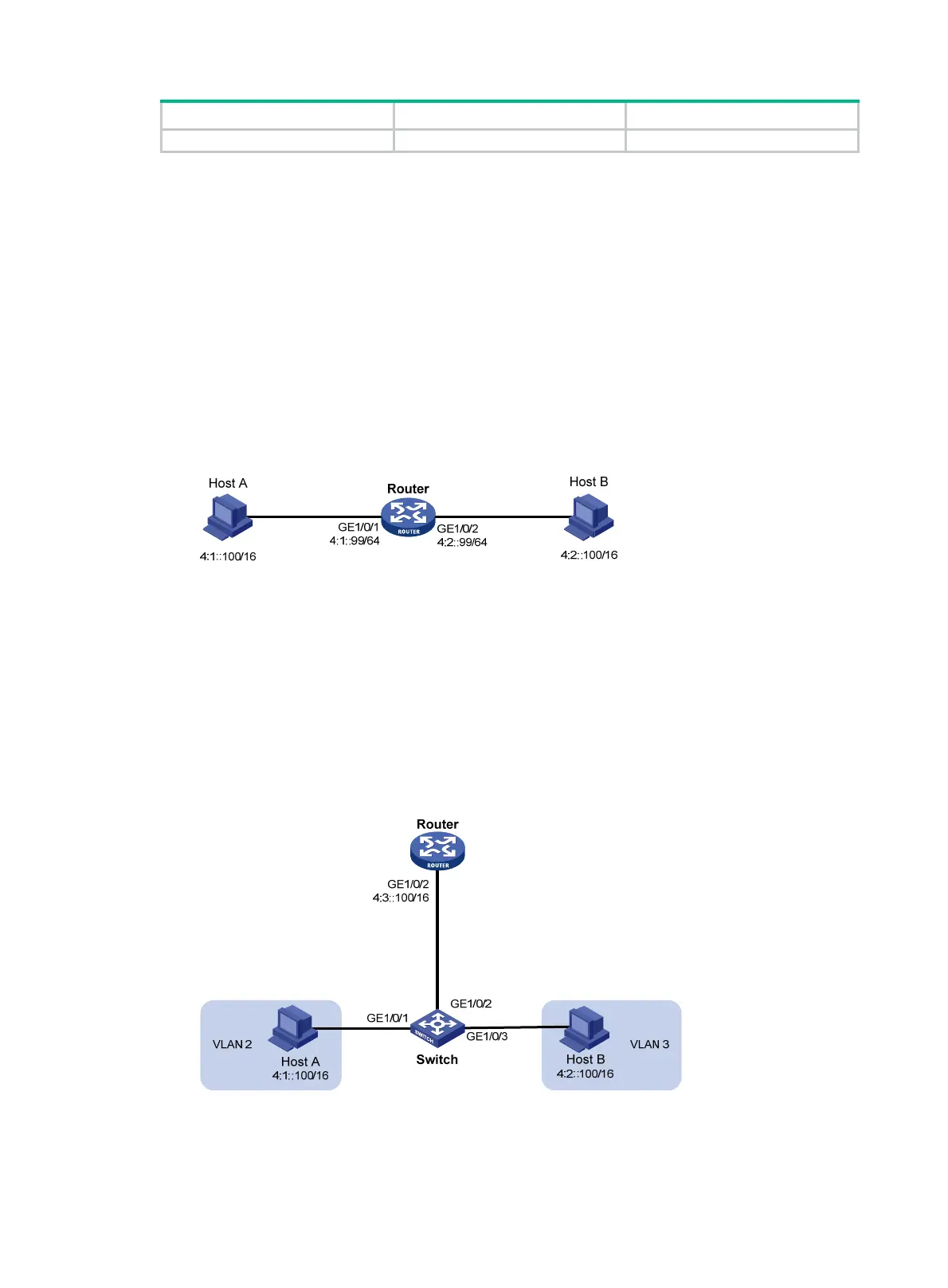
As shown in Figure 86, GigabitEthernet
2/0/1 with IPv6 address 4:1::99/64 and GigabitEthernet
2/0/2 with IPv6 address 4:2::99/64 belong to different subnets. Host A and Host B reside on the
same network but in different broadcast domains.
Figure 86 Application environment of ND proxy
Because Host A's IPv6 address is on the same subnet as Host B's, Host A directly sends an NS
message to obtain Host B's MAC address. However, Host B cannot receive the NS message
because they belong to different broadcast domains.
To solve this problem, enable common ND proxy on GigabitEthernet 2/0/1 and GigabitEthernet
2/0/2 of the router. The router replies to the NS message from Host A, and forwards packets
from other hosts to Host B.
• Local ND proxy.
As shown in Figure 87, Ho
st A belongs to VLAN 2 and Host B belongs to VLAN 3. Host A and
Host B connect to GigabitEthernet 2/0/1 and GigabitEthernet 2/0/3, respectively.
Figure 87 Application environment of local ND proxy
Because Host A's IPv6 address is on the same subnet as Host B's, Host A directly sends an NS
message to obtain Host B's MAC address. However, Host B cannot receive the NS message
because they belong to different VLANs.

 Loading...
Loading...











