Delta, Pulse Delta, and Differential Conductance I-17
Measurement units
The fundamental measurement for Differential Conductance is differential voltage (dV).
However, the dV reading can be converted into a differential conductance (dG), differen-
tial resistance (dR), or power (Watts) reading by the Model 622x.
With Ohms (dR) or Siemens (dG) measurement units selected, the reading is calculated as
follows:
dR = dV/dI
dG = dI/dV
With Power measurement units selected, power is calculated using Average Voltage and
Average Current and is explained in the following paragraphs.
Average Voltage and Power
Average Voltage calculation
Average Voltage is the average bias voltage that was present across the device when the
corresponding Differential Conductance reading was taken. For remote operation, the
Average Voltage reading for Differential Conductance can be included in the returned data
string.
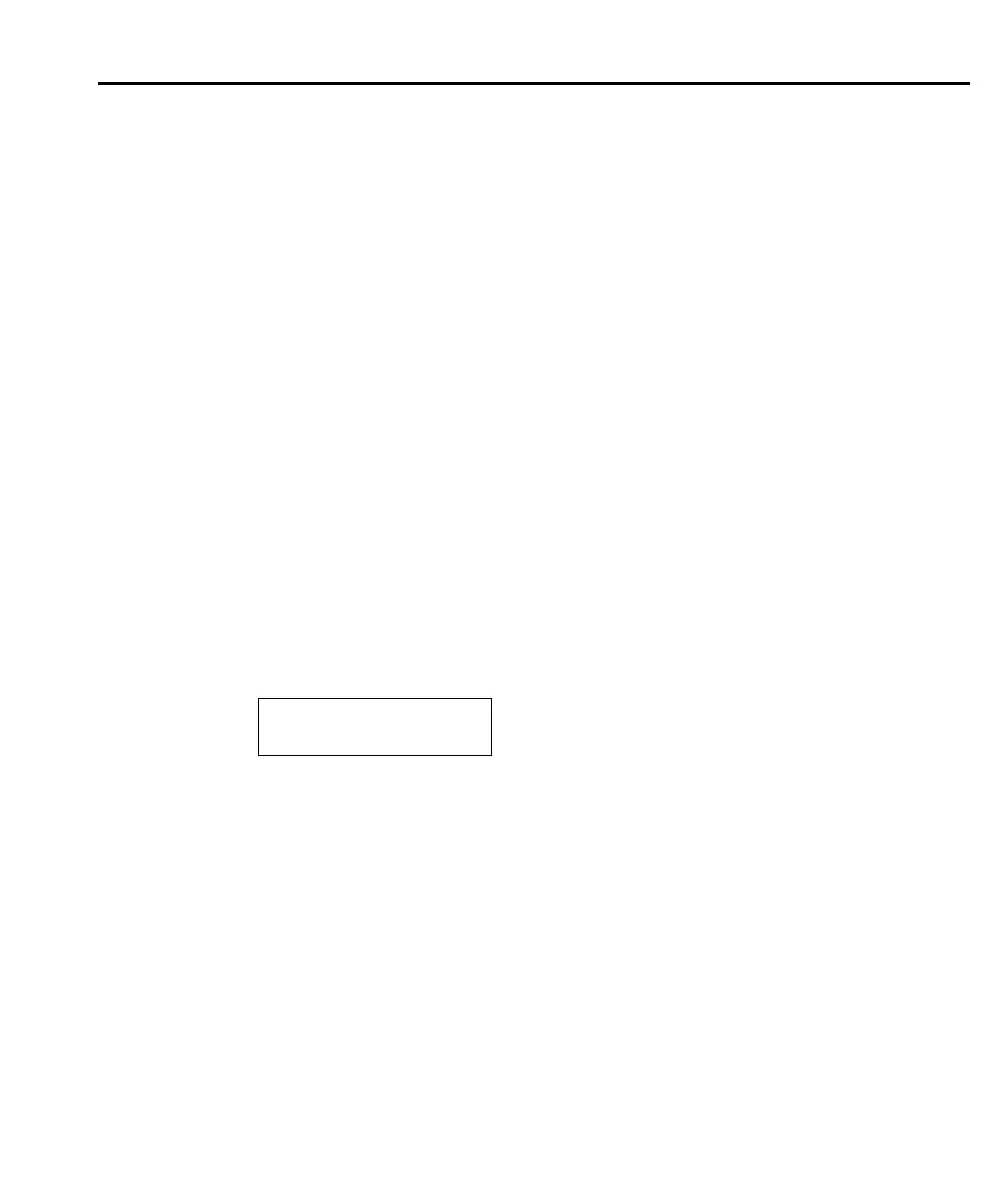
Average Voltage is calculated as follows:
Where: AvgVolt is the Average Voltage corresponding to a given the differential voltage
(dV) reading.
X, Y, and Z are the three A/D measurements for the dV reading.
AvgVolt
XY+()
2
------------------
ZY+()
2
-----------------+
2
-------------------------------------------=
AvgVolt
X 2YZ++
4
--------------------------=

 Loading...
Loading...