3-10 Range, Digits, Rate, and Filter
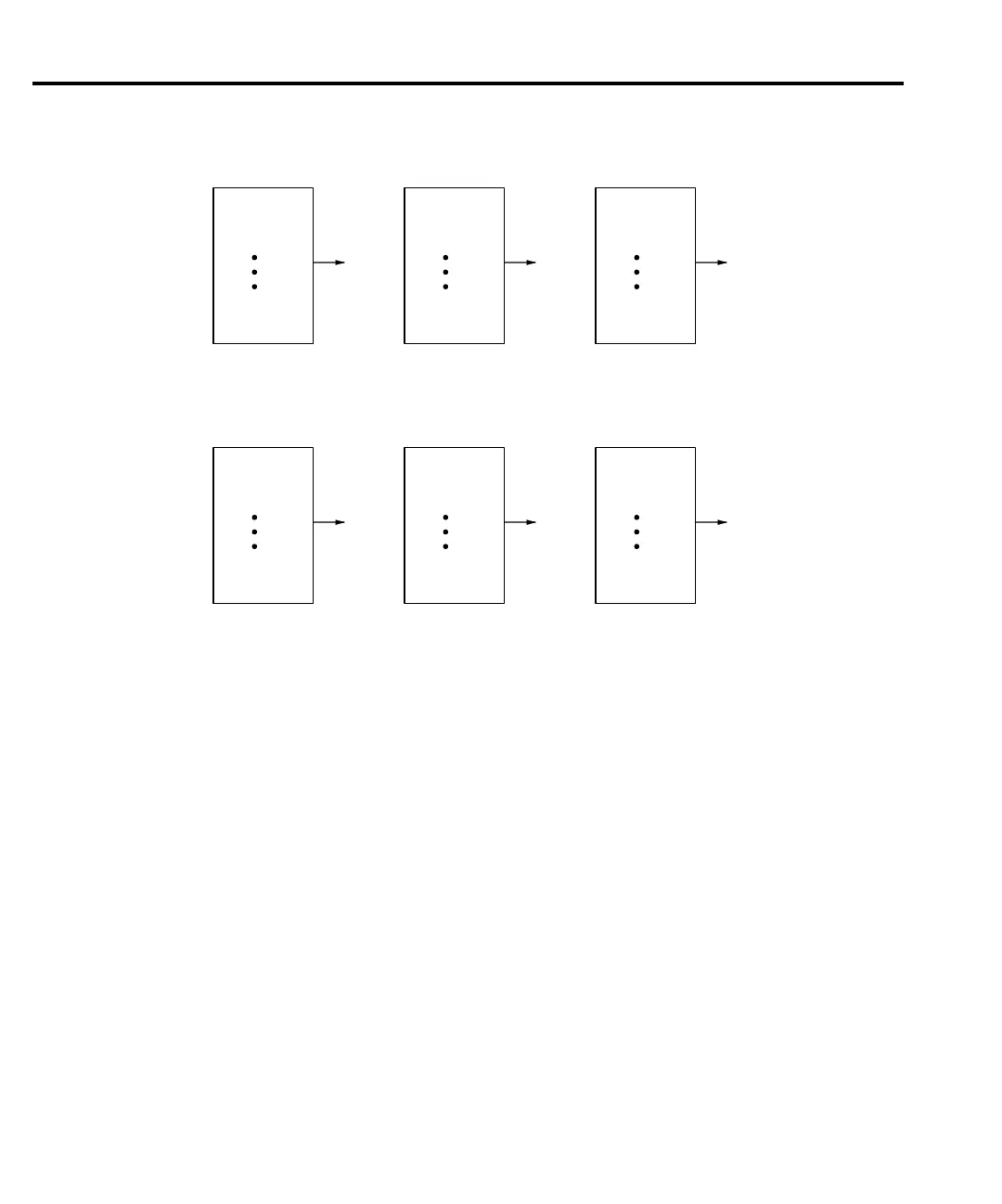
Figure 3-2
Moving and repeating filters
Digital filter example
Filter Count = 10
Filter Window = 0.01% of range
Filter Type = Moving
Ten readings fill the stack to yield a filtered reading. Now assume the next reading (which is
the 11
th
) is outside the window. A reading will be processed (displayed); however, the stack will
be loaded with that same reading. Each subsequent valid reading will then displace one of the
loaded readings in the stack. The FILT annunciator will flash until 10 new readings fill the stack.
NOTE Bit 8 of the Operation Event Status Register sets when the filter window has properly
settled. See “Status structure” in Section 11 for details.
Conversion #10
#9
#8
#7
#6
#5
#4
#3
#2
Conversion #1
Reading
#1
A. Type - Moving Average, Readings = 10
Conversion #11
#10
#9
#8
#7
#6
#5
#4
#3
Conversion #2
Reading
#2
Conversion #12
#11
#10
#9
#8
#7
#6
#5
#4
Conversion #3
Reading
#3
Conversion #10
#9
#8
#7
#6
#5
#4
#3
#2
Conversion #1
Reading
#1
B. Type - Repeating, Readings = 10
Conversion #20
#19
#18
#17
#16
#15
#14
#13
#12
Conversion #11
Reading
#2
Conversion #30
#29
#28
#27
#26
#25
#24
#23
#22
Conversion #21
Reading
#3

 Loading...
Loading...