Oscilloscope concepts
Read this section if you are a new oscilloscope user, or new to using a digital
oscilloscope.
Sampling and acquisition concepts
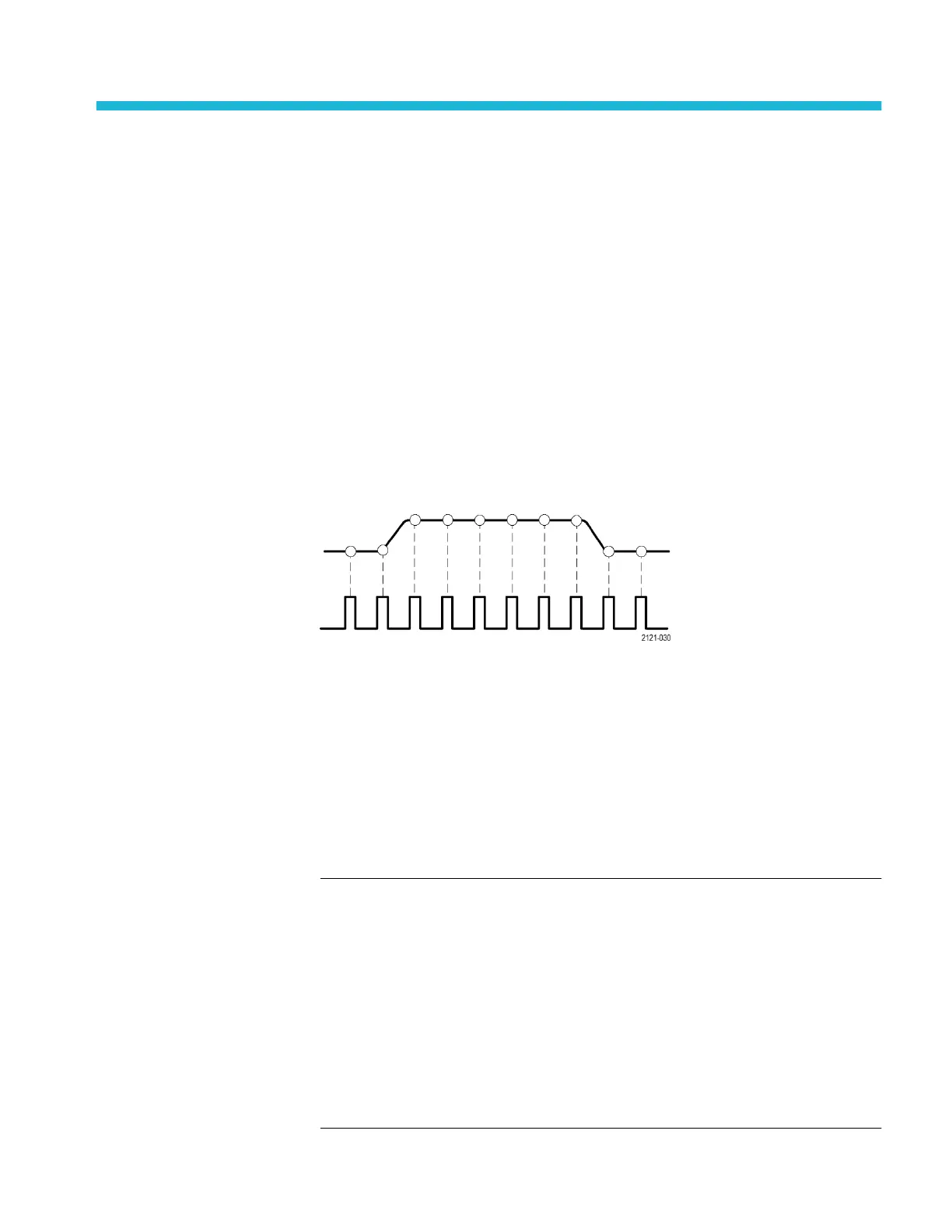
Before the oscilloscope can display or measure a signal, it must be sampled.
Sampling is the process of measuring the input signal amplitude value at regular
intervals (called the sampling rate, in samples per second), converting the
sampled levels into digital data, and storing the sampled values in memory to
create a waveform record. The oscilloscope uses the digitized values in the
waveform record to create, display, and measure waveforms. Each oscilloscope
channel has its own waveform record memory storage.
TBS2000B Series oscilloscopes use real-time sampling. In real-time sampling,
the oscilloscope samples and digitizes all of the sampled points at one time, in
sequence, stores the sampled data in memory, and then repeats the sampling and
storage process.
Use the Horizontal Scale knob to change the sample rate (samples per second).
The oscilloscope automatically sets the sample rate so that there are more than
enough samples to accurately capture the signal information. The sample rate is
shown on the screen at all times in the horizontal position/scale readout.
NOTE.
■
The maximum sample rate of 2 GS/s is only available when one channel per
channel pair is active (channel 1, 2 pair or channel 3, 4 pair).
■
For two-channel models, only one channel (either channel 1 or 2) can
sample at 2 Gs/s. If channel 1 and 2 are both active, then the maximum
sample rate changes to 1 GS/s.
■
On four-channel models, only two channels can sample at 2 GS/s (one
channel from each pair). If channel 1 or 2, and channel 3 or 4, are active, the
maximum sample rate is available. Turning on a 2nd channel (in either pair)
changes the maximum sampling rate to 1 GS/s.
TBS2000B Series Oscilloscopes User Manual 37

 Loading...
Loading...