RM23712 TPS
19
3.2.1.4 Input current
The maximum input current defines the maximum possible input current to ensure the proper function of the power supply to
meet all defined specifications.
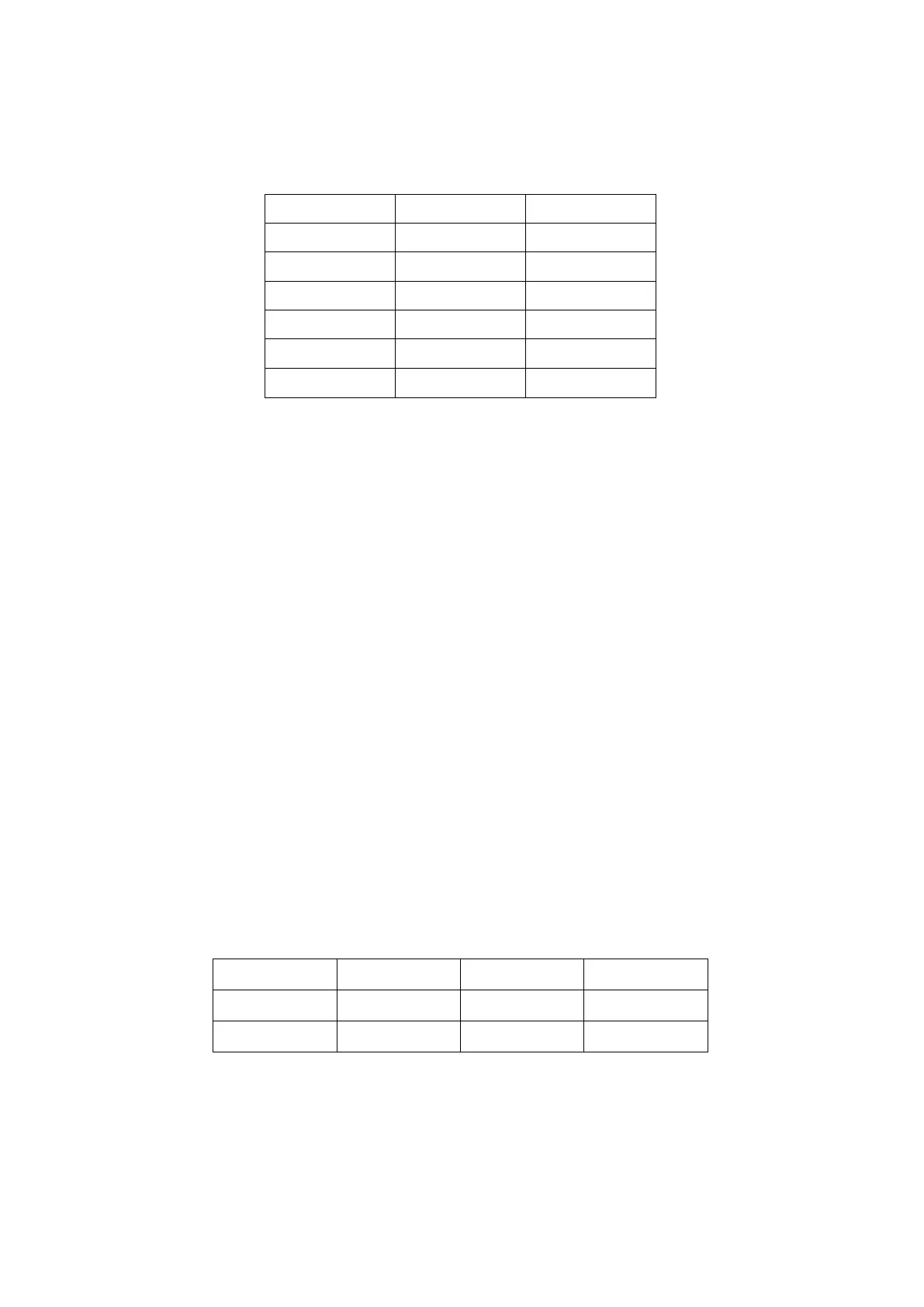
Table 13.Maximum input current
3.2.1.5 AC Line Fuse
The power supply shall incorporate one input fuse on the line side for input over-current protection
to prevent damage to the power supply and meet product safety requirements. AC inrush current
shall not cause the AC line fuse to blow under any conditions. All protection circuits in the power
supply shall not cause the AC fuse to blow unless a component in the power supply has failed. This
includes DC output load short conditions.
3.2.1.6 AC line inrush
AC line inrush current shall not exceed 55A peak, for up to one-quarter of the AC cycle, after which,
the input current should be no more than the specified maximum input current. The peak inrush
current shall be less than the ratings of its critical components (including input fuse, bulk rectifiers,
and surge limiting device).
The power supply must meet the inrush requirements for any rated AC voltage, during turn on at any
phase of AC voltage, during a single cycle AC dropout condition as well as upon recovery after AC
dropout of any duration, and over the specified temperature range (Top).
3.2.1.7 Input Power Factor Correction
The input Power Factor shall be greater than 0.98/115Vac and 0.95/230Vac.
Table 14.Power Factor correction
3.2.1.8 AC line dropout
An AC line dropout is a transient condition defined as the AC input to the power supply drops to 0
VAC at any phase of the AC line for any length of time. During an AC dropout the power supply must
meet dynamic voltage regulations requirements. An AC line dropout of any duration shall not cause
dripping of the control signals and protection circuits. If the AC dropout lasts longer than the holdup
 Loading...
Loading...