Dominant Wavelength/Excitation Purity
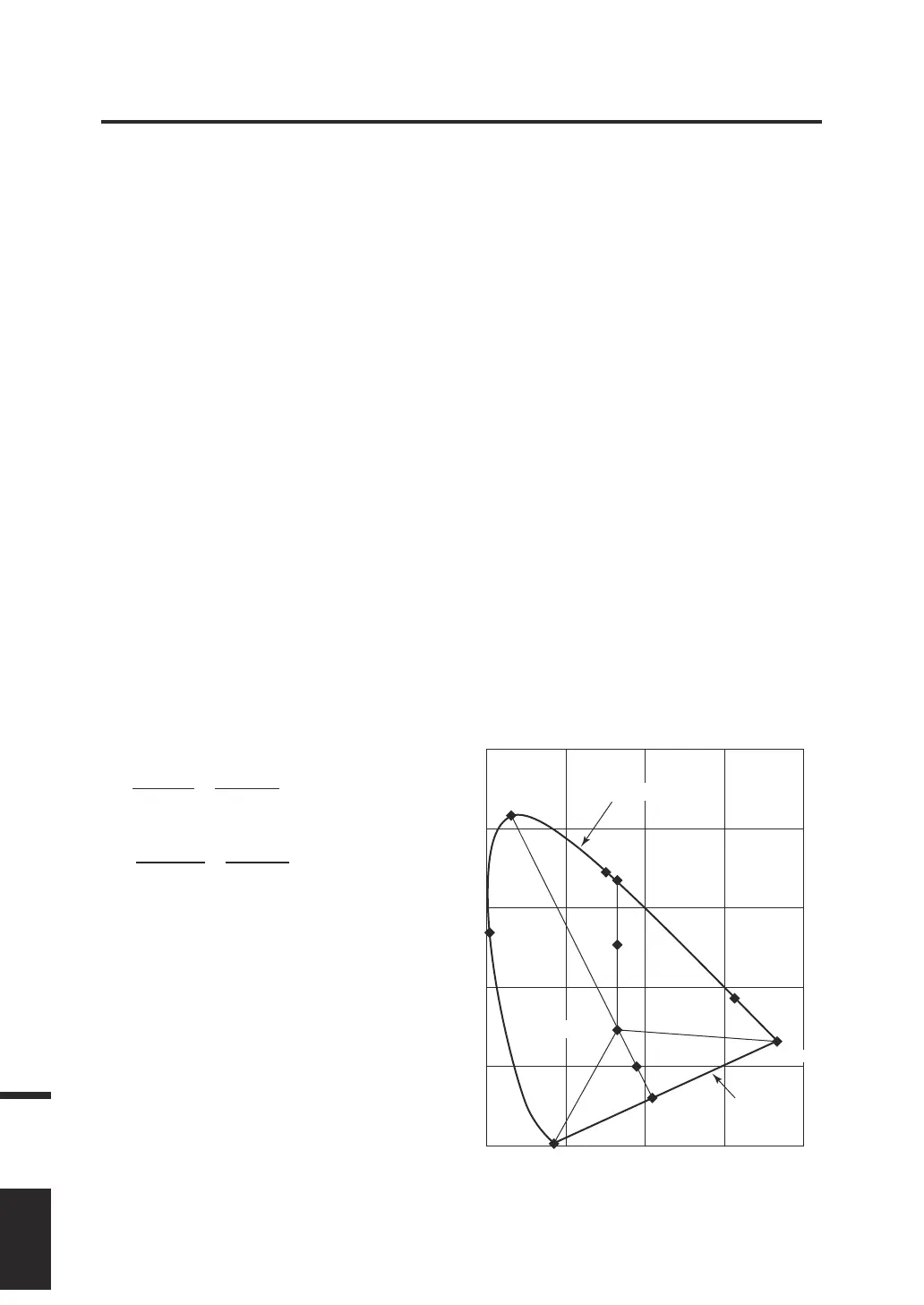
In the x, y chromaticity diagram shown below, the curve VScSR is the spectrum locus, and
point N is the white point.
Colors located in the region enclosed by the spectrum locus and the straight lines VN and NR
are referred to as spectral colors; and colors located in the triangle NVR with the white point
N at the apex and the purple boundary VR as the base are referred to as non-spectral colors.
< Dominant wavelength and excitation purity (spectral colors) >
When the chromaticity point obtained by measurement is C, the wavelength corresponding
to the intersection point S of the extension of NC with the spectrum locus (curve VScSR) is
referred to as a dominant wavelength and is indicated by the symbol λd.
The ratio of the lengths of the straight lines NC and NS is referred to as the excitation
purity of color excitation C and indicated by the symbol pe.
< Complementary wavelength (non-spectral colors) >
When the chromaticity point obtained by measurement is C', the extension of NC' toward
C' does not intersect with the spectrum locus but with the purple boundary. In this case, the
wavelength corresponding to the intersection point Sc of the extension of NC' toward N with
the spectrum locus is referred to as a complementary wavelength and is indicated by the
symbol λc. This instrument also indicates it with the symbol λd with a minus sign.
When the intersection point of the extension of the line NC' with the line VR (purple
boundary) is designated by S', the ratio of the lengths of NC' to NS' is referred to as
excitation purity of color excitation C' and is indicated by the symbol p'v.
The following equations are formulated where (xn , yn) is the chromaticity coordinates of
point N, (xc , yc) is the chromaticity coordinates of point C, (xλ , yλ) is the chromaticity
coordinates of point S, (xc', yc') is the chromaticity coordinates of point C', and (xp, yp) is the
chromaticity coordinates of point P:
Excitation purity (spectral colors)
x
c - n yc - n
pe= =
xλ- n yλ - n
Dominant wavelength on chromaticity diagram
y
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
0.2 0.4 0.6
x
550 nm
600 nm
780 nm
500 nm
380 nm
S
S
c
C
C'
S'
N
V
Spectrum locus
Purple
boundary
White point
R
Excitation purity (non-spectral colors)
x
c' - xn yc' - yn
pe'= =
xp - n yp - yn
100
Explanation and
Information
λ
d
& P
e

 Loading...
Loading...