BODY REPAIR
BASE OF BODY REPAIR
9-28
FRAME REPAIR PROCEDURES
M4090014000014
The frame is subjected to the following types of
loads.
• Vertical loads... Vertical loads may occur either
while stopped or during travel.
• Lateral (horizontal) loads... This type of loads
occurs during turning, start-off and braking.
• Torsional loads... Torsional loads occur while
traveling on roads with poor surface conditions.
These various types of loads are compounded under
various conditions, and are applied to the frame.
As a result, it is important, before attempting to repair
the frame, to carefully observe the shape of the dam-
aged part and to in that way fully understand the
cause of the damage.
CHECKING FOR FRAME CRACKING OR
FLANKING
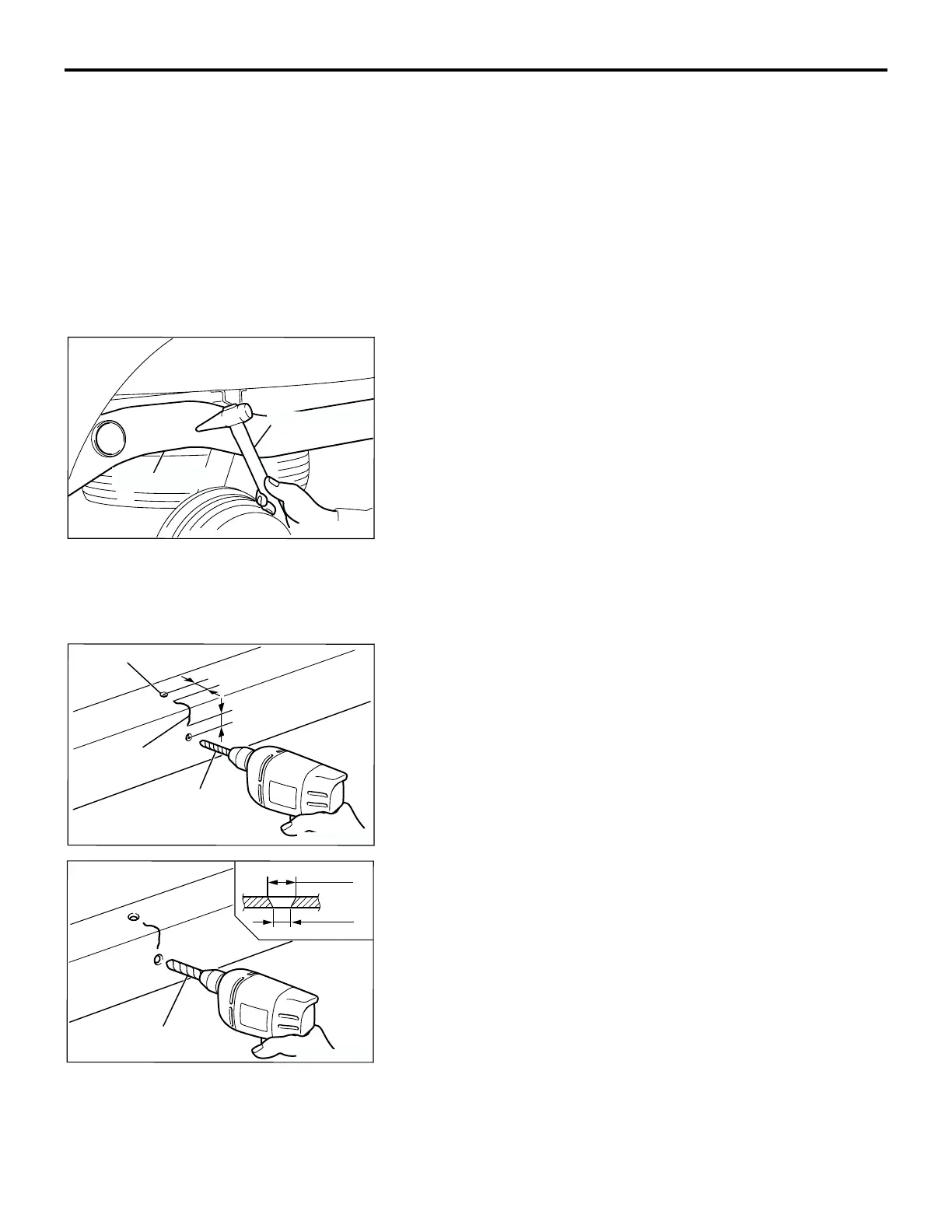
Check, by using a test hammer, for flaking or cracking of the
welded surface of the sidemembers, crossmembers and brack-
ets.
REPAIRING CRACKS
If the check reveals a crack(s) in the frame, repair as described
bellow.
1. Remove the components near the crack.
2. Make φ 6 - 8 mm (0.2 - 0.3 inch) holes (to prevent further
cracking), by using a drill, at points 7 - 8 mm (0.3 inch) from
the crack ends.
3. Use a φ 10 - 12 mm (0.4 - 0.5 inch) drill to bevel the hole
openings.
AB200127
AB
TEST HAMMER
SIDEMEMBER
AB200128
CRACK-STOP HOLE
CRACK
A
A
Ø6 - 8 mm
(0.2 - 0.3 in)
A : 7 - 8 mm (0.3in)
AB
AB200129
AB
Ø10 - 12 mm
(0.4 - 0.5 in)
Ø10 - 12 mm (0.4 - 0.5 in)
Ø6 - 8 mm
(0.2 - 0.3 in)

 Loading...
Loading...











