Chapter 1. Features and Capabilities
2 XMTC User’s Manual
1.3 Theory of Operation
The XMTC measures the concentration of a gas in a binary gas mixture by measuring the thermal conductivity of the
sample gas and comparing it to the thermal conductivity of a selected reference gas.
Two ultra-stable, glass-coated thermistors are used: one in contact with the sample gas, and the other in contact with a
selected reference gas. The thermistors are mounted so that they are in close proximity to the stainless steel walls of the
sample chamber. The entire sensor is heated to 55°C/131°F, (or 70°C/158°F) and the thermistors are heated above the
sensor temperature using a constant current source. The thermistors lose heat to the walls of the sample chamber at a
rate that is proportional to the thermal conductivity of the gas surrounding them. Thus, each thermistor will reach a
different equilibrium temperature. The temperature difference between the two thermistors is detected in an electrical
bridge circuit. It is then amplified and converted to a 4-20 mA output proportional to the concentration of one of the
constituents of the binary gas mixture. For example:
• To measure 0 to 25% H
2
in N
2
, the reference gas would be air (2-port version, sealed reference gas), and for
calibration, the zero gas would be 100% N
2
(i.e. 0% H
2
) and the span gas would be 25% H
2
in N
2
.
• To measure 90-100% H
2
in N
2
, the reference gas would be 100% H
2
(4-port version, flowing reference gas),
the zero gas would be 90% H
2
in N
2
, and the span gas would be 100% H
2
(the same as the reference gas).
Note: The XMTC has polarity adjustment jumpers which permit the measurement of gases (such as CO
2
) that have a
relative thermal conductivity less than air/nitrogen.
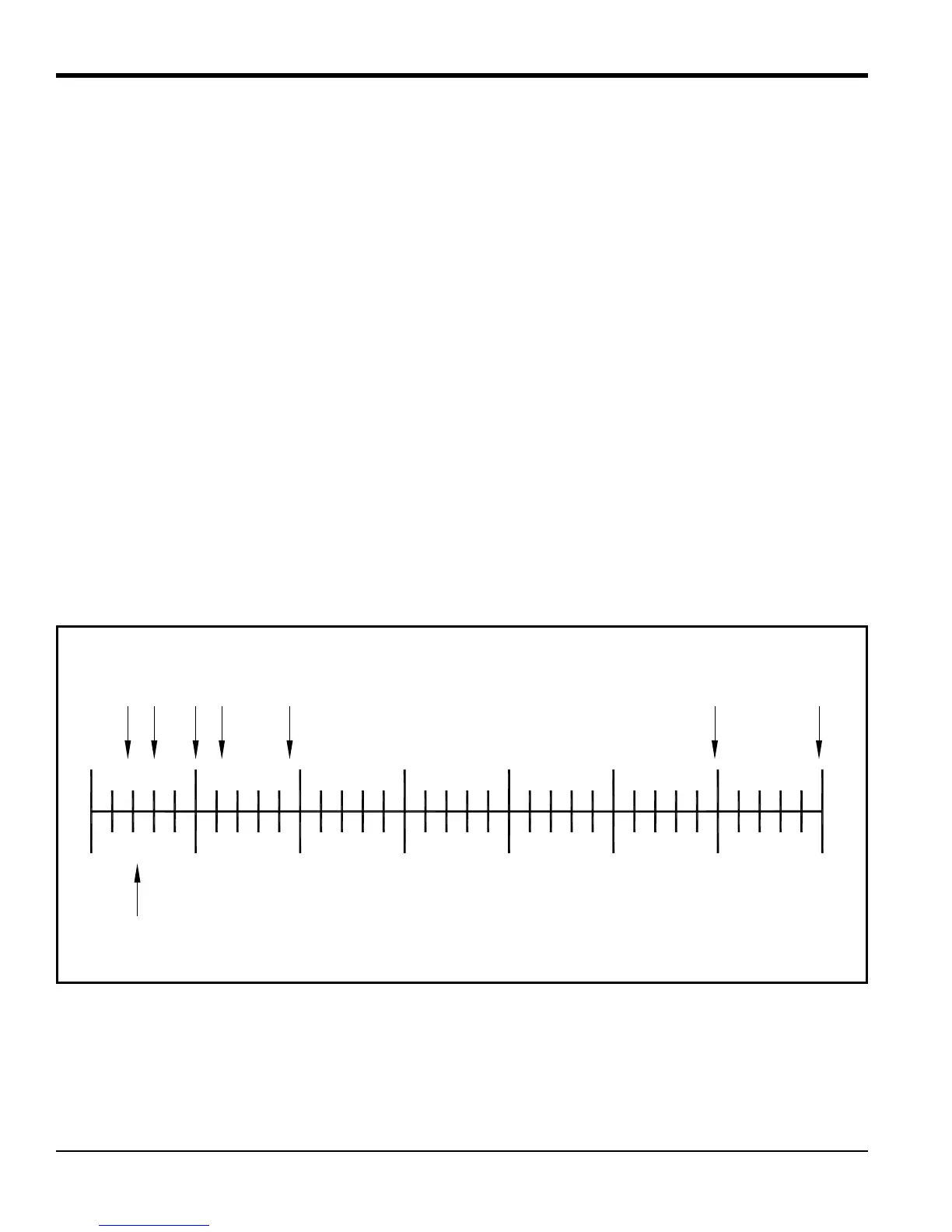
Appendix A, Supplemental Information, contains a table of Relative Thermal Conductivity of Common Gases. Figure 1
below shows some of these values graphically.
Figure 1: Relative Thermal Conductivity of Some Common Gases
0 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0 7.0
SO
2
CO
2
Air/N
2
CH
4
Ne
He
H
2
C
4
H
6

 Loading...
Loading...