2 INTRODUCTION TO SAMPLED VALUES
IEC 61850 Sampled Value specifications such as IEC 61850-9-2LE or IEC 61850-9-9, define Process Bus
communications between the different components of the substation automation system. IEDs with compatible
interfaces can communicate with the Process Bus and receive sampled value data from Merging Units. Analog
Merging Units digitize analog values from conventional CTs and VTs, replacing analog inputs. This simplifies the
installation by replacing the analog measurement wiring with the Process Bus Local Area Network. Using a fibre
optic network instead of heavy copper cables between the measuring device and the IED provides safer and more
economical cross-site cabling. It also allows IEDs to receive current and voltage sampled data through Digital
Merging Units from Low Power Instrument Transformers such as optical and Rogowski devices.
IEDs, which accept digital sampled values rather than analog signals have no need for expensive and heavy on-
board scaling CTs and VTs, making them smaller, lighter, safer and cheaper. An SV IED with the same size case as a
conventional IED would have more room for digital I/O, because valuable space is not taken up by the on-board
CTs and VTs.
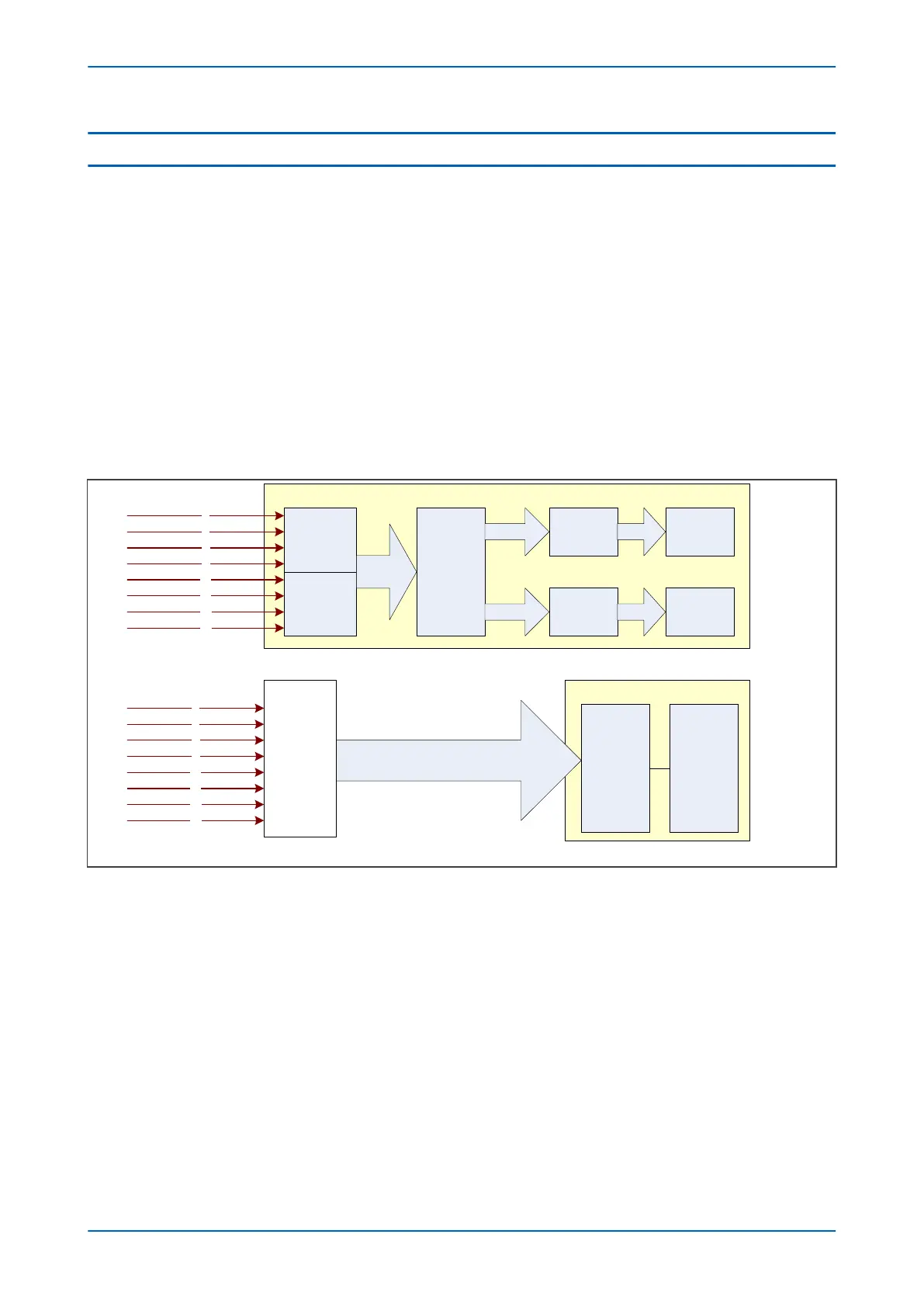
The following figure shows the difference between a conventional IED with analog inputs and a Sampled Values
IED with digital inputs:
Conventional IED
V03700
VA
VB
VC
VN
IA
IB
IC
IN
CT Inputs
VT Inputs
A/D
Conversion
Filtering and
Processing
Scaling
SV IED
VA
VB
VC
VN
IA
IB
IC
IN
Sampled Values
(in IEC61850 Ethernet frames)
Processing
Analog
Merging Unit
IEC 61850
SV
Interface
Conventional Protection IED
IEC61850 Sampled Value Protection System
Fast
protection
algorithms
Sampled
Values
Standard
protection
algorithms
Direct
comparison
Figure 31: Comparison of Conventional IED and Sampled Values IED
Chapter 6 - Sampled Value Operation P446SV
96 P446SV-TM-EN-1
 Loading...
Loading...











