5 - 14 5 - 14
MELSEC-Q
5 ASSIGNMENT OF I/O NUMBERS
(c) Be sure to set the same module type for the mounted module and the I/O
assignment.
If the module type of the I/O assignment is different from that of the actually
mounted module, the module may not work normally.
For the intelligent function module, make sure that the numbers of I/O
points are the same.
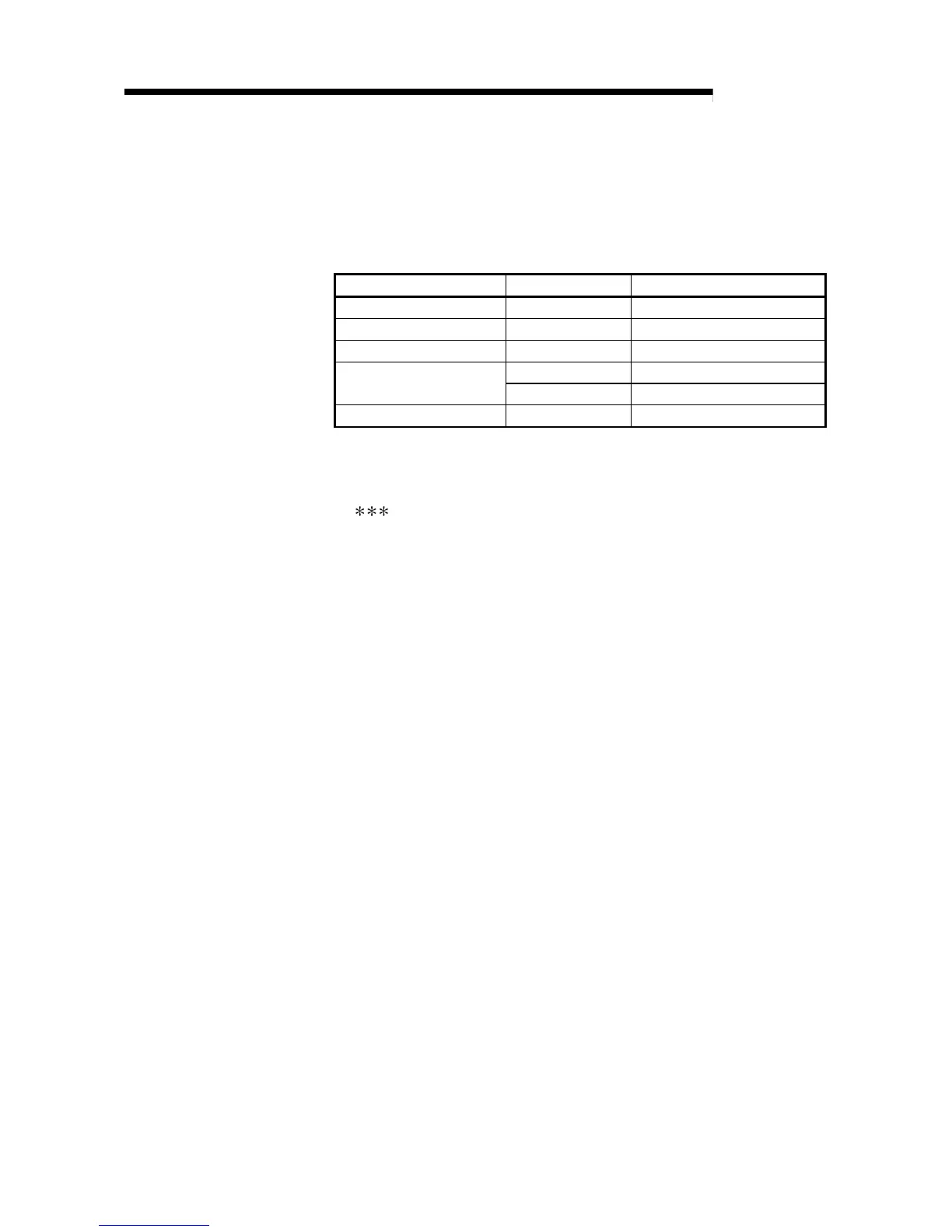
Actually installed module I/O assignment Result
Input module Output/Empty Empty
Output module Input/Empty Empty
Input module/output module Intelligent Error (SP. UNIT LAY ERR.)
Empty Empty
Intelligent function module
Input/output Error (SP. UNIT LAY ERR.)
Empty slot Intelligent No error occurs.
(d) Be sure to assign the I/O numbers so that the last I/O number is within the
range of FFF
H
or less. An error (SP. UNIT LAY ERR.) occurs when the last
I/O number exceeds FFF
H
. (System monitor of GX Developer shows
"
" as an I/O address.)

 Loading...
Loading...











