29-4
Catalyst 3550 Multilayer Switch Software Configuration Guide
78-11194-09
Chapter 29 Configuring QoS
Understanding QoS
Basic QoS Model
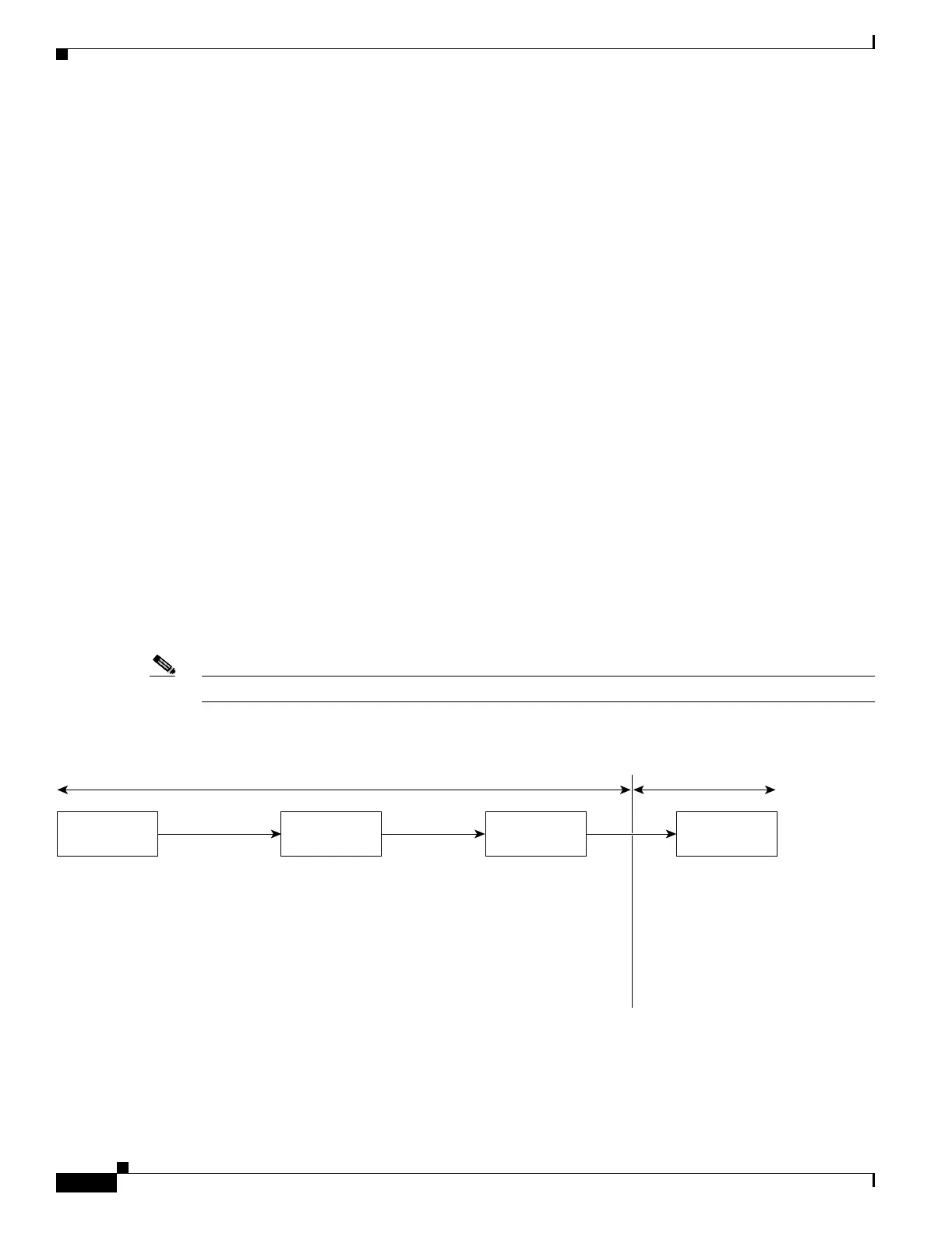
Figure 29-2 shows the basic QoS model. Actions at the ingress interface include classifying traffic,
policing, and marking:
• Classifying distinguishes one kind of traffic from another. The process generates an internal DSCP
for a packet, which identifies all the future QoS actions to be performed on this packet. For more
information, see the “Classification” section on page 29-5.
• Policing determines whether a packet is in or out of profile by comparing the internal DSCP to the
configured policer. The policer limits the bandwidth consumed by a flow of traffic. The result of this
determination is passed to the marker. For more information, see the “Policing and Marking” section
on page 29-8.
• Marking evaluates the policer and the configuration information for the action to be taken when a
packet is out of profile and decides what to do with the packet (pass through a packet without
modification, mark down the DSCP value in the packet, or drop the packet). For more information,
see the “Policing and Marking” section on page 29-8.
Actions at the egress interface include queueing and scheduling:
• Queueing evaluates the internal DSCP and determines which of the four egress queues in which to
place the packet. The DSCP value is mapped to a CoS value, which selects one of the queues. For
more information, see the “Mapping Tables” section on page 29-10.
• Scheduling services the four egress queues based on their configured weighted round robin (WRR)
weights and thresholds. One of the queues can be the expedite queue, which is serviced until empty
before the other queues are serviced. Congestion avoidance techniques include tail drop and
Weighted Random Early Detection (WRED) on Gigabit-capable Ethernet ports and tail drop (with
only one threshold) on 10/100 Ethernet ports. For more information, see the “Queueing and
Scheduling” section on page 29-11.
Note Policing and marking also can occur on egress interfaces.
Figure 29-2 Basic QoS Model
46975
Classification Policing
Generate DSCP
Actions at ingress Actions at egress
Mark
In profile or
out of profile
Inspect packet and
determine the DSCP
based on ACLs or
the configuration.
Map the Layer 2
CoS value to a
DSCP value.
Compare DSCP to
the configured
policer and
determine if the
packet is in profile or
out of profile.
Based on whether
the packet is in or
out of profile and the
configured
parameters,
determine whether
to pass through,
mark down, or drop
the packet. The
DSCP and CoS are
marked or changed
accordingly.
Queueing and
scheduling
Based on the CoS,
determine into which
of the egress
queues to place the
packet. Then service
the queues
according to the
configured weights.

 Loading...
Loading...











