Analog Output 10-3
Overview
The ANALOG OUTPUT provides a scaled, non-inverting voltage output up to ±1.2V. It is
typically used to drive a chart recorder. The Analog Output voltage is calculated as follows:
Analog Output = (Gain × Rdg/Rng) – Offset
where: Gain is the user entered gain factor.
Rdg is the reading on the Model 2182.
Rng is the measurement range.
Offset is the user entered offset value.
NOTE Gain and offset for Analog Output are not related to gain and offset for the mX+b
calculation (see Section 4).
Gain provides amplification for small analog output voltage signals, while offset allows you
to adjust the analog output to keep it between ±1.2V(maximum output) or reference the voltage
output to a specific value, such as zero.
For example, assume you are measuring 100mV on the 1V range. With gain set to 1, the
analog output would be 100mV. You can increase analog output sensitivity by setting gain to 10.
This increases the analog output to 1V. You can then set Offset to 1V to reference the 1V analog
output to zero. The Analog Output calculation looks like this:
Analog Output = (10 × 100mV/1V) – 1V = 0V
NOTE Analog Output Rel can be used to automatically reference the analog output voltage
to zero. See “Analog output rel.”
The factory default for Gain is 1 and the factory default for Offset is 0. Therefore, when using
the factory defaults, Gain and Offset drop out of the equation:
Analog Output = Rdg/Rng
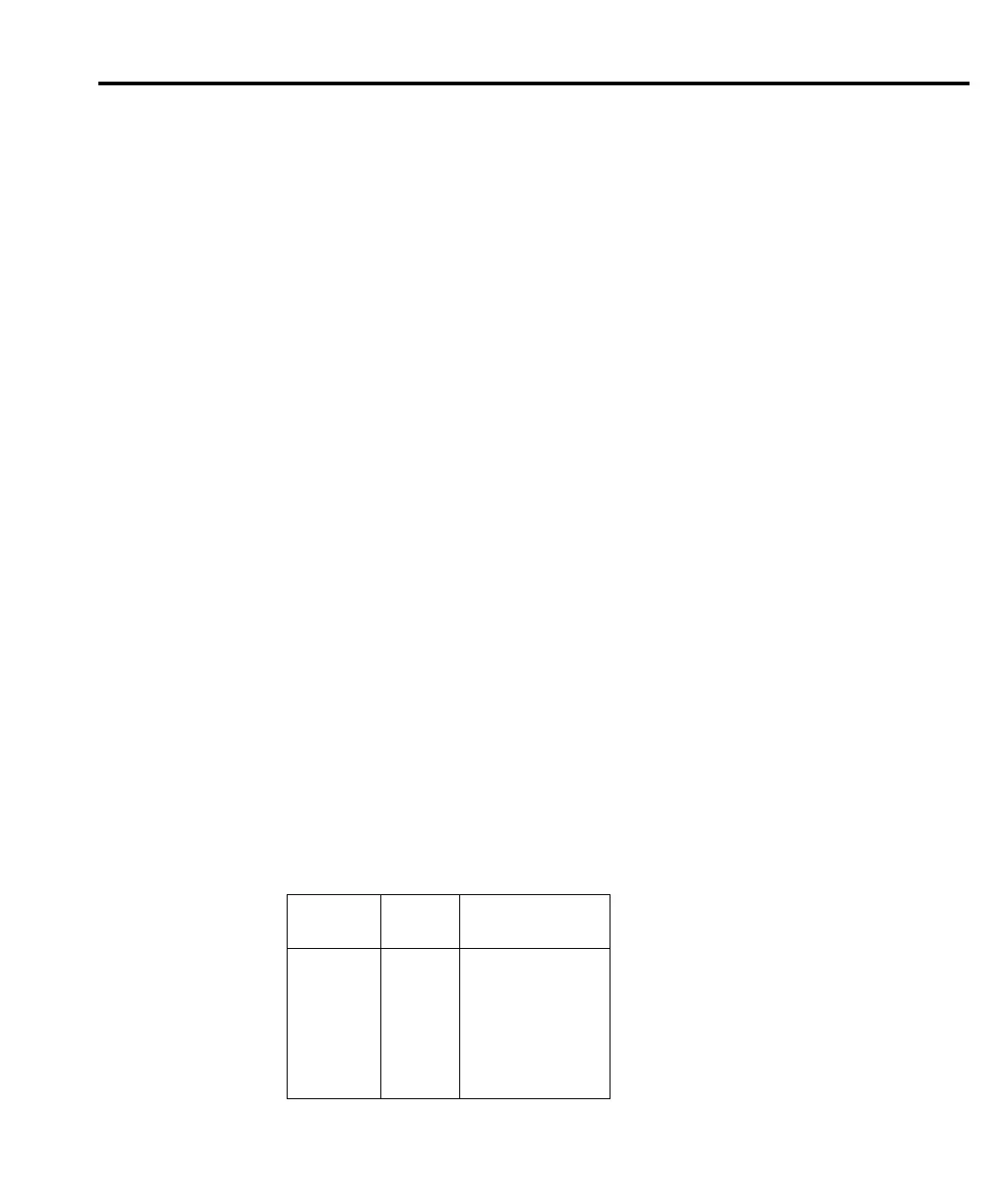
Table 10-1 shows analog output examples with Gain set to 1 and Offset set to 0.
Table 10-1
Analog output examples*
Reading Range
Analog Output
Voltage
1V 1V +1V
–1V 1V –1V
1V 10V 0.1V
12V 10 1.2V
50mV 100mV 0.5V
–1mV 1V –1mV
* Gain = 1, Offset = 0

 Loading...
Loading...