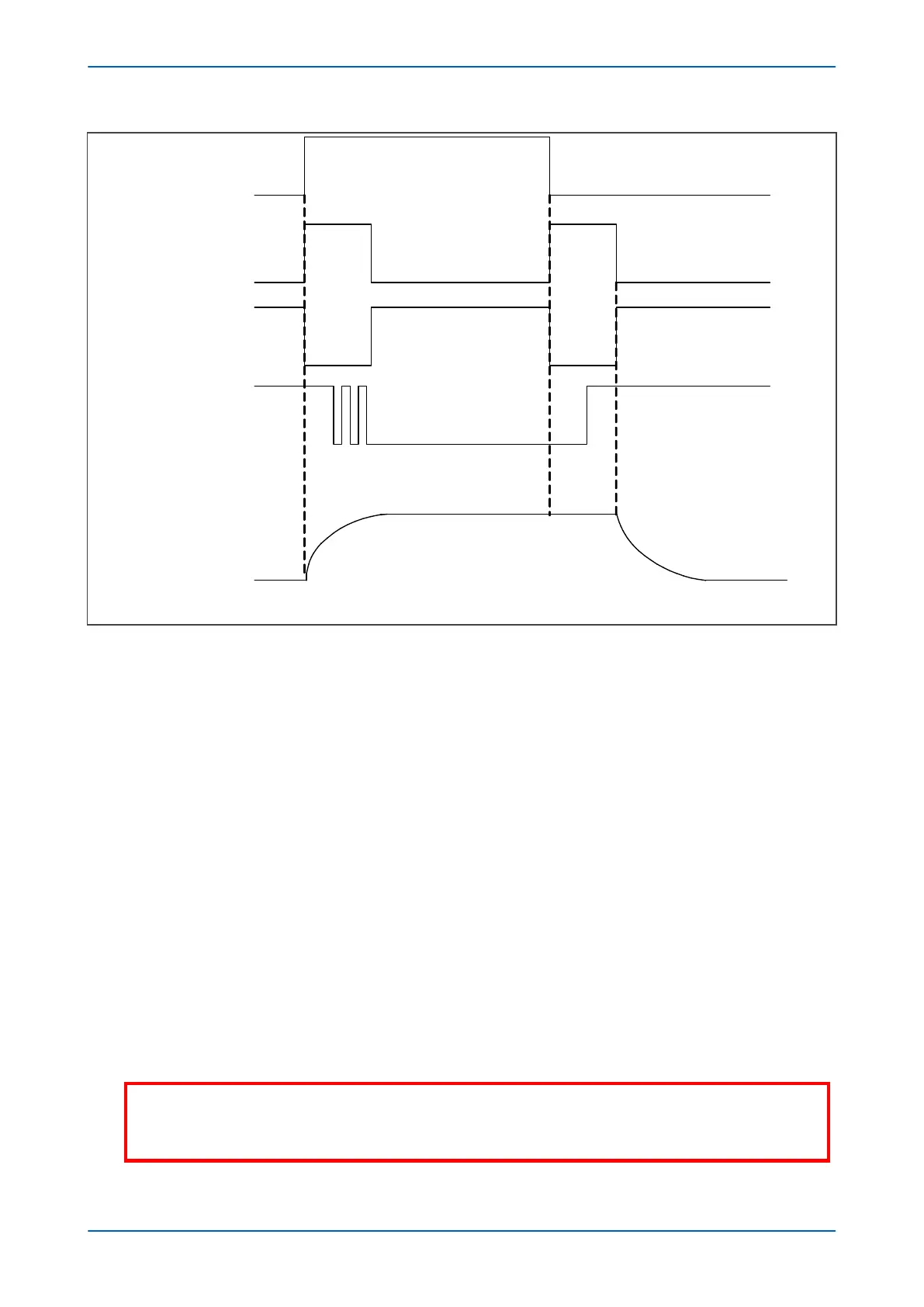
V00246
3.5ms + contact bounce
Load current
Relay contact
Databus
control input
MOSFET reset
MOSFET operate
on
7ms
on
3.5ms
Closed
on
7ms
off
Figure 24: High Break contact operation
High Break Contact Applications
● Efficient scheme engineering
In traditional hard wired scheme designs, High Break capability could only be achieved using external
electromechanical trip relays. Instead, these internal High Break contacts can be used thus reducing space
requirements.
● Accessibility of CB auxiliary contacts
It is common practise to use circuit breaker 52a (CB Closed) auxiliary contacts to break the trip coil current
on breaker opening, thereby easing the duty on the protection contacts. In some cases (such as operation
of disconnectors, or retrofitting), it may be that 52a contacts are either unavailable or unreliable. In such
cases, High Break contacts can be used to break the trip coil current in these applications.
● Breaker fail
In the event of failure of the local circuit breaker (stuck breaker), or defective auxiliary contacts (stuck
contacts), it is incorrect to use 52a contact action. The interrupting duty at the local breaker then falls on the
relay output contacts, which may not be rated to perform this duty. High Break contacts should be used in
this case to avoid the risk of burning out relay contacts.
● Initiation of teleprotection
The High Break contacts also offer fast making, which results in faster tripping. In addition, fast keying of
teleprotection is a benefit. Fast keying bypasses the usual contact operation time, such that permissive,
blocking and intertrip commands can be routed faster.
Warning:
These relay contacts are POLARITY SENSITIVE. External wiring must comply with the polarity
requirements described in the external connection diagram to ensure correct operation.
P446SV Chapter 3 - Hardware Design
P446SV-TM-EN-1 55
 Loading...
Loading...











