2-26 Voltage and Temperature Measurements
Standard cell comparisons
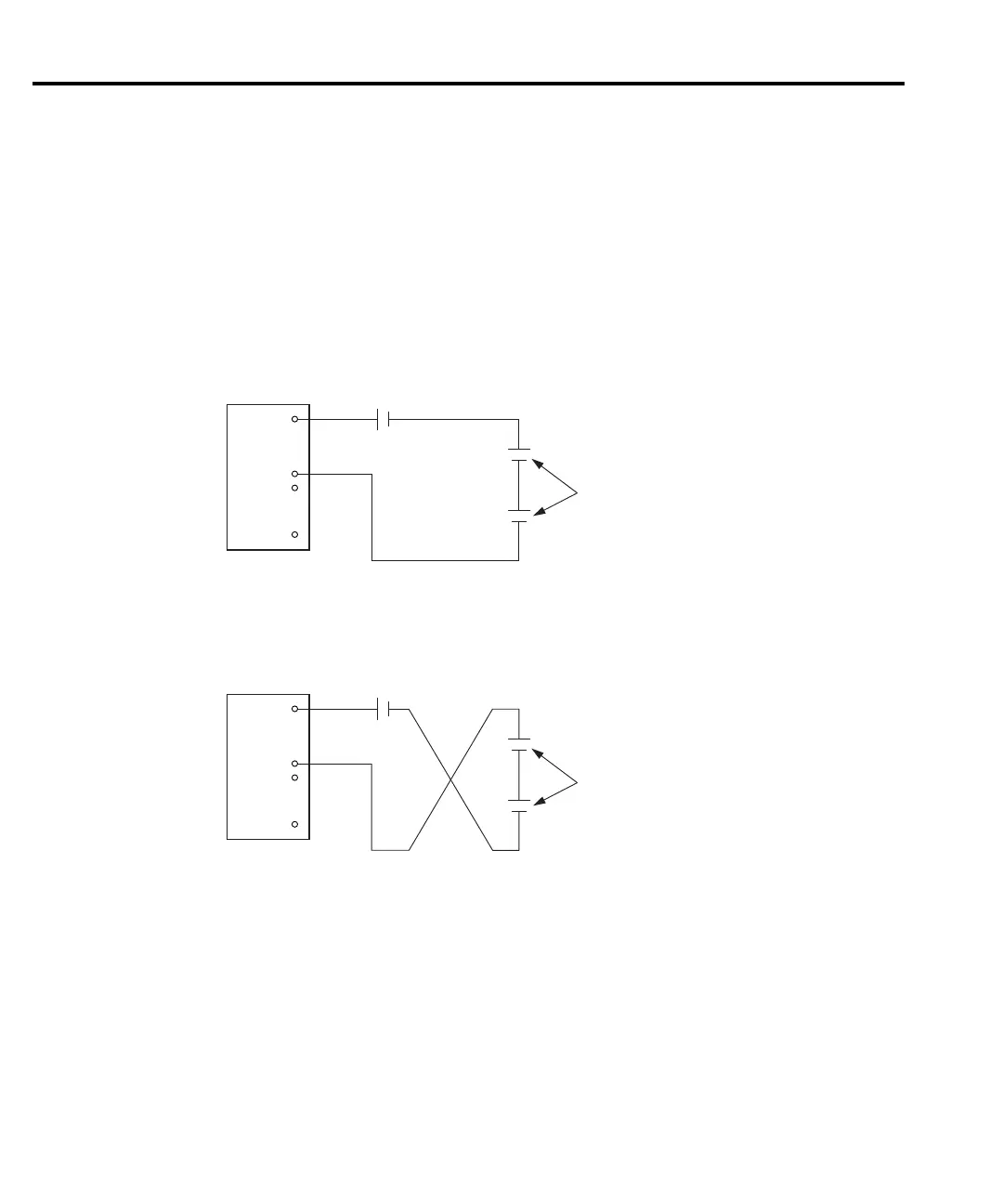
Standard cell comparisons are conducted by measuring the potential difference between a
reference and an unknown standard cell. All cell differences are determined in series opposition
configuration. The positive terminals of the standard cells (V1 and V2) are connected to the HI
and LO inputs of the nanovoltmeter, as shown in Figure 2-13A. The Model 2107 Input Cable
(supplied with the Model 2182) should be used to connect the cells to the nanovoltmeter in order
to minimize errors caused by thermal EMFs (V
EMF
).
Figure 2-13
Standard cell comparison measurements
Once the measurement connections have been made, care must be taken to avoid errors from
thermally generated potentials. To minimize the effects of thermal EMFs, a second measurement
is taken with the nanovoltmeter leads reversed, as shown in Figure 2-13B. The small voltage
difference is calculated by averaging the absolute values of the two readings. Calculation of
standard deviation across several redundant readings will help provide this assurance.
Once stability has been achieved, the actual voltage difference between the cells is measured.
For each comparison, several readings are usually averaged. This process of comparing is then
repeated each week, month, or year, depending upon the standards laboratory. The results can
then be plotted and compared over time.
HI
HI
LO
LO
DCV1
CH 1
CH 2
2182
+
-
V
EMF
+
-
+
-
V1
V2
Standard Cells
HI
HI
LO
LO
DCV1
CH 1
CH 2
2182
+
-
+
-
+
-
V1
V2
Standard Cells
A) Reading #1
Reading #1 = V1 - V2 + V
EMF
B) Reading #2
Reading #2 = V
EMF
Thermal EMFs
V
EMF
Thermal EMFs
+ (V
2
- V
1
)

 Loading...
Loading...