88
Explanation
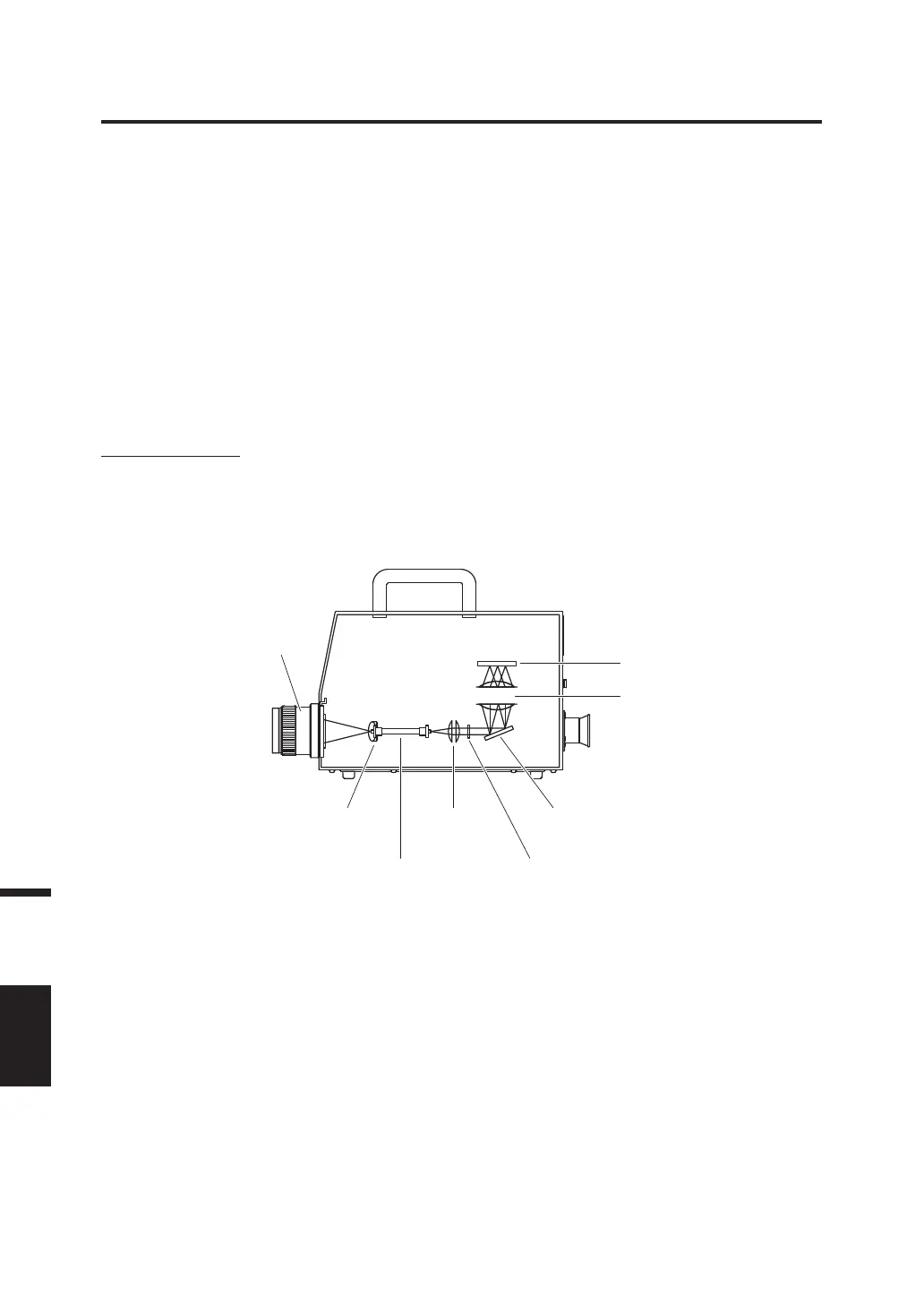
Measurement Principles
Light energy passes through the objective lens. The lights from the measurement area pass through the
hole in the center of the aperture mirror to the optical fiber, while the remaining light is guided to the
finder optics by the aperture mirror. As a result, the part equivalent to the measurement area looks like a
black circle when observed through the finder.
The light entering the optic fiber is reflected repeatedly so that it is mixed and becomes virtually
uniform. It then passes through the collimator lens to the plane diffraction grating.
After being dispersed by the grating, the light is focused by the condenser lens according to
wavelength, and an array sensor is located at this focus point.
The amount of detected energy for each wavelength is then converted to a digital value by an A/D
converter, based on which, the spectral radiant luminance and chromaticity are calculated.
Sensor Section
The sensor section has a photo diode array consisting of 512 elements. The array is always kept at
constant temperature using a Peltier cooler, irrespective of the ambient temperature. This can reduce
dark current and improve S/N ratio of the sensor, thus enabling measurement of low luminance.
Aperture
mirror
Collimator
lens
Plane diffraction
grating
Array sensor

 Loading...
Loading...