57
DHCP server configuration examples
DHCP networking includes the following types:
• The DHCP server and clients reside on the same subnet.
• The DHCP server and clients are not on the same subnet and communicate with each other
through a DHCP relay agent.
The DHCP server configuration for the two types is identical.
Static IP address assignment configuration example
Network requirements
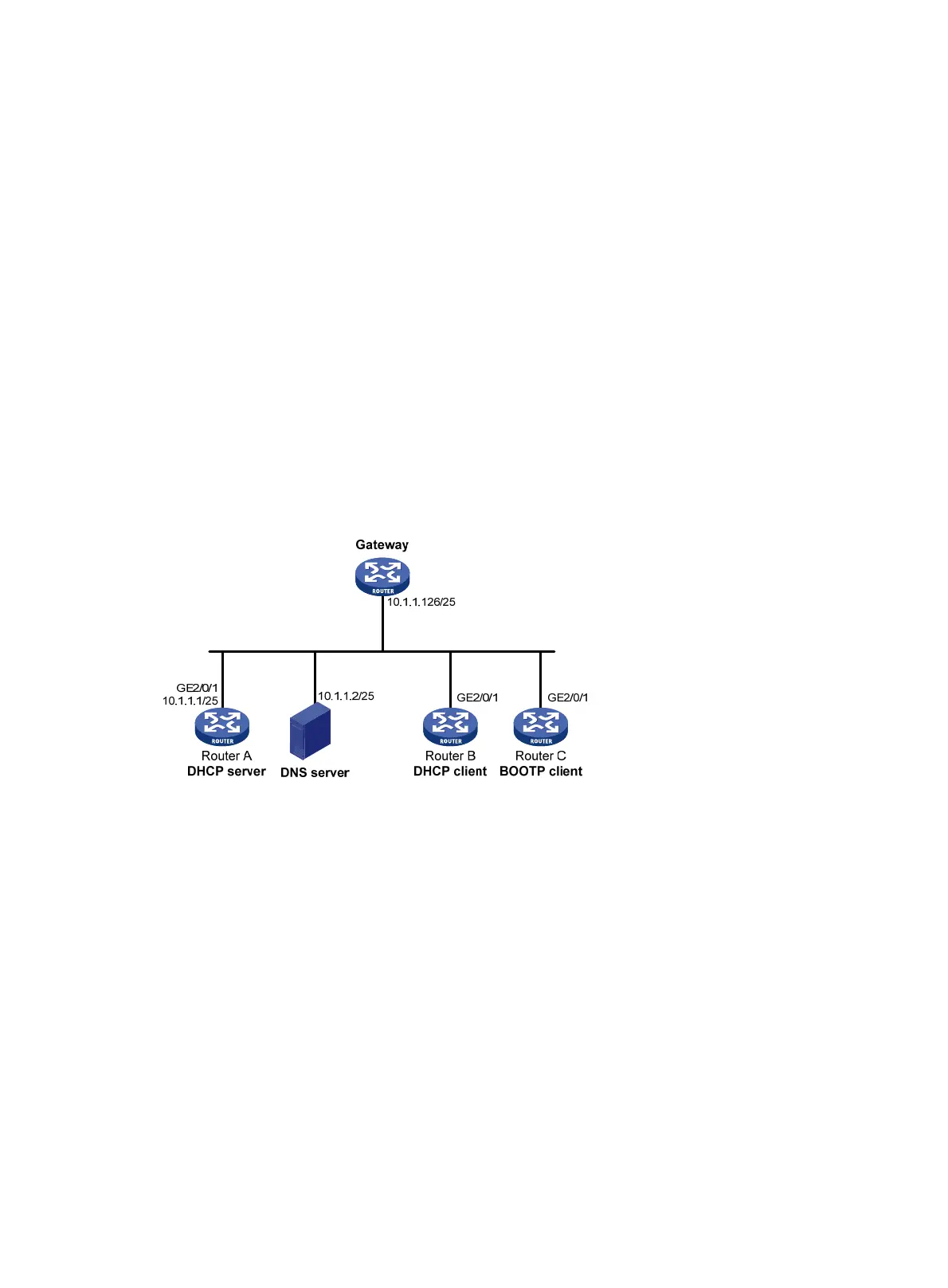
As shown in Figure 24, Router A (DHCP server) assigns a static IP address, a DNS server address,
and a gateway address to Router B (DHCP client) and Router C (BOOTP client).
The client ID of the interface GigabitEthernet 2/0/1 on Router B is:
0030-3030-662e-6532-3030-2e30-3030-322d-4574-6865-726e-6574.
The MAC address of the interface GigabitEthernet 2/0/1 on Router C is 000f-e200-01c0.
Figure 24 Network diagram
Configuration procedure
1. Specify an IP address for GigabitEthernet 2/0/1 on Router A:
<RouterA> system-view
[RouterA] interface gigabitethernet 2/0/1
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] ip address 10.1.1.1 25
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] quit
2. Configure the DHCP server:
# Enable DHCP.
[RouterA] dhcp enable
# Enable the DHCP server on GigabitEthernet 2/0/1.
[RouterA] interface gigabitethernet 2/0/1
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] dhcp select server
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] quit
# Create DHCP address pool 0.
[RouterA] dhcp server ip-pool 0
# Configure a static binding for Router B.

 Loading...
Loading...











