Renesas RA Family RA4 Quick Design Guide
R01AN5988EU0100 Rev.1.00 Page 40 of 51
Jul.21.21
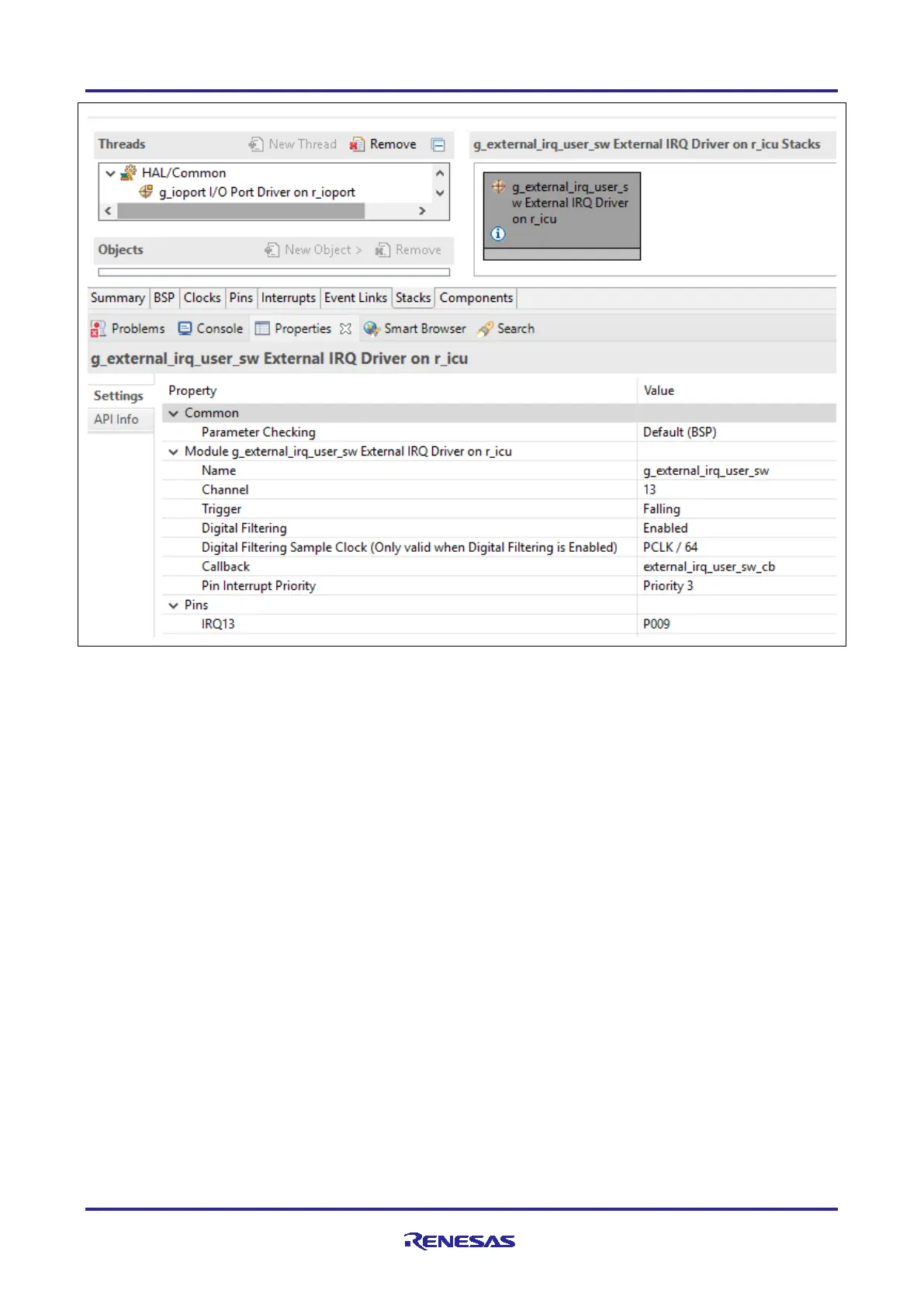
Figure 31. Configure IRQ13 using the Renesas FSP Configurator
10.5 Unused Pins
Note: Some pins require specific termination: See the “Handling of Unused Pins” section of the Hardware
User’s Manual for specific recommendations.
Unused pins that are left floating can consume extra power and leave the system more susceptible to noise
problems. Terminate unused pins with one of the methods detailed here:
1. The first option is to set the pin to an input (the default state after reset) and connect the pin to Vcc or
Vss using a resistor. There is no difference to the MCU between one connection or another. However,
there may be an advantage from a system noise perspective. Vss is probably the most typical choice.
Avoid connecting a pin directly to Vcc or Vss since an accidental write to the port’s direction register that
sets the pin to an output could create a shorted output.
2. A second method is to set the pin to an output. The pin level may be set high or low. However, setting
the pin as an output and making the output low connects the pin internally to the ground plane. This may
help with overall system noise concerns.
A disadvantage of setting unused pins to outputs is that the configuration of the port must be done via
software control. While the MCU is held in reset and until the direction register is set for output, the pin
will be a floating input and may draw extra current. If the extra current can be tolerated during this time,
this method eliminates the external resistors required in the first method.
3. A variation on leaving the pins as inputs and terminating them with external resistors uses the internal
pull-ups available on many ports of the MCU. This has the same limitation as setting the pins to outputs
(requires the program to set up the port) but it does limit the effect of accidental pin shorts to ground,
adjacent pins or Vcc since the device will not be driving the pin.

 Loading...
Loading...