5-28 Image Optimization
1. A region with qualified image in B mode may not be optimal for Smart 3D
imaging. E.g. adequate AF isolation for one section plane doesn’t mean the
whole desired region is isolated by AF.
2. More practices are needed for a high success rate of qualified Smart 3D
imaging.
3. Even with good fetal condition, to acquire an approving Smart 3D image may
need more than one scanning.
5.12.2 Overview
Ultrasound data based on three-dimensional imaging methods can be used to image any
structure where a view can’t be achieved by standard 2D-mode to improve understanding of
complex structures.
Terms
Volume: a three-dimensional content.
Volume data: the image data set of a 3D object rendered from 2D image sequence.
3D image (VR): the image displayed to represent the volume data.
View point: a position for viewing volume data/3D image.
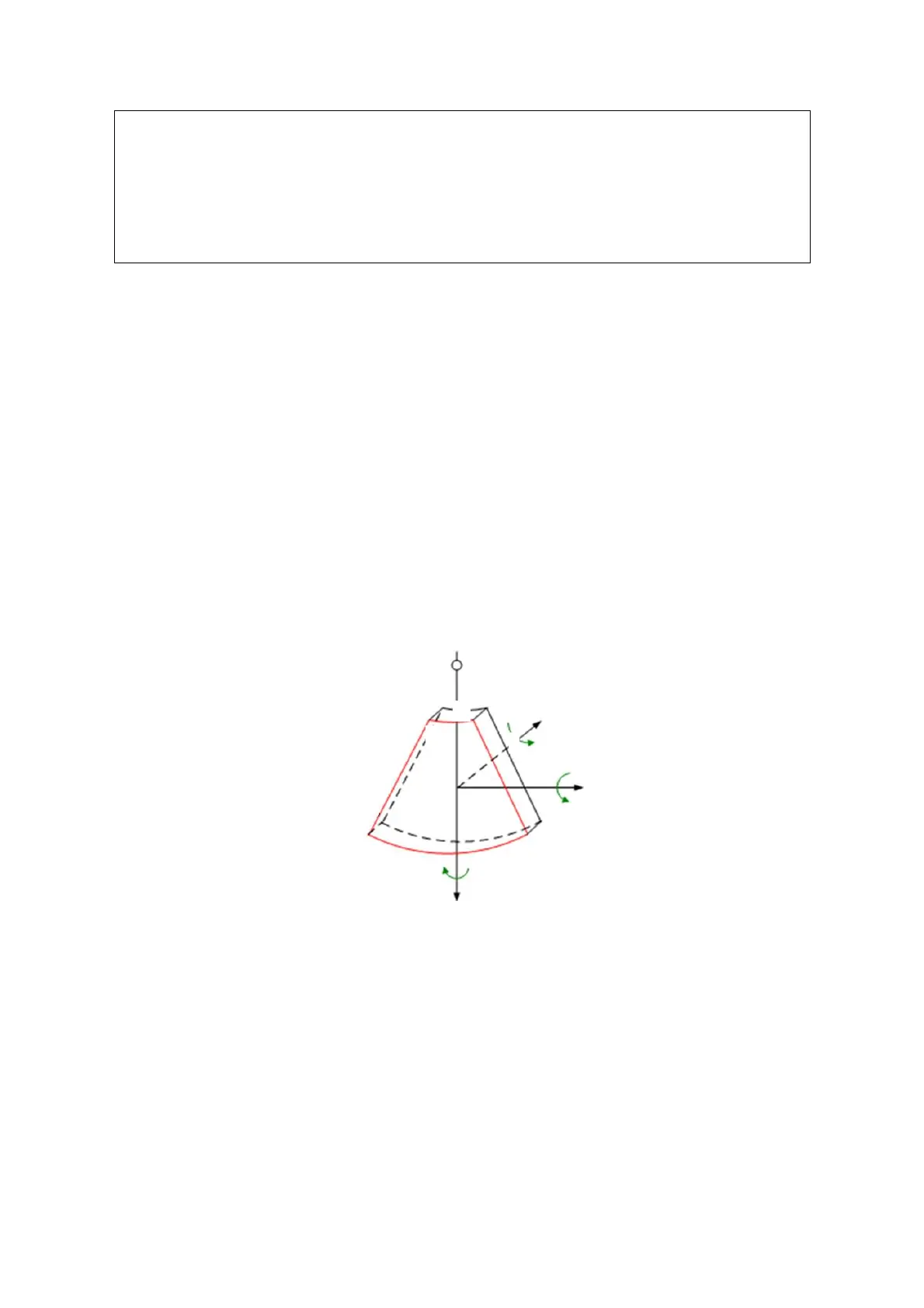
Section image (or MultiPlaner Rendering as MPR): tangent planes of the 3D image
that obtained by algorithm. As shown in the figure below, XY-paralleled plane is C-
section, XZ-paralleled plane is B-section, and YZ-paralleled plane is A-section. The
probe is moved along the X-axis.
ROI (Region of Interest): a volume box used to determine the height and width of
scanning volume.
VOI (Volume of Interest): a volume box used to determine the area of a sectional
plane for 3D imaging.
ROI and VOI
Before image acquisition after the system enters Smart 3D imaging, a B image with ROI
displays on the screen. A line (shown in the following figure) that shows the upper edge
position of VOI is inside ROI.

 Loading...
Loading...