16-2
Catalyst 3750 Switch Software Configuration Guide
78-16180-02
Chapter 16 Configuring Voice VLAN
Understanding Voice VLAN
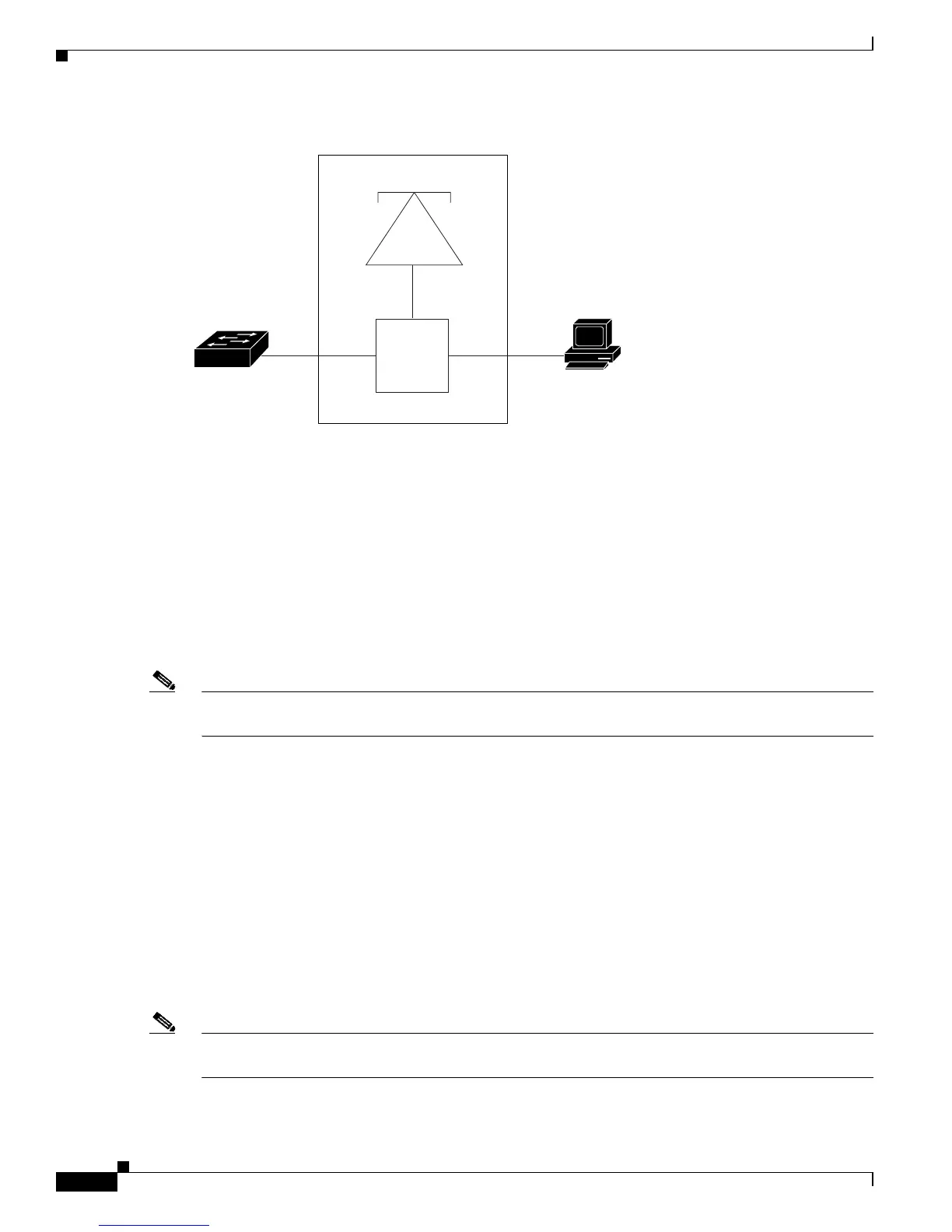
Figure 16-1 Cisco 7960 IP Phone Connected to a Switch
Cisco IP Phone Voice Traffic
You can configure an access port with an attached Cisco IP Phone to use one VLAN for voice traffic and
another VLAN for data traffic from a device attached to the phone. You can configure access ports on
the switch to send Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) packets that instruct an attached Cisco IP Phone to
send voice traffic to the switch in any of these ways:
• In the voice VLAN tagged with a Layer 2 CoS priority value
• In the access VLAN tagged with a Layer 2 CoS priority value
• In the access VLAN, untagged (no Layer 2 CoS priority value)
Note In all configurations, the voice traffic carries a Layer 3 IP precedence value (the default is 5 for voice
traffic and 3 for voice control traffic).
Cisco IP Phone Data Traffic
The switch can also process tagged data traffic (traffic in 802.1Q or 802.1p frame types) from the device
attached to the access port on the Cisco IP Phone (see Figure 16-1). You can configure Layer 2 access
ports on the switch to send CDP packets that instruct the attached Cisco IP Phone to configure the IP
phone access port in one of these modes:
• In trusted mode, all traffic received through the access port on the Cisco IP Phone passes through
the IP phone unchanged.
• In untrusted mode, all traffic in 802.1Q or 802.1p frames received through the access port on the IP
phone receive a configured Layer 2 CoS value. The default Layer 2 CoS value is 0. Untrusted mode
is the default.
Note Untagged traffic from the device attached to the Cisco IP Phone passes through the IP phone unchanged,
regardless of the trust state of the access port on the IP phone.
3-port
switch
P1 P3
P2
Access
port
Cisco IP Phone 7960
PC
101351
Phone
ASIC
 Loading...
Loading...











