
 Loading...
Loading...
Do you have a question about the Yaesu FTDX9000D and is the answer not in the manual?
| Brand | Yaesu |
|---|---|
| Model | FTDX9000D |
| Category | Transceiver |
| Language | English |
Instructions for connecting AC power, including details on front and rear power switches.
Importance of setting the local time for correct function of several features.
Guide on how to change transceiver settings using the menu system and saving changes.
Instructions on connecting and selecting front panel XLR or rear panel 8-pin microphone connectors.
Procedure for adjusting the main dial torque and restarting power after fluctuations.
Procedures for resetting memories, menu settings, or performing a full reset of the transceiver.
Description of the front panel layout, VFD display, LEDs, and tuning dial for visibility and ease of use.
Details on DSP, µ-Tuning filters, VRF, Roofing filters, and Contour filter for enhanced reception.
Information on Sloped AGC, AF Limiter, Adjacent Channel Monitor, and receiver front-end design.
Description of the final amplifier design, Class-A operation, and parametric microphone equalizer.
Lists accessories supplied with the transceiver, including FH-2, CF Card, and cables.
Lists available optional accessories for the transceiver, such as microphones and headphones.
Guidance on selecting antennas, coaxial cable quality, and impedance matching.
Importance and methods for establishing an effective ground system for safety and performance.
Illustration and instructions for connecting antenna coaxial and AC power cables correctly.
Details on connecting microphones, headphones, and the FH-2 remote control keypad.
Information on connecting CW keying devices, computer interfaces, and GPS receivers.
Guide for connecting the VL-1000 linear amplifier and interfacing with other linear amplifiers.
Explanation of the MOX, VOX, DIM switches, PHONES jack, and POWER switch functions.
Details on KEY jack, XLR microphone connector, IPO switch, Antenna Select, and TUNE switch.
Explanation of METER, MONI switches, and associated knobs for AGC and attenuation.
Controls for Speech Processor, VOX delay, CW Keyer, Noise Blanker, and Squelch.
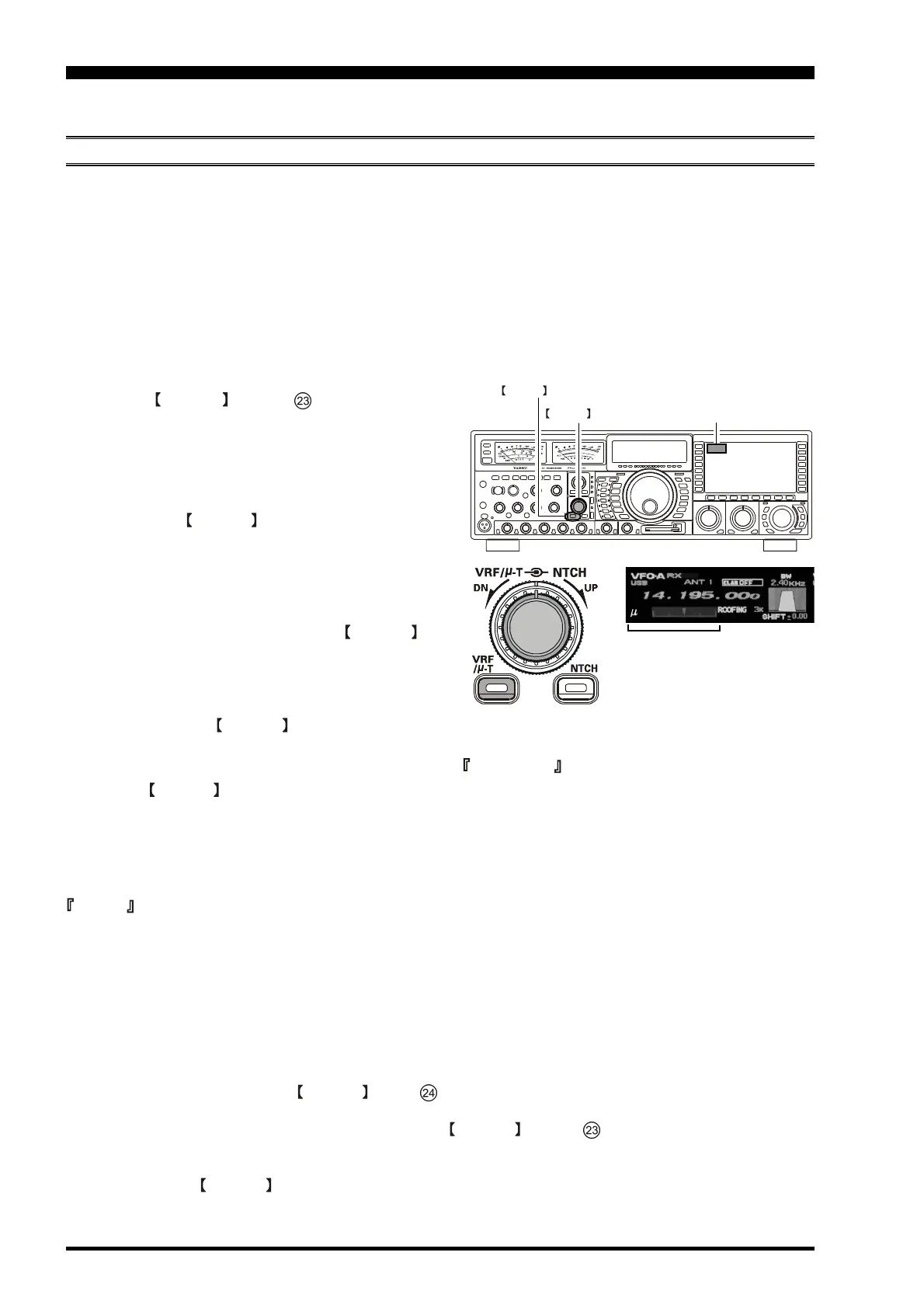
Switches and knobs for VRF, µ-TUNE, and IF Notch filters for interference rejection.
Controls for IF bandwidth, Contour filter, Digital Noise Reduction, and Digital Notch Filter.
Buttons for VFO/Memory modes, band selection, and indicators like BUSY and SPLIT.
Explanation of frequency displays, TX/RX indicators, S-meters, and status indicators.
Switches and knobs for Sub band receiver functions like Roofing, AGC, VRF, and Notch filters.
Controls for Sub band DSP filters (Shape, Slope, Narrow) and noise reduction.
Controls for RF Power, BIAS adjustment, and engaging Class-A transmission mode.
Details on the CF card slot and adjustment of AF/RF GAIN controls.
Controls for P.BACK (audio playback), AFL, SHIFT/WIDTH, ACM, and Clarifier functions.
Using the CLAR/VFO-B knob for frequency tuning, band selection, and mode selection.
Using FAST/RX, BAND/MHz/TX, B-MODE/CLEAR, and A/B switches for frequency management.
Description of ANT, RX OUT, and RX ANT jacks for antenna and signal routing.
Details on power switch, AC IN, MIC jack, and REMOTE connector for external control.
Connectors for +13.8V, PTT, PATCH, EXT SPKR, AF OUT, RTTY, PACKET, TRV, ACC, TXGND, BAND DATA, and EXT ALC.
Connectors for KEY, CAT, GND, COM, KEY BOARD, AUDIO OUT/IN, DISPLAY, and USB.
Indicators for Main and Sub band transmit/receive status.
Main and Sub band frequency display fields, showing operating frequency and status.
Indications for CLAR, Memory Recall (MR), Memory Tune (MT), Repeater Shift, and frequency control mode.
Keys for band selection, 50 MHz access, TRV control, and General Coverage VFO.
Engaging direct frequency entry and accessing the Menu system for configuration.
Explains the use of 'Function' keys associated with each TFT page for operational capability.
Steps for powering on the transceiver, initial boot-up, and setting AF GAIN and MAIN RX.
Engaging the Sub RX switch for Dual Receive and selecting operating bands.
Selecting antennas using ANTENNA SELECT switches and operating modes using MODE keys.
Adjusting the SQL control and using the main tuning dial for band operation.
Using the CLAR button and knob to offset transmit/receive frequencies.
Instructions for operating on the 60-meter band using fixed memory channels.
Operating procedure for simultaneous reception using Main and Sub receivers.
Capability for full duplex operation and precautions for RF isolation between antennas.
Configuring headphone mixing and using sideband/bandwidth diversity for enhanced reception.
Recording/playback of receiver audio and customizing band selection with 'My Bands'.
Utilizing triple band-stack VFO selection and swapping AF/RF gain control functions.
Setting up custom switches and techniques for keyboard frequency entry and scanning.
Selecting TX/RX antennas using front panel switches and the RX-only antenna option.
Configuring audio output to internal speakers for stereo or monaural modes.
Overview of receiver circuitry including µ-Tune, VRF, Roofing filters, and DSP functions.
Explanation of the IPO function to bypass RF amplifiers for improved receiver characteristics.
Using the ATT knob to insert RF attenuation for strong signals or high noise.
Manual adjustment of receiver RF and IF stage gain levels for optimal reception.
Detailed guide on using the µ-Tune system for advanced preselection and interference rejection.
Detailed guide on using the VRF system for RF preselection and comparison with fixed filters.
Explanation of narrow-band Roofing Filters for protection of downstream circuitry.
Using the Contour filter for gentle IF passband perturbation to suppress or enhance components.
Varying the DSP filter passband to reduce or eliminate interference.
Adjusting the width of the DSP IF passband to eliminate interference or enhance fidelity.
Using the IF Notch filter to slice out interfering beat notes from the receiver passband.
Using the DNR system to effectively reduce random noise levels.
Using the DNF filter to cancel interfering beat notes within the receiver passband.
Using the IF Noise Blanker to reduce noise from automotive ignition systems.
Explanation of the AGC system for maintaining constant audio output level and stage protection.
Description of the innovative Sloped AGC system for improved signal separation.
Silencing the Main receiver temporarily and using AFL for audio output level limiting.
Visual indicator of encroachment by other stations in CW mode using ACM.
Selecting operating modes (LSB, USB, CW, AM) and adjusting frequency using controls.
Using PTT/MOX for transmission and adjusting microphone gain for proper ALC levels.
Procedure to enable 48-volt phantom power for condenser microphones via the XLR connector.
Step-by-step guide on operating the Automatic Antenna Tuner for impedance matching.
Explanation of ATU operation, tuning data storage, and SWR conditions affecting memory.
Procedure for replacing the ATU backup battery to maintain tuner memories.
Using the Speech Processor to increase talk power and improve intelligibility.
Adjusting the transmitted bandwidth for varied fidelity or talk power levels.
Using the Three-Band Parametric Microphone Equalizer for precise audio control.
Using Class-A operation for ultra-low distortion transmission at 75 Watts.
Utilizing the Voice Memory capability with the FH-2 Remote Control Keypad for recording audio.
Using the built-in electronic keyer for CW operation, including break-in modes.
Using the SPOT system for zero-beating and precise frequency matching with other stations.
Using CW Reverse for interference rejection and adjusting CW delay time.
Programming CW messages into memory and using the FH-2 keypad for playback.
Programming CW messages using text entry and managing contest numbers.
Steps for selecting the FM operating mode and desired operating frequency.
Utilizing repeaters and configuring CTCSS tones for repeater access.
Setting repeater shift directions and magnitudes, and using Tone Squelch.
Storing and recalling operating parameters using the five QMB memory channels.
Enabling memory groups and selecting specific groups for organized memory recall.
Storing current operating parameters into memory and recalling them for use.
Viewing memory channel status and erasing stored data.
Transferring memory data to VFO-A and tuning off memory channels.
Activating transmission and reception on 5167.5 kHz via the Menu for emergency use.
Operating on the 60-meter band using pre-programmed memory channels.
Scanning frequencies on the Main VFO or through memory channels.
Using PMS to limit scanning within specific frequency ranges or sub-bands.
Basic setup procedures for Packet operation, including subcarrier frequency.
Setup steps for RTTY operation, including mode selection and polarity settings.
Guidelines for setting up various SSB-based data modes and interfacing with sound cards.
How to navigate, select, and change settings within the transceiver's menu system.
Procedure to reset all menu settings to their original factory defaults.
Overview of menu item groupings: AGC, DISPLAY, FH-2 SETUP, GENERAL, MODE-AM/FM/SSB, RX AUDIO, RX DSP, SCOPE, TUNING, TX AUDIO, TX GNRL.
General specifications including frequency range, stability, power consumption, and dimensions.
Transmitter specifications including power output, modulation, harmonic radiation, and suppression.
Receiver specifications including circuit type, sensitivity, selectivity, and image rejection.











