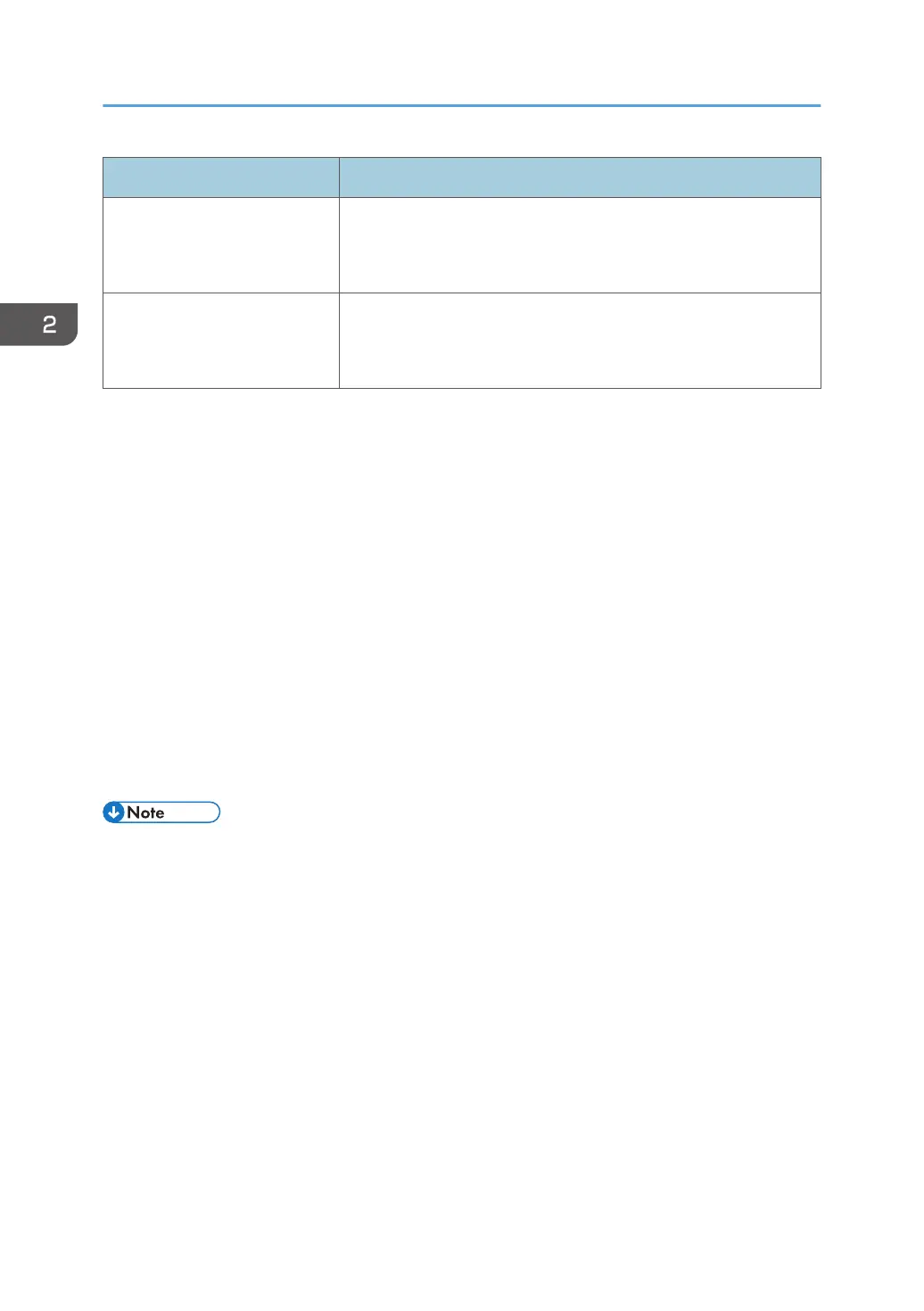
Type Details
Windows authentication Authentication is performed using the domain controller of the
Windows server on the same network as the machine.
Authentication can be applied to each user.
LDAP authentication Authentication is performed using the LDAP server on the same
network as the machine.
Authentication can be applied to each user.
If the user authentication method is switched halfway
• A user code account that has no more than 8 digits and is used for User Code authentication
can be carried over and used as a login user name even after the authentication method has
switched from User Code authentication to Basic authentication, Windows authentication, or
LDAP authentication. In this case, since no password is provided for the User Code
authentication, the login password is set as blank.
• When authentication switches to an external authentication method (Windows authentication
or LDAP authentication), authentication cannot be enabled unless the external authentication
device has the carried over user code account previously registered. However, the user code
account will be stored in the machine's Address Book even if an authentication failure occurs.
• From a security perspective, when switching from User Code authentication to another
authentication method, we recommend that you delete accounts you do not use or set up a
login password. For details about deleting accounts, see "Deleting a Registered Name",
Connecting the Machine/ System Settings. For details about changing passwords, see
page 30 "Specifying Login User Names and Passwords".
• After the main power turns on, extended features may not appear in the list of user authentication
items in the User Authentication Management menu. If this happens, wait a while, and then open
the User Authentication Management menu again.
• User authentication can also be specified via Web Image Monitor. For details, see Web Image
Monitor Help.
2. Configuring User Authentication
26
 Loading...
Loading...