416
To provide differentiated services, traffic classes must be associated with certain traffic control actions or
resource allocation actions. What traffic control actions to adopt depends on the current phase and the
resources of the network. For example, CAR is adopted to police packets when they enter the network;
GTS is performed on packets when they flow out of the node; queue scheduling is performed when
congestion happens; congestion avoidance measures are taken when the congestion deteriorates.
Packet precedences
This section introduces IP precedence, ToS precedence, differentiated services codepoint (DSCP) values,
and 802.1p precedence.
1. IP precedence, ToS precedence, and DSCP values
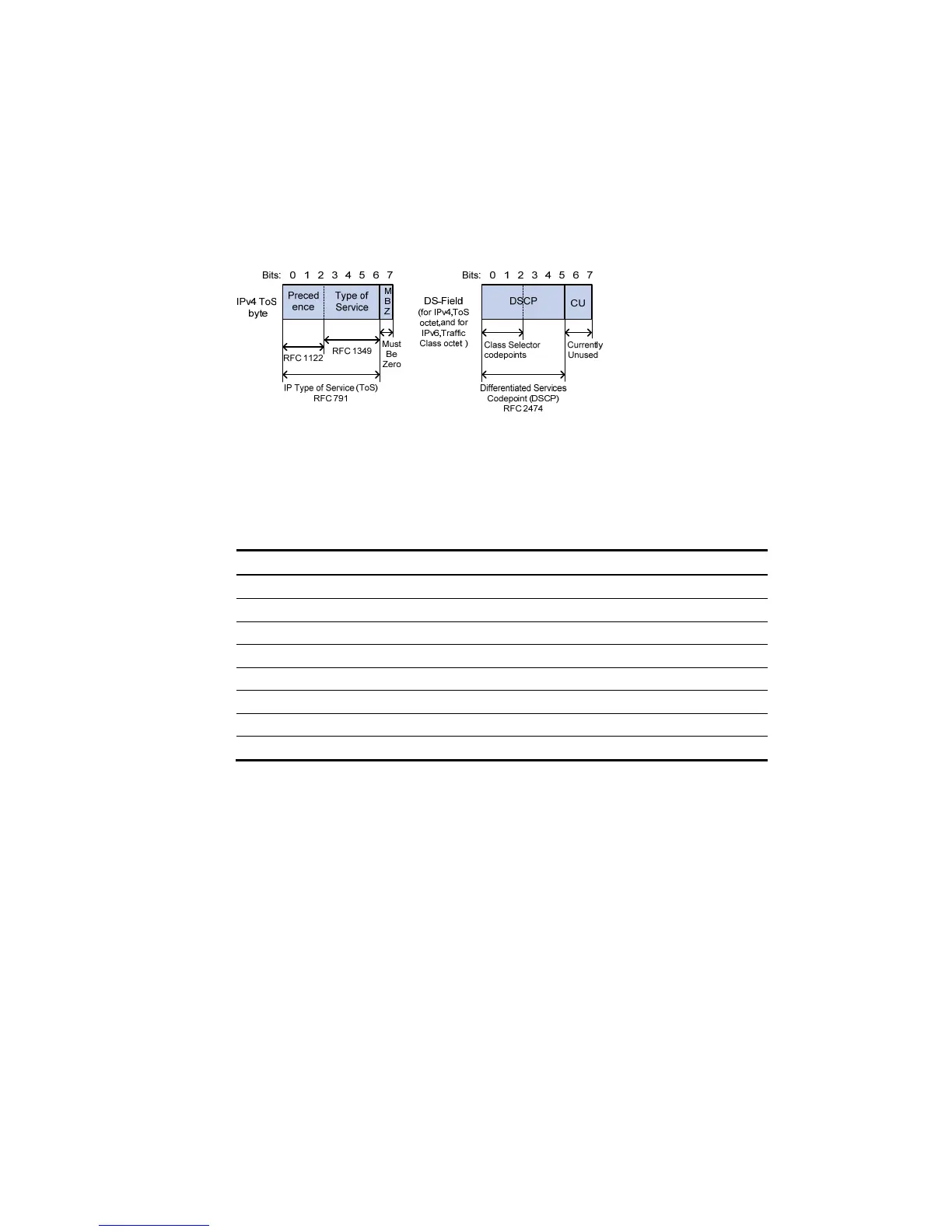
Figure 389 DS field and ToS bytes
As shown in Figure 389, the ToS field of the IP header contains eight bits: the first three bits (0 to 2)
represent IP precedence from 0 to 7; the subsequent four bits (3 to 6) represent a ToS value from 0 to 15.
According to RFC 2474, the ToS field of the IP header is redefined as the differentiated services (DS) field,
where a DSCP value is represented by the first six bits (0 to 5) and is in the range 0 to 63. The remaining
two bits (6 and 7) are reserved.
Table 153 Description on IP Precedence
IP Precedence (decimal) IP Precedence (binary) Description
0 000 Routine
1 001 priority
2 010 immediate
3 011 flash
4 100 flash-override
5 101 critical
6 110 internet
7 111 network
In a network in the Diff-Serve model, traffic is grouped into the following four classes, and packets are
processed according to their DSCP values.
Expedited Forwarding (EF) class: In this class, packets are forwarded regardless of link share of
other traffic. The class is suitable for preferential services requiring low delay, low packet loss, low
jitter, and high bandwidth.
Assured forwarding (AF) class: This class is divided into four subclasses (AF 1 to AF 4), each
containing three drop priorities for more granular classification. The QoS level of the AF class is
lower than that of the EF class.
 Loading...
Loading...











