
 Loading...
Loading...
Do you have a question about the Yamaha AN1x and is the answer not in the manual?
| Polyphony | 10 voices |
|---|---|
| Oscillators | 2 per voice |
| LFO | 2 LFOs with multiple waveforms |
| Arpeggiator | Yes |
| MIDI | In, Out, Thru |
| Display | LCD |
| Weight | 8.5 kg |
| Year Released | 1997 |
| Synthesis Type | Analog Physical Modeling |
| Effects | Chorus, Delay, Distortion |
| Keyboard | 61 keys |
| Memory | 128 patches |
| Control | Pitch bend, modulation wheel, ribbon controller |
| Outputs | Stereo outputs, headphone output |
General safety precautions to avoid injury or death from electrical hazards.
Precautions to avoid physical injury or damage to the instrument or property.
Explains the manual structure and how to use it effectively for understanding the AN1x.
Highlights the key capabilities and innovative aspects of the AN1x synthesizer.
Describes controls like SCENE, RIBBON, PITCH, and MODULATION wheels for performance.
Explains the eight assignable control knobs and their group selector switches.
Details MIDI terminals and audio output/phone jacks on the rear panel.
Overview of the LCD, parameter switches, keyboard, and function buttons.
Describes various jacks like Footswitch, Foot Controller, Output, Phones, DC IN.
Discusses the history and enduring appeal of analog synth sounds.
Highlights the AN1x's analog modeling and digital enhancements.
Explains why analog synthesis remains popular due to its punch and interactivity.
Describes how AN1x digitally models analog components for sound generation.
Explains the term 'voice' and its meaning across different synthesizer models.
Details what constitutes a voice, including parameter settings and data.
Details the components of voice data stored in the AN1x's memory.
Describes global parameters that remain active regardless of voice selection.
Explains the storage of Step Sequencer User Patterns.
Describes the signal flow through VCO, VCF, VCA, and Effect modules.
Explains pitch, tone, and amplitude as fundamental sound characteristics.
Details the function and complexity of the Voltage Controlled Oscillator.
Explains the mixing and filtering stages of the signal path.
Details related to the Voltage Controlled Oscillator module.
Details related to the mixer and filter modules.
Details related to the Voltage Controlled Amplifier module.
Details related to the effects processing module.
Explains how controllers interact with modules and parameters.
Describes how to set up and use the AN1x as a standalone instrument.
Explains connecting the AN1x to a MIDI sequencer.
Provides instructions for connecting power and peripherals safely.
Explains how to save AN1x data to an external storage device.
Steps to safely turn on the AN1x and achieve a comfortable listening level.
How to access and listen to the AN1x's demonstration songs.
Explains the primary operating modes, including Voice Play/Edit.
Describes two procedures for selecting voices from memory.
How voices are organized into categories and named.
Explains the two Scene memories per voice and their function.
Function to retrieve previously edited voice data.
Describes the X-axis (slide) and Z-axis (pressure) control.
Operation and assignment of control knobs and their group selectors.
Connecting and assigning footswitches and foot controllers.
Switches for selecting Layer modes and Portamento.
A guided tour of the AN1x's factory preset voices.
Steps 1 & 2: Selecting voices and checking their status.
Step 3: Morphing between Scenes using Scene Control.
Step 4: Editing sound characteristics using control knobs.
Step 5: Comparing the differences between Layer modes.
Steps 6 & 7: Modifying Poly mode and Arpeggiator/Sequencer settings.
Steps 8 & 9: Modifying Arp tempo, effects, and EQ.
How to assign parameters to controllers via Control Matrix/Utility.
Details stored parameters and the structure of Scene memories.
How to select and use Scenes for performance.
How Scene data is loaded and maintained in edit buffers.
Morphing between Scene 1 and 2 sounds using controllers.
How Scene Control functions differ in DUAL and SPLIT Layer modes.
Procedure for storing Scene settings to edit buffers.
Loading Scene data from other voices and swapping Scene data.
How the LAYER switch selects between the six available Layer modes.
Descriptions of SINGLE and UNISON Layer modes.
Descriptions of DUAL, DUAL UNISON, SPLIT, and SPLIT UNISON modes.
Describes the portamento effect for smooth pitch glides between notes.
How to turn the Portamento function on and off using the panel switch.
Adjusting the duration of the portamento effect.
Choosing portamento behavior based on Poly mode settings.
Function of switches that select parameter groups for control knobs.
Real-time control and editing of parameters using the control knobs.
Visual feedback for parameter values and coarse/fine editing modes.
System-wide knob parameter assignments using Utility Setup.
Voice-specific knob parameter assignments using Control Matrix.
Using knobs to edit Note, Velocity, Gate Time, and Control Change events.
Descriptions of Voice, Sequencer, and Utility menus.
Steps for editing parameters via the panel matrix.
General steps required for editing voices from scratch.
How to choose a voice to edit using the PROGRAM CHANGE keypad.
Adjusting Layer and Poly modes for voice editing.
Using knobs and parameter groups to edit sound characteristics.
Assigning effects, Free EG, Arp/Seq, and Control Matrix settings.
Procedure for saving the edited voice to memory.
Overview of procedures for creating specific sound types.
Editing oscillator waveform and determining the fundamental pitch.
Editing the filter to shape the tone or timbre of the voice.
Editing the amplifier to control the volume of the sound.
Editing the Low Frequency Oscillator for modulation effects.
Explains the four sync algorithm connection types for VCOs.
Explains PEG parameters like Decay, Depth, and Switch.
Adjusting filter cutoff frequency and resonance.
Explains FEG parameters: Attack, Decay, Sustain, Release, Depth.
Adjusting levels for VCO1, VCO2, Ring Modulator, and Noise signals.
Controls for Attack, Decay, Sustain, and Release times.
Adjusting tremolo effect and response to playing strength.
Adjusting feedback level and overall output volume.
Explains LFO function and parameters for modulation.
Adjusting LFO waveform type and speed.
How to perform a Voice Store operation to save edited data.
How to activate or deactivate the Arpeggiator or Step Sequencer.
Explains Arpeggiator patterns, Subdivide, and Play Effect parameters.
How to turn the Arpeggiator on using the panel switch.
How to set the tempo in BPM or synchronize with MIDI.
How the Hold function affects pattern playback continuity.
How to choose from the 30 available Arpeggiator pattern types.
How to set the timing subdivision (resolution) for patterns.
Tips for experimenting with different arpeggio patterns and settings.
How KbdMode setting affects pattern triggering and playback.
How SceneSw parameter selects which Scene plays the Arpeggiator pattern.
How Arpeggiator patterns play in DUAL Layer mode.
How Arpeggiator patterns play in SPLIT Layer mode.
How Arpeggiator patterns play in SINGLE Layer mode.
Explains how Type, Subdivide, and note count determine pattern length.
Adjusting the lower and higher velocity values for steps.
Designating the MIDI channel for pattern data output.
Creating 16-step patterns using knobs and events.
How to turn the Step Sequencer on and off using the panel switch.
Setting tempo in BPM or synchronizing with external MIDI.
Explains the Hold function and additional modes for step sequences.
Describes the two banks of Step Sequencer patterns.
How to play one pattern using Voice Pattern data.
How to trigger multiple patterns via keyboard keys.
How to store custom edited patterns to User banks.
How to choose pattern banks and specific pattern numbers.
How KbdMode setting affects pattern selection and playback.
Description of the norm Keyboard Mode for pattern playback.
Description of shift&norm Keyboard Mode for pattern playback.
Description of sel&norm Keyboard Mode for pattern playback.
Description of sel&shift Keyboard Mode for pattern playback.
Explains how Type, Subdivide, and note count determine pattern length.
How Base Unit and Length set pattern timing resolution and length.
Determines the loop cycle for sequence patterns (forward, backward, alternate).
Sets the type of MIDI CC output for sequencer playback steps.
Saves edited Step Sequencer patterns to User bank locations.
Adjusts rhythm to create a 'swing' feel by shifting beats.
Sets the velocity ratio between lower and higher values for steps.
Adjusts note length (duration) for steps.
Guidance on learning Step Sequencer parameters via factory examples.
Overview of using control knobs for Step Sequencer event editing.
Lists Note, Velocity, Gate Time, and Control Change as editable events.
Adjusts note duration for steps.
Sets the MIDI CC value output by sequencer steps.
Repeats a step for fine-tuning events based on tempo and base unit.
Saving current Voice Pattern data as voice data.
Saving edited patterns to User Pattern memory locations.
Designating the MIDI channel for Arpeggiator/Seq pattern data output.
Explains the Free EG's capability to record knob movements per track.
How recorded knob movements automatically affect sound during playback.
Settings that affect all four tracks of data for recording and play.
How Free EG recording or playback is triggered.
Determines the loop cycle for Free EG sequences.
Sets the recording and playback time for Free EG sequences.
Adjusts Free EG length based on keyboard notes played.
Selecting which Free EG track to use for recording or playback.
Assigning a specific knob parameter to a track.
Designating which Scene the Free EG track will play.
How to execute a Free EG recording operation.
Copying Free EG data between tracks or voices.
Undoing or redoing the most previous Free EG copy or record operation.
Explains how knob positions are recorded as base position values.
How AN1x controllers provide expressive control over sound.
Differentiates controller types and their use in control.
Sets the type of MIDI CC output for sequencer playback steps.
How to assign CC messages to controllers like wheels and knobs.
Lists assignable controllers like MW, FC, Knobs, and SCENE.
How MIDI CCs are routed to the AN1x tone generator and control depth.
Selecting sets for Pitch Bend and parameter assignments.
Determining which parameter is assigned to a set number or common set.
Assigning controllers (MIDI CC) to parameters.
Determining the control range of the source controller.
Selecting a voice by entering its number via the keypad.
Selecting voices sequentially using the +/- keys.
How to edit voice parameters in real-time using control knobs.
Detailed steps for using knobs to edit parameters.
Parameters related to Pitch Envelope Generator and Low Frequency Oscillator.
Controls the time for pitch to reach basic pitch from PEG Depth.
Determines the pitch amount in semitones for the PEG.
Determines which VCO the PEG is applied to.
Adjusting the time it takes for pitch to reach the subsequent note.
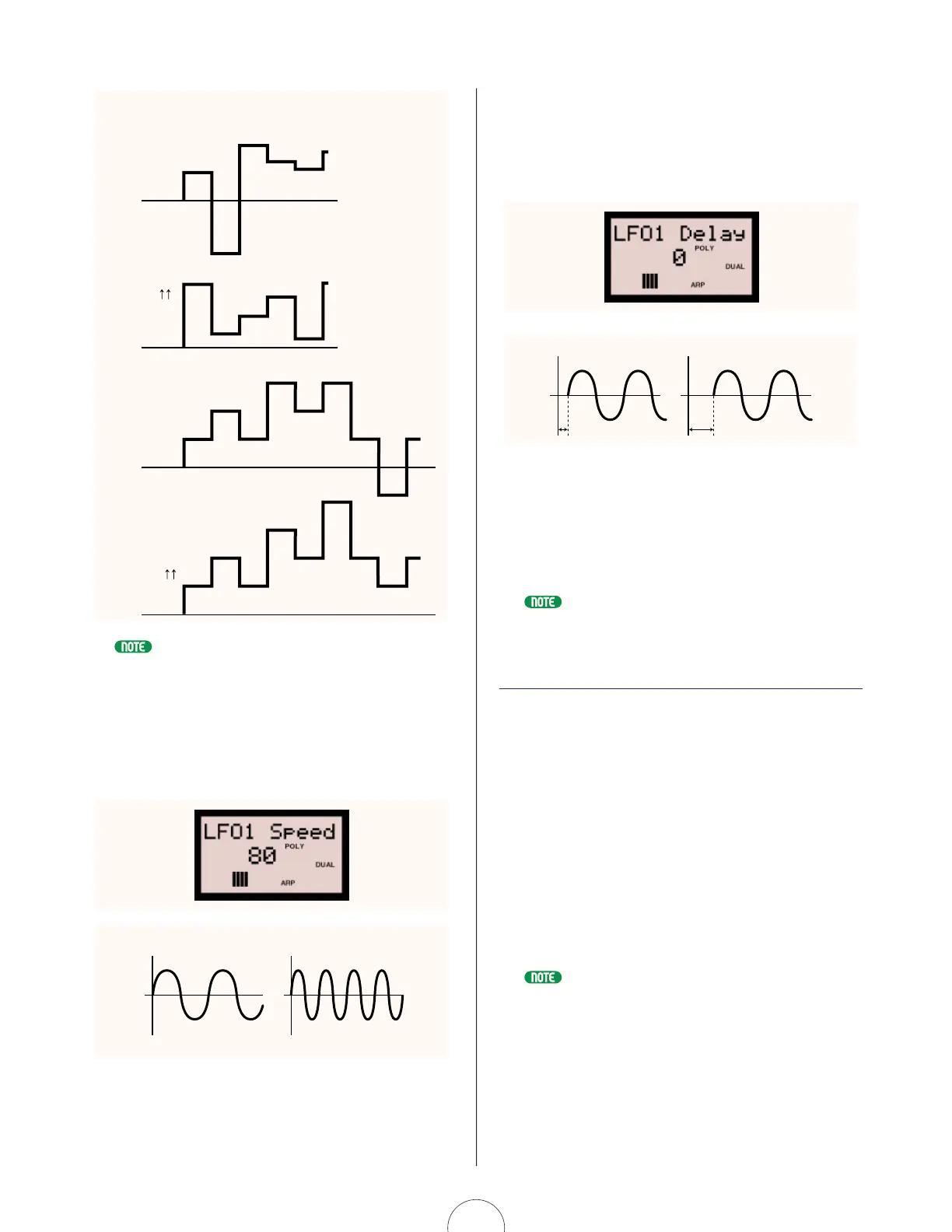
Describes the 21 available LFO1 waveform types.
Visual representation of Triangle waveforms.
Visual representation of Square waveforms.
Visual representation of Sawtooth waveforms.
Controls the rate of LFO1 modulation.
Adjusts the delay time of the modulation.
Describes LFO2 speed, similar to LFO1 Speed.
Explains synchronization and FM for VCO oscillators.
Explains the four sync algorithm connection types for VCOs.
Adjusts pitch difference between master and slave VCOs.
Adjusts the depth of sync pitch control over time.
Selects the source for time-based sync pitch modulation.
Selects oscillator for LFO1 modulation.
Controls the amount of modulation from FM Source 1.
Determines the source controlling FM Depth.
Determines the source wave modulating VCO1.
Choosing the waveform for VCO1.
Descriptions of Saw, Pulse, Saw2, and Mix waveforms.
Descriptions of the Inner waveforms available with Sync ON.
Adjusting the VCO1 pitch in semitones.
Adjusts VCO1 pitch in cent steps.
Adjusts the sharpness or smoothness of the VCO1 wave.
Determines the width of the VCO1 pulse wave.
Controls the depth of pulse width modulation.
Selects the source wave for pulse width changes over time.
Controls the depth of pitch modulation by LFO1.
Choosing the waveform for VCO2 when SYNC is off.
Parameter descriptions for VCO2 are the same as for VCO1.
Sets the attack time of the FEG.
Sets the decay time of the FEG.
Sets the sustain level of the FEG.
Sets the release time of the FEG.
Determines the cutoff frequency of the VCF.
Adjusts resonance boost or emphasis near the cutoff frequency.
Determines the range of movement for the cutoff frequency.
How VCF responds to keyboard playing strength.
Balances VCO1 level relative to other signals.
Balances VCO2 level relative to other signals.
Controls the balance of the Ring Modulator level.
Balances the Noise signal level relative to other signals.
Determines the cutoff frequency of the High Pass Filter.
Selects the type of filter (LPF, BPF, HPF, BEF) used by the VCF.
Controls depth of filter modulation by LFO1.
Adjusts cutoff frequency shift based on played notes.
Overview of VCA functions like Attack, Decay, Volume, and modulation.
Sets the attack time of the AEG.
Sets the decay time of the AEG.
Sets the sustain level of the AEG.
Sets the release time of the AEG.
Controls feedback level from VCA to mixer.
Sets the overall output level from the VCA.
Controls depth of amplitude modulation by LFO1.
Sets VCA response to keyboard playing strength.
Using knobs as individual controllers for specified parameters.
Details on assigning parameters to knobs 1 through 8.
Descriptions of Voice, Sequencer, and Utility menus.
Description of the menu for Step Sequencer parameters.
Description of the menu for global system parameters.
Steps for editing parameters via the panel matrix.
Parameters for Scene, Layer, and Control Matrix.
How Poly mode, Portamento, and LFO Reset affect response.
Determines polyphony and response to notes.
Characteristics of portamento based on Poly mode.
Determines the start point of LFO cycles.
How to assign controllers to AN1x parameters.
Selecting sets for Pitch Bend and parameter assignments.
Determining which parameter is assigned to a set.
Assigning controllers (MIDI CC) to parameters.
Determining the control range of the source controller.
Activating direct editing of assigned parameters.
How the two assignment functions work together.
Sets the stereo panning position of sounds.
Adjusts the amplitude between left and right outputs.
Adjusts detuning for creating thicker unison sounds.
Sets the tempo for the Arpeggiator and Step Sequencer.
Divides the keyboard for Split mode and Arp/Seq.
Controls Variation Effect type and EQ settings.
Selects the variation effect type or EQ parameter.
Selects effect type and changes data values for effects or EQ.
Steps to set up the desired variation effects.
Steps to set up the equalizer parameters.
Balances wet (effect) and dry (original) signal levels.
Selects Connect, Delay effect, and Reverb effect parameters.
Selects delay/reverb type and changes data values.
Steps to configure delay and reverb effects.
How to bypass effects for original sound.
Choosing a category for voice naming.
Positioning the cursor for voice naming.
Selecting characters for voice names.
Step-by-step guide to naming voices using the LCD and keypad.
Explains the special 4-track recorder for knob movements.
Settings that affect all four tracks of data for recording and play.
How Free EG recording or playback is triggered.
Adjusts Free EG length based on keyboard notes played.
Setting current track, parameter, and Scene for Free EG.
Determines the loop cycle for Free EG sequences.
Sets the recording and playback time for Free EG.
Selecting which Free EG track to use.
Assigning a knob parameter to a track.
Designating which Scene the Free EG track will play.
How to execute a Free EG recording operation.
Copying Free EG data between tracks or voices.
Steps for copying Free EG data.
Undoing or redoing the most previous Free EG copy or record operation.
Steps for recording Free EG data.
Designates Arpeggiator or Step Sequencer for playback.
Selecting Arpeggiator patterns or User Pattern numbers.
How KbdMode affects Arp/Seq pattern response.
Description of norm Keyboard Mode for pattern playback.
Description of shift&norm Keyboard Mode for pattern playback.
Description of sel&norm Keyboard Mode for pattern playback.
Description of sel&shift Keyboard Mode for pattern playback.
Designates Hold setting for Arpeggiator and Step Sequencer.
Selects which Scene the Arpeggiator or Step Sequencer pattern will play.
Designates the MIDI channel for pattern data output.
Designates the timing subdivision value for the Arpeggiator pattern.
Adjusts rhythm to create a 'swing' feel by shifting beats.
Sets the velocity ratio for Arpeggiator/Seq steps.
Adjusts the note length (duration) for steps.
Parameters related to sequencer steps and editing.
Designates the type of event data for knob input.
Designates the step series (1-8 or 9-16) for data entry.
Turns the Step Hold function on or off.
Selects the Voice or User pattern bank.
Selects the Voice or User pattern number.
How Voice Patterns are loaded based on KbdMode.
Designates timing resolution for sequence patterns.
Determines the length of the sequence pattern based on steps.
Determines the loop cycle for sequence patterns.
Sets the type of MIDI CC output for sequencer play.
Saves edited Step Sequencer patterns to User bank locations.
Global parameters affecting tuning, transpose, velocity, and MIDI settings.
Sets the master tuning pitch for the AN1x's tone generator.
Sets the keyboard transposition setting in semitones.
Sets the keyboard velocity curve for response to playing strength.
Describes different velocity curves: norm, soft, easy, wide, hard, fixed.
Related to transmission and reception of MIDI messages to/from external devices.
Sets the MIDI channel for transmitting messages.
Sets the MIDI channel for receiving messages.
Sets the MIDI device number for bulk dumps and SysEx messages.
Enables/disables the internal tone generator from the keyboard.
Initiates data transfer operations to external MIDI devices.
Steps to send data (voices, patterns, system) to an external device.
Designating CC messages controlled by wheels, knobs, etc.
Selects the controller to which a Control Number is assigned.
Designates the CC number (parameter type) the device will control.
Procedure to recall previously edited voice data.
How to initialize a voice to create from scratch.
Choosing from eight types of initial voice settings.
Overview of Voice Store and Scene Store operations.
Procedure to save edited voice data to memory locations.
Saving Scene Control settings to Scene switches.
Selecting the active Scene via the SCENE switches.
Morphing between Scene 1 and 2 sounds using controllers.
Functions for exchanging or loading Scene data.
How to restore original voices, scenes, and parameters.
Step-by-step guide to creating a synth bass sound.
How to add vibrato using controls and Control Matrix.
Step-by-step guide to creating a strings sound.
Fine-tuning VCA response to playing strength.
Modifying VCF cutoff and its velocity response.
Controlling vibrato with MW via Control Matrix.
Adjusting VCO Edge, Sync/FM, Pitch for EP sound.
Adding octave-down VCO2 for fuller EP sound.
Adjusting velocity sensitivity for VCA.
Adjusting FEG Sustain and Decay for EP sound.
Adjusting VCF cutoff and its velocity response.
Applying chorus effect for a wider sound.
Adding reverb to the sound.
Using Control Matrix for key tracking AEG Decay.
Using Control Matrix for key tracking FEG Decay.
Using Control Matrix for Sync Pitch adjustment.
Setting pulse wave and edge for organ tone.
Adding octave-down VCO2 for fuller organ sound.
Applying rotary speaker effect to the organ sound.
Using Modulation Wheel to control rotary speaker speed.
Using PEG to add a harder attack (click) to the sound.
Initial setup for creating a characteristic synth brass sound.
Utilizing VCO1 and VCO2 for a richer brass sound.
Fine-tuning the interval between oscillators for brass tone.
Adjusting parameters for a characteristic brass tone.
Using PEG to enhance the brass characteristics of VCO1.
Adding vibrato using controls and Control Matrix.
Adjusting Sync Algorithm for slow sound movement.
Reducing LFO1 speed for a typical synth lead sound.
Selecting sine wave for a typical synth lead sound.
Adjusting Portamento Time for a lead sound.
Using Poly mode for legato playing.
Using Unison mode for a thicker sound.
Applying a delay effect to the synth lead sound.
Explains what MIDI is and its purpose in musical instrument communication.
Explanation of Channel and System MIDI messages handled by the AN1x.
Details on channel messages like Note On/Off, Velocity, and Control Change.
How Control Change messages control AN1x parameters.
Messages controlling vibrato depth using the Modulation Wheel.
Messages controlling the duration of portamento.
Messages for setting parameter values specified by RPN.
Messages controlling the AN1x's volume.
Messages controlling the stereo panning position of each voice.
Messages controlling intonation expression.
Messages controlling sustain on/off.
Messages controlling portamento on/off.
Messages adjusting the VCF resonance.
Messages directly adjusting AEG release time.
Messages directly adjusting AEG attack time.
Messages directly adjusting VCF cutoff frequency.
Messages adjusting the send level for the Reverb effect.
Messages adjusting the dry/wet balance for the Chorus effect.
Messages adjusting the send level for the Delay effect.
Messages for increasing/decreasing MSB value.
Messages for controlling RPN parameters.
Control AN1x functions like volume, tuning, effects.
Effective for system parameters when received.
Performs functions like All Sounds Off upon no MIDI data.
Two modes for Control Change parameters.
Indicates low backup battery; data may not be saved.
Cannot send bulk data when Device Number is off.
Error due to improper Device Number setting.
Scene Control function not activated for SysEx message.
Error occurred during MIDI data receive.
Indicates too much MIDI information received.
Received SysEx message address is incorrect.
Received SysEx message data is incorrect.
Received SysEx message size is incorrect.
Received SysEx Check Sum message is incorrect.
Message displayed during bulk data reception.
Checks for common causes of no audio output.
Troubleshooting issues with Arpeggiator or Step Sequencer.
Diagnosing causes of distorted audio.
Checking settings for low volume output.
Troubleshooting problems related to incorrect pitch.
Addressing issues causing choppy audio playback.
Resolving issues where only one note sounds at a time.
Troubleshooting effect bypass or settings.
Checking if the Portamento switch is set to ON.
Troubleshooting problems with saving data.
Template for recording voice parameter settings.
Template for Scene and Common parameter assignments.
Template for assigning parameters to control knobs.
Number of keys and touch sensitivity information.
Analog physical modeling specifications.
Maximum notes of polyphony and simultaneous timbres.
Number and types of effects (Variation, EQ, Delay, Reverb).
Number of user voices available for storage.
Details on preset patterns and voice patterns.
Number of parameter tracks and maximum recording time.
List of available controllers on the AN1x.
List of panel switches and their functions.
Details on the LCD display and connection ports.
Audio output specifications and power requirements.
Physical size and weight of the AN1x unit.
Warning against unauthorized modifications to the unit.
Instructions for using high-quality shielded cables for connections.
Details on device testing and interference compliance for Class 'B' devices.
Information regarding product batteries, including replacement and charging.
Safety precautions for battery handling and disposal.
Guidelines for the disposal of products containing lead, batteries, etc.
Location of product identification information like model and serial number.