Rockwell Automation Publication 1734-UM013N-EN-P - September 2017 31
Safety Inputs, Safety Outputs and Safety Data Chapter 2
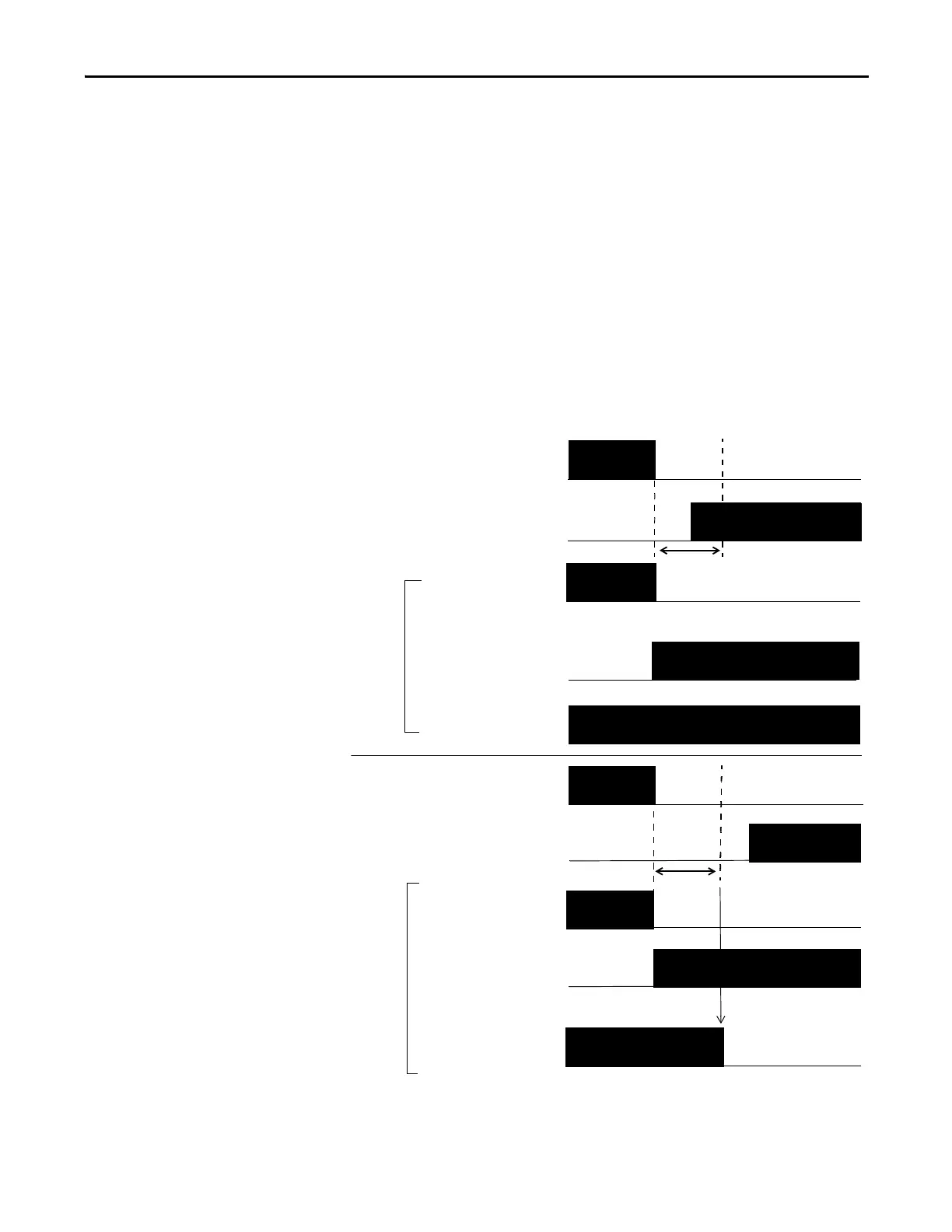
Dual-channels, Complementary
In Complementary mode, the inputs of a pair must be in the opposite
(complementary) state. When a transition occurs in one channel of the pair
before the transition of the second channel of the pair, a discrepancy occurs. If the
second channel transitions to the appropriate state before the discrepancy time
elapsing, the inputs are considered complementary.
If the second transition does not occur before the discrepancy time elapses, the
channels will fault. The fault state of complementary inputs is the
even-numbered input that is turned off and the odd-numbered input turned ON.
Note that if faulted, both channel status bits are set low. When configured as a
complementary dual-channel pair, the data bits for both channels are sent to the
controller in complementary, or opposite states.
Figure 9 - Complementary, Normal Operation and Fault Detection (Not to Scale)
ON
OFF
IN0
Safety Input 0
Data
IN1
Fault Detected
Discrepancy Time
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
IN0
Safety Input 0, 1
Status
IN1
Fault Detection
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
Discrepancy Time
Safety Input 0, 1
Status
Safety Input 1
Data
Safety Input 1
Data
Safety Input 0
Data
Normal
Operation
Safety
I/O
Network
Data Sent
to the
Controller
Safety
I/O
Network
Data Sent
to the
Controller

 Loading...
Loading...











